Kentucky: Who Pays? 7th Edition
Kentucky
Download PDF
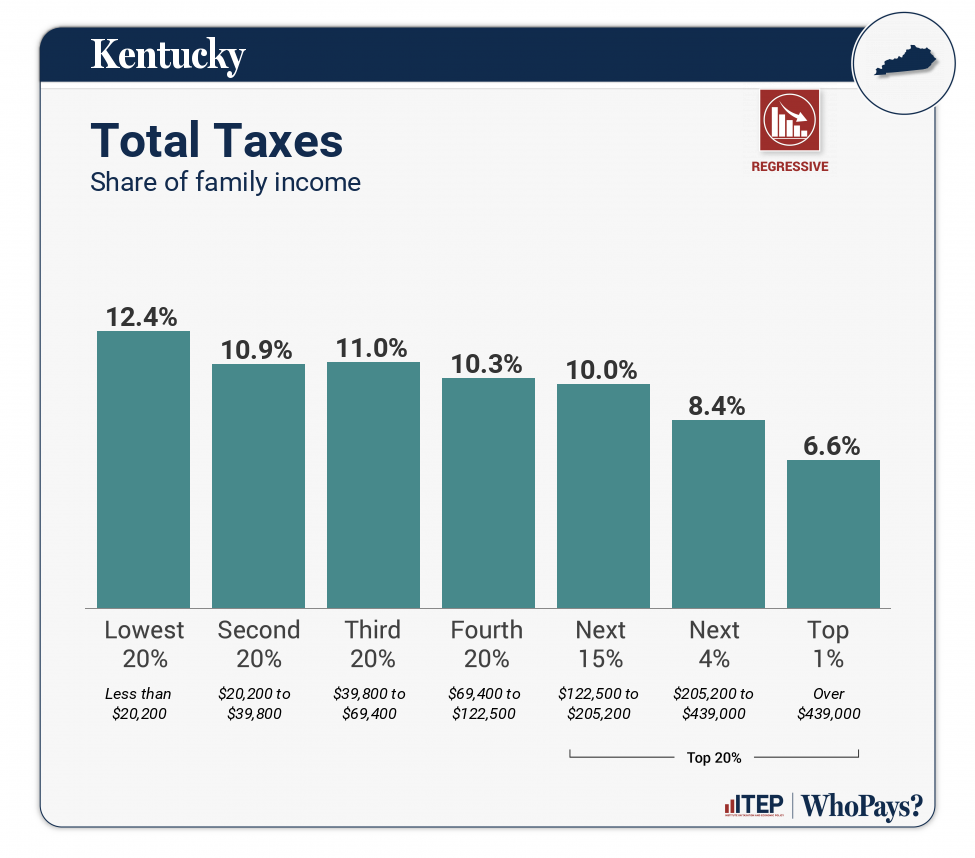
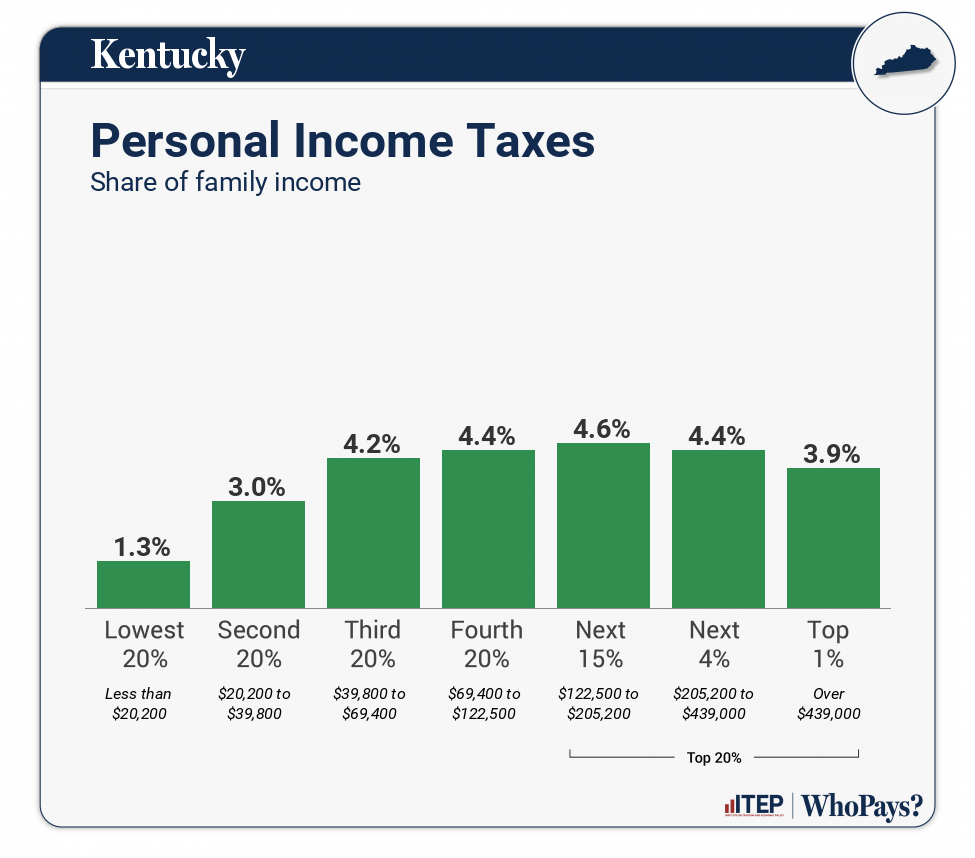
All figures and charts show 2024 tax law in Kentucky, presented at 2023 income levels. Senior taxpayers are excluded for reasons detailed in the methodology. Our analysis includes nearly all (99.6 percent) state and local tax revenue collected in Kentucky. These figures depict Kentucky’s flat personal income tax rate of 4 percent. Due to a tax trigger that could decrease the rate to zero over time, we also model full elimination of this tax. As seen in Appendix E, this will decrease the overall tax rate paid by the top 1 percent of households by 3.1 percentage points and cause the state to move 9 spots in the ITEP Inequality Index rankings, from 17th to 8th most regressive.
State and local tax shares of family income
| Top 20% | |||||||
| Income Group | Lowest 20% | Second 20% | Middle 20% | Fourth 20% | Next 15% | Next 4% | Top 1% |
| Income Range | Less than $20,200 | $20,200 to $39,800 | $39,800 to $69,400 | $69,400 to $122,500 | $122,500 to $205,200 | $205,200 to $439,000 | Over $439,000 |
| Average Income in Group | $11,000 | $29,300 | $53,600 | $92,500 | $149,200 | $272,800 | $843,600 |
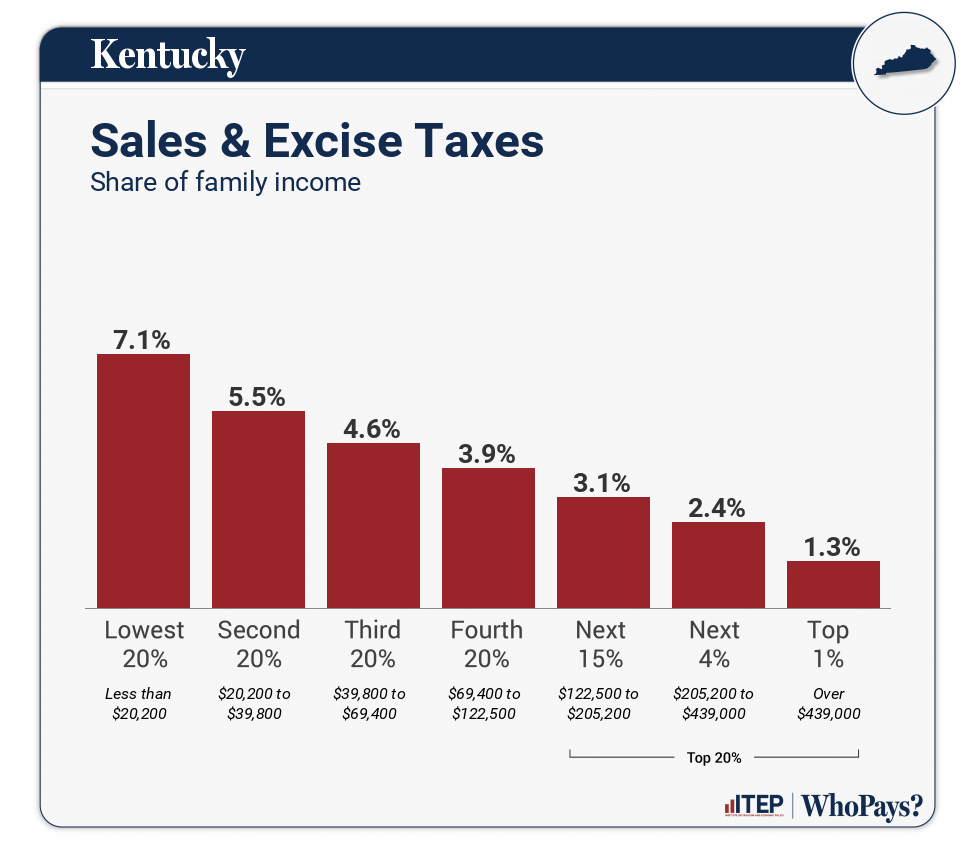
| Sales & Excise Taxes | 7.1% | 5.5% | 4.6% | 3.9% | 3.1% | 2.4% | 1.3% |
| General Sales–Individuals | 2.8% | 2.5% | 2.2% | 1.9% | 1.5% | 1% | 0.4% |
| Other Sales & Excise–Ind | 2.6% | 1.4% | 1% | 0.7% | 0.6% | 0.4% | 0.2% |
| Sales & Excise–Business | 1.8% | 1.6% | 1.4% | 1.3% | 1.1% | 1% | 0.7% |
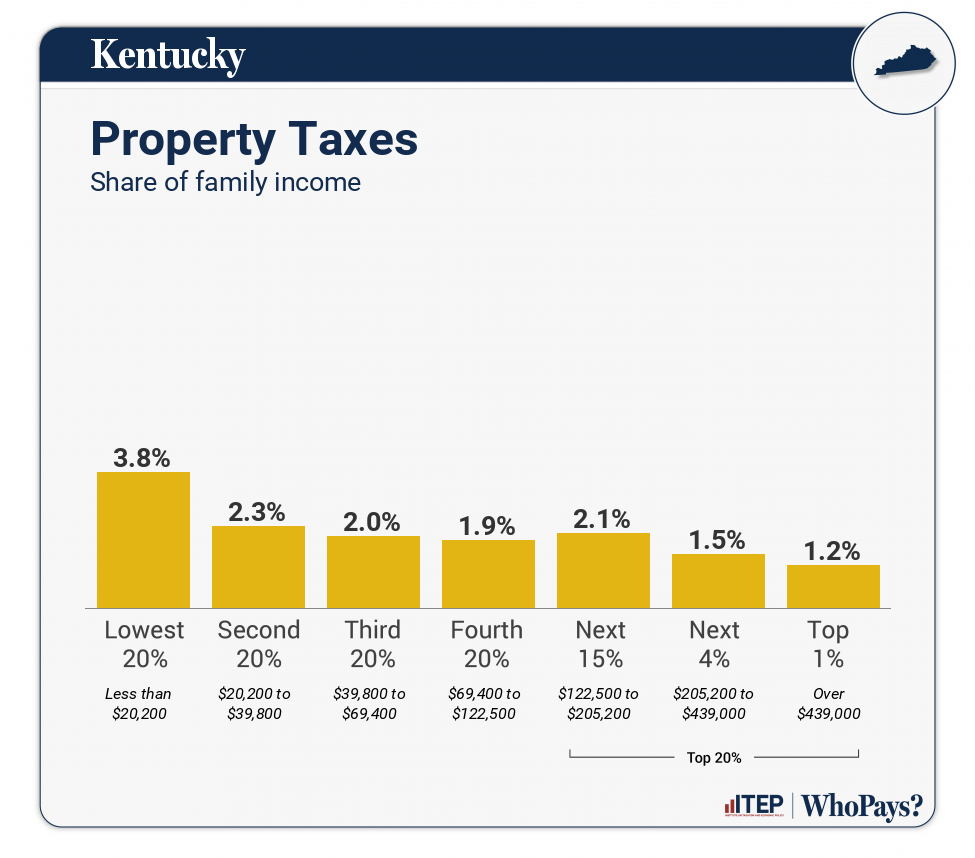
| Property Taxes | 3.8% | 2.3% | 2% | 1.9% | 2.1% | 1.5% | 1.2% |
| Home, Rent, Car–Individuals | 3.5% | 1.9% | 1.7% | 1.7% | 1.8% | 1.1% | 0.6% |
| Other Property Taxes | 0.3% | 0.3% | 0.3% | 0.3% | 0.3% | 0.4% | 0.6% |
| Income Taxes | 1.3% | 3% | 4.3% | 4.4% | 4.6% | 4.4% | 4% |
| Personal Income Taxes | 1.3% | 3% | 4.2% | 4.4% | 4.6% | 4.4% | 3.9% |
| Corporate Income Taxes | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0.1% |
| Other Taxes | 0.1% | 0.1% | 0.1% | 0.1% | 0.1% | 0.1% | 0.1% |
| TOTAL TAXES | 12.4% | 10.9% | 11% | 10.3% | 10% | 8.4% | 6.6% |
| Individual figures may not sum to totals due to rounding. | |||||||
ITEP Tax Inequality Index
ITEP’s Tax Inequality Index measures the effects of each state’s tax system on income inequality. According to this measure, Kentucky has the 17th most regressive state and local tax system in the country. Income disparities are larger in Kentucky after state and local taxes are collected than before. (See Appendix B for state-by-state rankings and the report methodology for additional detail.)
Tax features driving the data in Kentucky
|
Requires combined reporting for the corporate tax, including some profits booked in tax havens
Sales tax base excludes groceries
Levies a state inheritance tax
|
|
|
No refundable income tax credits to offset sales, excise and property taxes
Real estate transfer tax does not include higher rate on high-value sales
Local income taxes exclude investment income
Personal income tax uses a flat rate
Offers itemized deductions
|