August 6, 2024
August 6, 2024
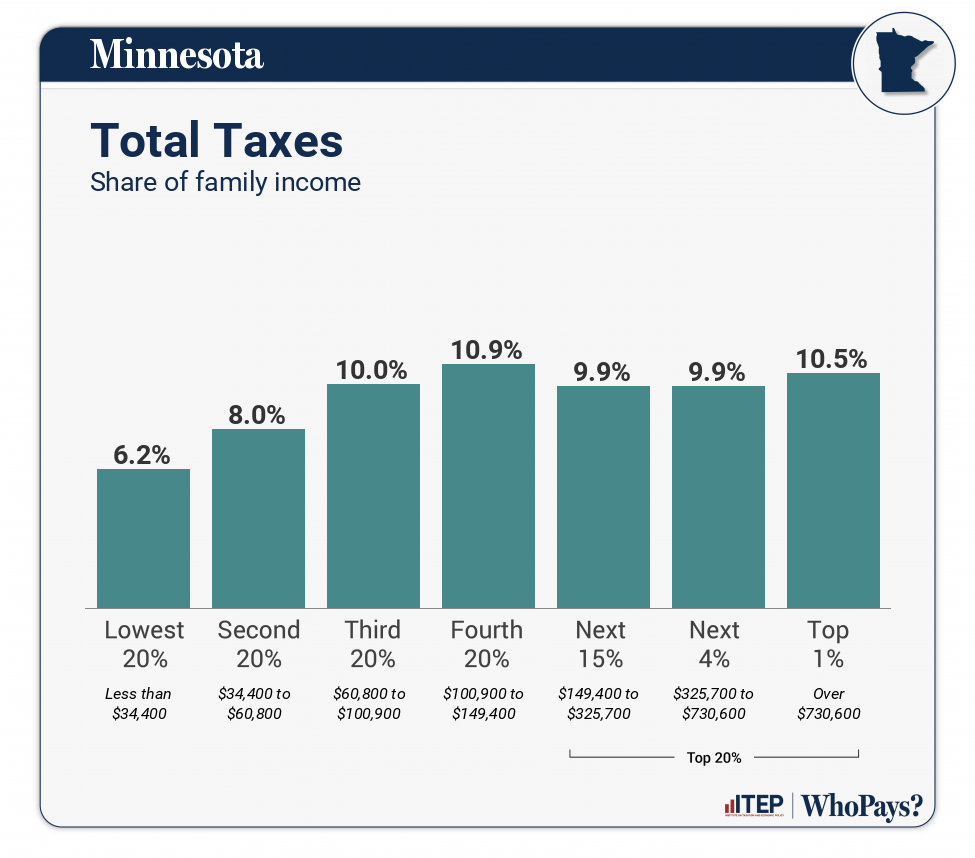
Most state tax systems fall short of the public’s perception of fairness by charging the rich lower tax rates than everyone else. Minnesota is among a small group of states that has chosen a different path. In Who Pays?, our comprehensive study of state and local taxes, Minnesota stands apart from the pack with a moderately progressive tax system that asks slightly more of the rich than of low- and middle-income families.
Recent reforms signed by Gov. Tim Walz, the Democratic Party’s presumptive Vice-Presidential nominee, have contributed to this reality. Our analysis shows that taxes on working-class families declined markedly over the last few years in Minnesota, while taxes on high-income people went up slightly over this same period.
The most notable changes were signed into law by Gov. Walz in 2023 as part of a sweeping tax reform package. Some changes were temporary, like taxpayer rebate checks and expanded property tax credits. But the bill also included a host of important, permanent reforms.
Chief among those was a new Child Tax Credit that is expected to slash child poverty in Minnesota by one-third, according to Columbia University’s Center on Poverty and Social Policy. The link between Child Tax Credits and child wellbeing is well established, as the financial security afforded by these credits is associated with improved child and maternal health, better educational achievement, and stronger future economic outcomes.
Other tax cuts signed by Gov. Walz include expanded exemptions for Social Security income and for student loan forgiveness, plus an extension of the Child Care Tax Credit to newborn children.
To help pay for these and other substantial tax cuts, the 2023 bill included a variety of well-targeted tax increases on high-income people and profitable corporations. Certain tax deductions claimed by high-income filers have been scaled back. Capital gains, dividends, and other investment income over $1 million per year is now subject to a modest 1 percent surtax. And multinational corporations reporting income overseas now face higher taxes as well, as the state opted to piggyback on a law written by Congressional Republicans targeting companies’ “low-taxed income.”
While the Minnesota tax code is somewhat progressive, it is far from radical. The state has embraced practical, administrable reforms that have lowered taxes for working-class families, reduced child poverty, and addressed the public’s frustrations with the tax treatment of multinational companies and wealthy people. At the end of the day, Minnesota does better than most states in living up to what most people would consider to be a bare minimum standard of tax fairness: the idea that wealthy people should not pay lower tax rates than everyone else.