
Who Pays?
NC Policy Watch: Low-income Tax Payers in NC Pay More of Their Income in State and Local Taxes Each Year Than the Richest Taxpayers
October 17, 2018
Sales taxes play a critical role in the regressive and consequently inequitable nature of the North Carolina tax system. Like most other states, North Carolina relies on sales and excise taxes (30.7% of the 2018-2019 approved budget) as a primary mechanism to raise revenue. However, in North Carolina, sales and excise taxes are the most regressive taxes when compared to income and property taxes. The lowest 20% of North Carolina workers pay 6.1 percent in sales taxes as a percentage of their income while the top 1 percent pays less than 1 percent in sales taxes as a percentage of…
Alabama Arise: The Less You Make, the More You Pay: Alabama’s Taxes Remain Upside Down
October 17, 2018
Low-income Alabamians pay twice as much in state and local taxes as a share of their income compared to the state’s wealthiest residents, according to a study released Wednesday, Oct. 17, 2018, by the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy (ITEP), a nonprofit research organization based in Washington, D.C. The study, Who Pays?, analyzes major state and local taxes in all 50 states, including personal and corporate income taxes, property taxes, sales and other excise taxes.
Uprise RI: Low-income Taxpayers in Rhode Island Pay Over 50 Percent More in Taxes Than the Wealthiest
October 17, 2018
There’s a practical reason for Rhode Island and all states to be concerned about regressive tax structures, according to ITEP. If the nation fails to address growing income inequality, states will have difficulty raising the revenue they need over time. The more income that goes to the wealthy (and the lower a state’s overall tax rate on the wealthy), the slower a state’s revenue grows over time.
Arkansas Times: Report: Arkansas Taxes Unfair ….. To the Poor
October 17, 2018
Arkansas Advocates for Children and Families is highlighting a new report relevant to ongoing legislative discussions of "tax reform." It does not suggest the problem is taxation on the rich.
KUOW: Washington State Tops ‘Terrible Ten’ List for Taxes
October 17, 2018
Washington State's tax system is widening the gap between the rich and the poor. That's according to the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy (ITEP) based in Washington, D.C. “What you see is that Washington’s tax system couldn’t possibly be further from hitting people evenly,” Carl Davis said. “People are having to devote very different shares of their household budgets to funding state and local government.”
Topeka-Capital Journal: New Study: Kansas’ Tax Policy Ranks as 23rd Most Regressive in the Nation
October 17, 2018
A 50-state study of tax systems found Kansas’ lowest-income residents pay 1.5 times more in taxes as a percent of income compared with the wealthiest residents, ranking the state 23rd in the nation on an equity index. “State lawmakers have control over how their tax systems are structured,” said Meg Wiehe, the institute’s deputy director and a study author. “They can and should enact more equitable tax policies that raise adequate revenue in a fair, sustainable way.”
Budget and Policy Center: Washington State Again Ranks Worst In The Nation For Our State Tax Code
October 17, 2018
Despite the many ways Washington state takes prides in its spirit of innovation, it still ranks dead last when it comes to its tax code, according to a new study by the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy (ITEP). Our state has the most upside-down tax code in the country, forcing people with the lowest incomes to pay 17.8 percent in state and local taxes as a percent of their income – while the state’s wealthiest residents pay just 3 percent.
West Virginia Center on Budget & Policy: Low-Income West Virginians Pay Far More in Taxes as a Percent of Income Than Wealthiest West Virginians
October 17, 2018
West Virginia's tax system is regarded as regressive because the lower one's income, the higher one's effective tax rate. While West Virginia has a progressive personal income (meaning the higher one's income, the higher one's effective personal income tax rate), it also, like most other states, relies heavily on the more regressive sales and excise taxes to raise revenue. Low-income West Virginians pay up to 6.6 percent of their income on sales and excise taxes, while the wealthiest in the state pay less than one percent of income in state and local sales taxes.
Public Assets Institute: New report: Vermont’s Tax System Is Among the Least Regressive
October 17, 2018
Tax systems generally favor the wealthy, but Vermont’s system is skewed less than most other states when it comes to high-income taxpayers. That was the key finding of a study released today by the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy (ITEP) and Public Assets Institute.
Louisiana Budget Project: Louisiana’s Tax Code is Still Regressive
October 17, 2018
The wealthiest households in Louisiana continue to pay state and local taxes at a lower rate than those in the middle class and below, according to a new analysis that breaks down the tax rates by income brackets in every state. The report, Who Pays? A Distributional Analysis of the Tax Systems in All 50 States found that households with incomes in the lowest 20 percent pay nearly twice as much of their income in taxes as households in the top 1 percent. Louisiana has the 14th most regressive tax code in the country, according to the report by the…
Better Wyoming: New Report: Low-income Residents in Wyoming Pay an Effective Tax Rate More Than Three Times Higher Than the State’s Wealthiest One Percent
October 17, 2018
A new study released today by the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy (ITEP) and Better Wyoming finds that the lowest-income Wyomingites pay an effective tax rate more than three times higher than the state’s richest residents. Wyoming’s tax rate gap between the working poor and the ultra-rich is one of the worst in the nation.
The Half Sheet: Virginia’s Tax System Is Upside Down
October 17, 2018
Virginia’s state and local taxes help to shape economic opportunity across the state. That’s because state and local revenues pay for the building blocks of thriving communities: schools, roads, libraries, and other public services. Unfortunately, the current state and local tax system is upside down. Families in Virginia have taxes withheld from their paychecks, and they also pay taxes when they shop at local businesses, buy groceries, or fill their gas tanks. But updated analysis from the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy (ITEP) shows that Virginia’s low- and moderate-income households pay a higher share of their incomes toward state…
Oklahoma Policy Institute: New Analysis: Low-income Taxpayers in Oklahoma Pay More than Twice the Tax Rate Paid by the Richest Oklahomans
October 17, 2018
While Oklahoma has a reputation as a low tax state, poor and middle-income Oklahomans are actually paying a greater share of their income in taxes than the national average, while the richest 5 percent of households — with annual incomes of $194,500 or more — pay less.
Budget and Policy Center: Unacceptable. Washington Still Has the Nation’s Most Inequitable State Tax Code
October 17, 2018
Washington state continues to have the most upside-down tax code of any U.S. state, according to a new report from the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy (ITEP). It wrongly requires people with the lowest incomes to pay six times more in taxes as a percent of their income than the state’s wealthiest residents to fund investments that benefit all Washingtonians.
Florida Policy Institute: Florida Has Third Most Unfair State and Local Tax System
October 17, 2018
Florida’s reputation as a “low-tax” state belies the reality that it is, in fact, a high-tax state for low- and moderate-income residents. Floridians with the lowest incomes — those earning less than $18,700 — contribute 12.7 percent of their incomes to state and local taxes, while the wealthiest top 1 percent — those with incomes of more than $548,700 — contribute just 2.3 percent of their income.
Kentucky Center for Economic Policy: New Report: Wealthiest Kentuckians Pay the Lowest Tax Rate and the Problem Is Worsening
October 17, 2018
The study, Who Pays? A Distributional Analysis of the Tax Systems in All 50 States, evaluates the major components of state and local tax systems – including personal and corporate income taxes, property taxes, sales taxes and other excise taxes – for their overall distributional impact across income groups. For example, Kentucky’s low income tax credit means that people in poverty do not pay state income taxes. However, because the state fails to provide refundable tax credits to offset sales, excise and property taxes paid by low-income people, and because the state has a flat as opposed to graduated income…
Indiana Institute for Working Families: New Analysis: Indiana’s Tax System is Among the Dozen Most Regressive in the Country
October 17, 2018
The new ‘Who Pays?’ analysis follows the Institute’s August report ‘The Status of Working Families in Indiana, 2018’ which found the wealthiest Indiana earners have received an extra $2,446 from combined state income, corporate, and fuel tax changes since 2012, while taxes for the bottom 60% of middle class and working families have increased by an average $36.
Insider NJ: New Analysis: Middle Class Taxpayers in New Jersey Still Paying More Than Tax Rate Paid by Richest 1 Percent of New Jerseyans
October 17, 2018
A new study released today by the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy (ITEP) and New Jersey Policy Perspective (NJPP) finds that New Jersey’s middle class families pay more in taxes as a percent of their income compared to the state’s wealthiest residents.
Politico Morning Tax: Desperately Seeking Clarity
October 17, 2018
MOST STATE TAX SYSTEMS REGRESSIVE: No state has more regressive taxes on its citizens than Washington, followed by Texas, Florida, South Dakota and Nevada, according to a distributional analysis of state tax systems that will be released today by the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy. Most states take a larger share of income from low- and middle-income families than from wealthy families, it said. The 10 most regressive in the rankings tax their residents in the bottom 20 percent of the income scale at rates up to six times higher than the wealthy, while their middle-income families pay a rate up to…
Public News Service: Report: NM Tax Overhaul Would Benefit Kids, Families
October 17, 2018
Regressive tax systems hurt children and families, according to a new report from the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy - and by that standard, it says New Mexico has the 19th-worst tax system in the United States. The study showed that as a share of their income, the lowest-income New Mexicans are paying state and local tax rates almost double those of the state's wealthiest residents.
New Report Finds that Upside-down State and Local Tax Systems Persist, Contributing to Inequality in Most States
October 17, 2018 • By Aidan Davis
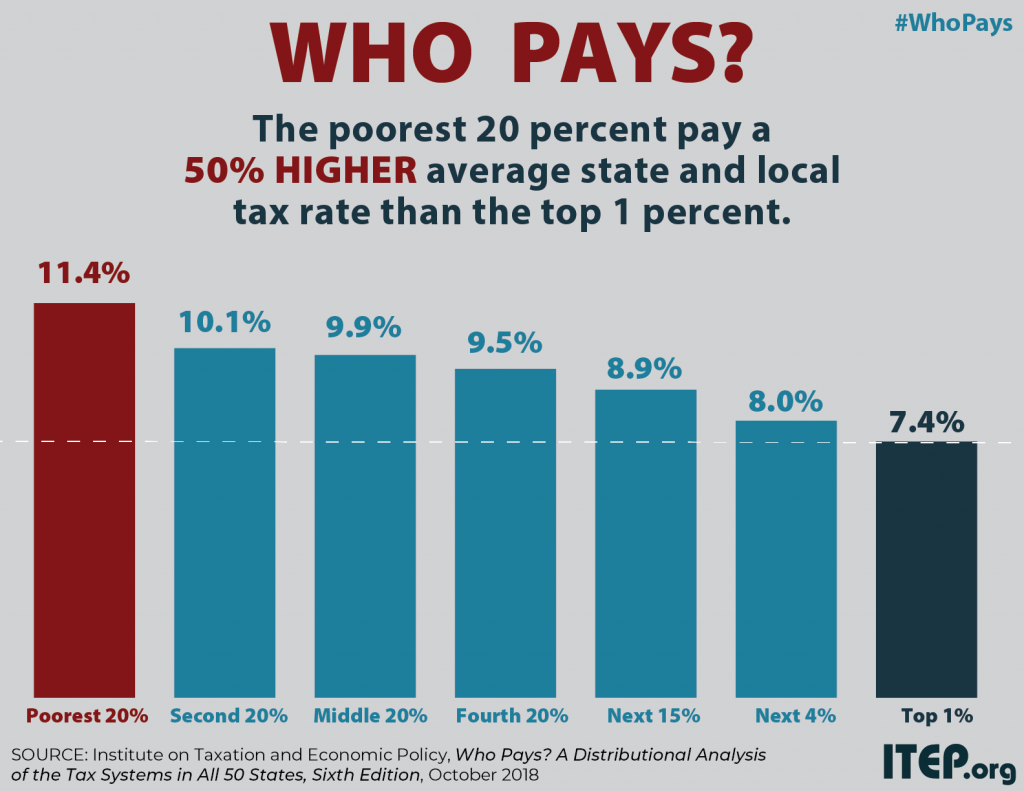
State and local tax systems in 45 states worsen income inequality by making incomes more unequal after taxes. The worst among these are identified in ITEP’s Terrible 10. Washington, Texas, Florida, South Dakota, Nevada, Tennessee, Pennsylvania, Illinois, Oklahoma, and Wyoming hold the dubious honor of having the most regressive state and local tax systems in the nation. These states ask far more of their lower- and middle-income residents than of their wealthiest taxpayers.
Low Tax for Whom? Texas is a “Low Tax State” Overall, But Not for Families Living in Poverty
October 17, 2018 • By ITEP Staff
Texas’s tax system has vastly different impacts on taxpayers at different income levels. For instance, the lowest-income 20 percent of Texans contribute 13 percent of their income in state and local taxes — considerably more than any other income group in the state. For low-income families, Texas is far from being a low tax state; in fact, it is tied with Arizona as the sixth highest-tax state in the country for low-income families.
Low Tax for Whom? Washington is a “Low Tax State” Overall, But Not for Families Living in Poverty
October 17, 2018 • By ITEP Staff
Washington’s tax system has vastly different impacts on taxpayers at different income levels. For instance, the lowest-income 20 percent of Washingtonians contribute 17.8 percent of their income in state and local taxes — considerably more than any other income group in the state. For low-income families, Washington is far from being a low tax state; in fact, it is the highest-tax state in the country for low-income families.
Low Tax for Whom? Arizona is a “Low Tax State” Overall, But Not for Families Living in Poverty
October 17, 2018 • By ITEP Staff
Arizona’s tax system has vastly different impacts on taxpayers at different income levels. For instance, the lowest-income 20 percent of Arizonans contribute 13 percent of their income in state and local taxes — considerably more than any other income group in the state. For low-income families, Arizona is far from being a low tax state; in fact, it is tied with Texas as the sixth highest-tax state in the country for low-income families.
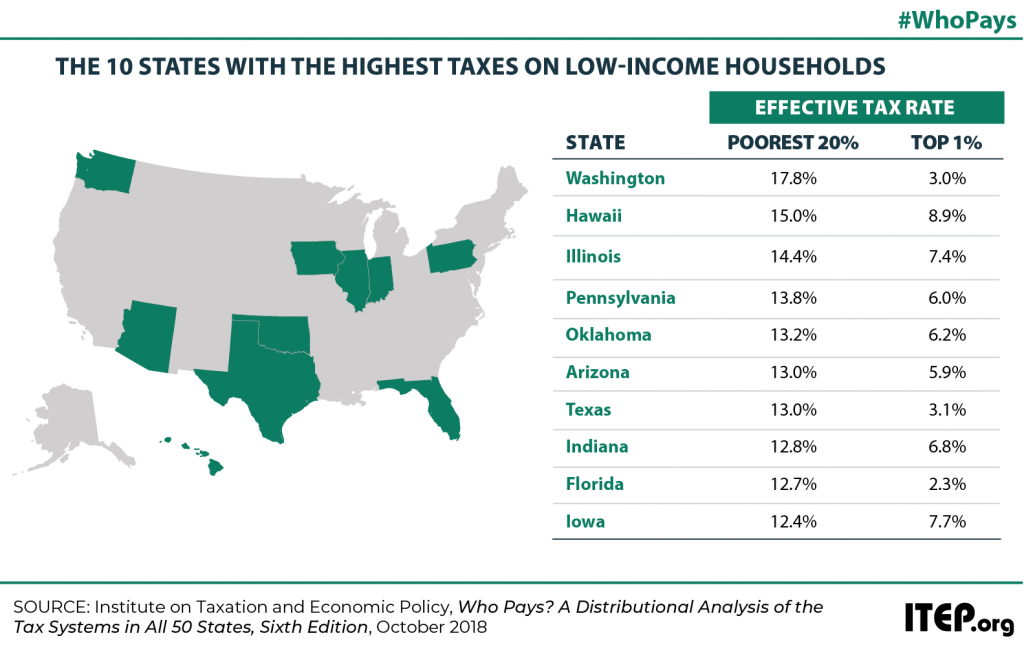
ITEP analysis reveals that many states traditionally considered to be “low-tax states” are actually high-tax for their poorest residents. The “low tax” label is typically assigned to states that either lack a personal income tax or that collect a comparatively low amount of tax revenue overall. But a focus on these measures can cause lawmakers to overlook the fact that state tax systems impact different taxpayers in very different ways, and that low-income taxpayers often do not experience these states as being even remotely “low tax.”
