This brief was updated July 2017
The Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) is a policy designed to bolster the earnings of low-wage workers and offset some of the taxes they pay, providing the opportunity for struggling families to step up and out of poverty toward meaningful economic security. The federal EITC has kept millions of Americans out of poverty since its enactment in the mid-1970s. Over the past several decades, the effectiveness of the EITC has been magnified as many states have enacted and later expanded their own credits.
The continued expansion of the EITC is as important as ever given the continuing challenges facing our country’s growing class of low-wage workers. Despite recent productivity gains, too many workers are facing low and slow-growing wages, while simultaneously feeling the squeeze of the growing costs of food, housing, child care, and other basic household expenses. To make matters worse, in all but one state, low-wage workers pay a higher share of their incomes in state and local taxes than high-income earners, leaving them with even fewer resources to make ends meet.1
The effectiveness of the EITC as an anti-poverty policy can be increased by expanding the credit at both the federal and state levels. To this end, this policy brief provides an overview of the federal and state EITCs and highlights recent trends to strengthen these credits.
The Federal Earned Income Tax Credit
The federal EITC has been rewarding work and boosting the income of lowwage workers since it was introduced in 1975. Since that time, the EITC has been improved to lift and keep more working families out of poverty. The most recent improvements enhanced the credit for families with three or more children and for married couples. First enacted temporarily as part of the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act (ARRA) in 2009, these changes were made permanent in late 2015.
The federal EITC returned nearly $67 billion in wages to 28 million working families and individuals in 2014.2 Used mostly as a source of temporary support, the EITC helps millions of families each year cope with low wages, job loss, reduced hours, or reduced pay. Recognized widely as an effective antipoverty tool, the federal EITC lifted an estimated 6.2 million people, including more than three million children, out of poverty in 2013, according to data from the Census Bureau.
To encourage greater participation in the workforce, the EITC is based on earned income, such as salaries and wages. For example, for each dollar earned up to $13,930 in 2016, families with three children will receive a tax credit equal to 45 percent of those earnings, up to a maximum credit of $6,269. Because the credit is designed to provide targeted tax cuts to the working poor, there are income limits that restrict eligibility for the credit. Families are eligible for the maximum credit until income reaches $18,190 (or $23,740 for married-couple families). Above this income level, the value of the credit is gradually reduced to zero and is unavailable when family income exceeds the maximum eligibility level. The maximum eligibility level for a family with three or more children is $47,955 if the head of household is single and $53,505 if married. For taxpayers without children, the credit is less generous: the maximum credit is $506 and the income limit is $14,880 for singles and $20,430 for married couples.
State Earned Income Tax Credits
In addition to helping working families afford the necessities that keep them working, EITCs at the state level play a very important function in improving the fairness of upside down state and local tax systems. Unlike federal taxes, state and local taxes are regressive, requiring low- and moderate-income families to pay more of their income in taxes than wealthier taxpayers. According to ITEP’s 2015 Who Pays? report, the poorest 20 percent of Americans pay 10.9 percent of their incomes in state and local taxes. By contrast, middle-income taxpayers pay 9.4 percent and the wealthiest one percent of taxpayers pay just 5.4 percent of their incomes in state and local taxes. Heavy use of regressive sales and property taxes (all of which low-income working families pay) drive up the high state and local tax rates faced by the poorest Americans.
A refundable state EITC is among the most effective and targeted tax reduction strategy to help offset these regressive taxes. Refundability is key to the EITC’s success, especially at the state level. If a credit is refundable, taxpayers receive a refund for the portion of the credit that exceeds their income tax bill. Refundable credits can therefore be used to help offset all taxes paid, not just income taxes, thereby offsetting some of the regressive effects of state and local sales, excise, and property taxes.
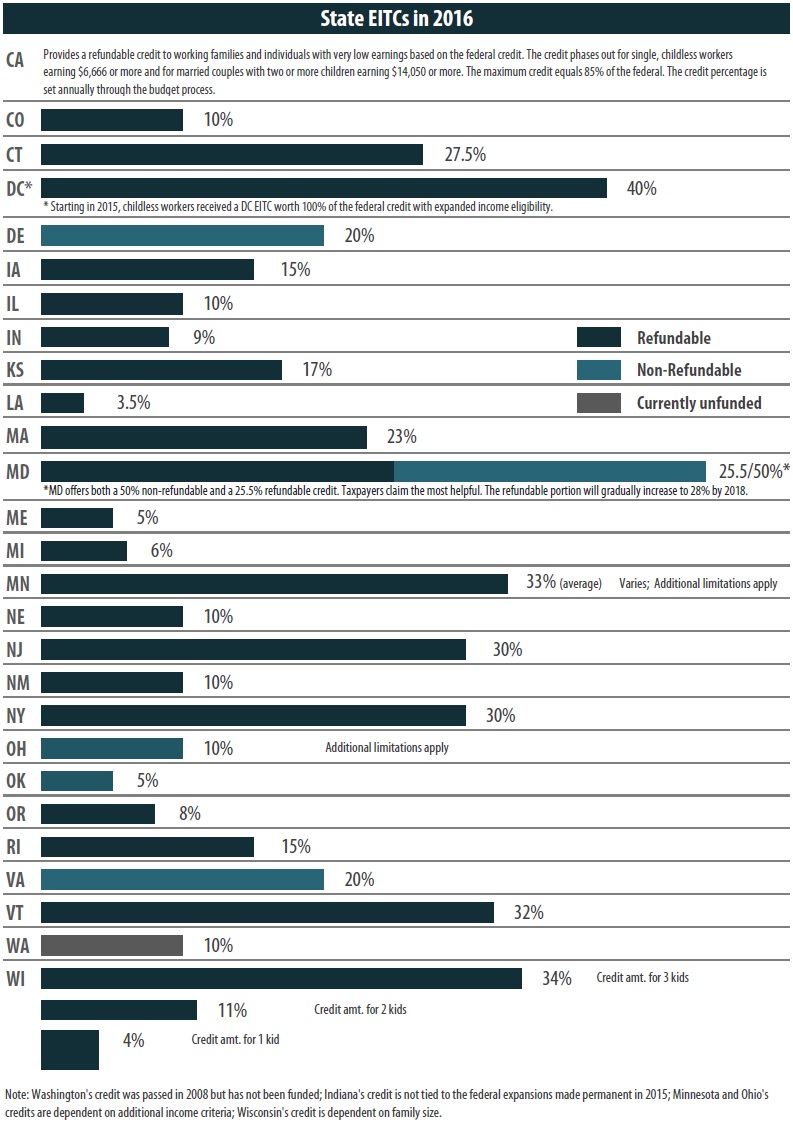
To date, more than half of the states (twenty-six states and DC) offer state EITCs based on the federal credit (see chart on the following page). Most states allow taxpayers to calculate their EITC as a percentage of the federal credit. This approach makes the credit easy for state taxpayers to claim (since they have already calculated the amount of their federal credit) and straightforward for state tax administrators. However, states vary dramatically in the generosity of their credits. For example, the EITC provided by the District of Columbia amounts to 40 percent of the federal credit (100 percent for childless workers), while seven states have credits that are worth less than 10 percent of the federal credit. Four states (Delaware, Ohio, Virginia, and recently Oklahoma) allow only a non-refundable credit, limiting the ability of the credit to offset regressive state and local taxes.
New Trends and Forward Momentum
There have been a number of advancements in EITC policy at the state and federal level in recent years. In 2015, California became the 26th state to enact an EITC loosely based on the federal credit (though targeted only to those living in deep poverty). Also in 2015, Massachusetts and New Jersey lawmakers boosted the value of their state credits, and Maine lawmakers converted the state’s nonrefundable EITC to a fully refundable credit. Lawmakers in Rhode Island enacted back-to-back EITC increases in both 2015 and 2016. Oregon lawmakers, in 2016, increased their credit from 8 to 11 percent of the federal credit only for taxpayers with one or more dependents under three years of age.
There have also been some recent efforts to expand the EITC for workers without children. While the federal EITC provides a great deal of help for families with children, its impact is quite limited for those without children; the maximum credit is much smaller and the income limits are more restrictive. For instance, under current law, an adult without dependent children or noncustodial parent working full-time at the federal minimum wage is ineligible for the EITC. Yet, if this person had children they would receive the maximum EITC. Under the current system, these low-wage workers continue to be taxed deeper into poverty.
President Obama proposed expanding the federal EITC to workers without children in 2014 and again reiterated support in his 2015 State of the Union address and 2016-2017 budget proposal. Multiple proposals from both sides of the aisle have been put forward on the federal stage. At the state level, the District of Columbia is leading the way. Since January 2015, more childless workers qualify for DC’s EITC thanks to higher income eligibility thresholds and a credit expanded to 100 percent of the federal credit (up from 40 percent).
Improving Tax Fairness with State EITCs
Whether lawmakers consider enacting an EITC in one of the 25 states that do not yet have one, or expanding an existing credit to more workers trying to get by on low wages, they would be wise to continue the positive trend of strengthening and enacting state EITCs. This would result in improved fairness of state and local taxes, reward work, and help families meet their basic need.
1 Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy, Who Pays? A Distributional Analysis of the Tax System in All Fifty States, 5th Edition, January 2015. www.whopays.org
2 https://www.eitc.irs.gov/EITC-Central/eitcstats