
Corporate Taxes
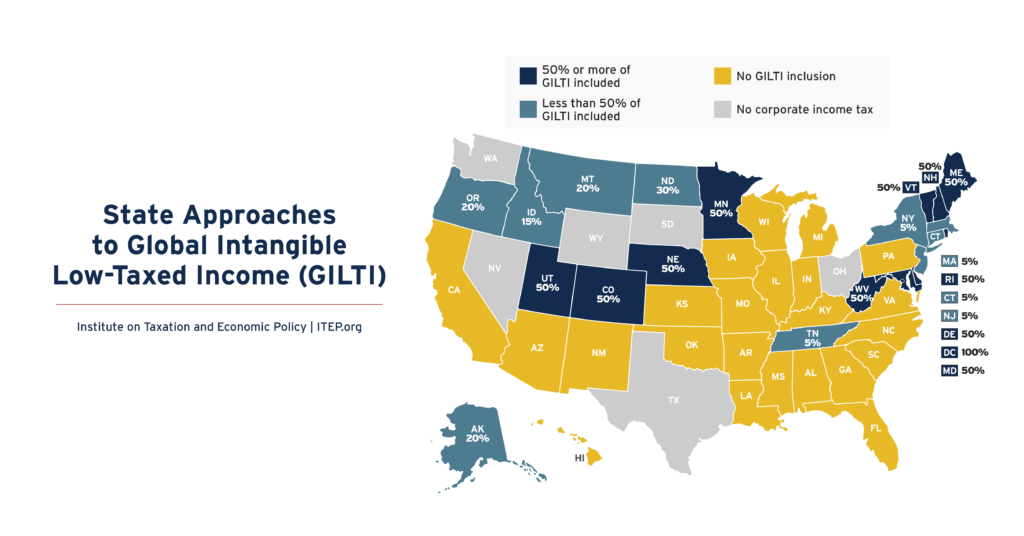
Many states with corporate income taxes include some amount of federally defined Global Intangible Low-Taxed Income (GILTI) in their tax bases. Twenty-one states plus D.C. include some amount of GILTI in their tax calculations in 2025.
Revenue Effect of Mandatory Worldwide Combined Reporting by State
February 21, 2025 • By ITEP Staff

Universal adoption of mandatory worldwide combined reporting (WWCR) in states with corporate income taxes would boost state tax revenue by $18.7 billion per year. The revenue effects of mandatory WWCR would vary across states. We estimate that 38 states and the District of Columbia would experience revenue increases totaling $19.1 billion. The top 10 states […]
Corporate Income Tax Filing Methods: States with Water’s Edge or Worldwide Combined Reporting
February 21, 2025 • By ITEP Staff
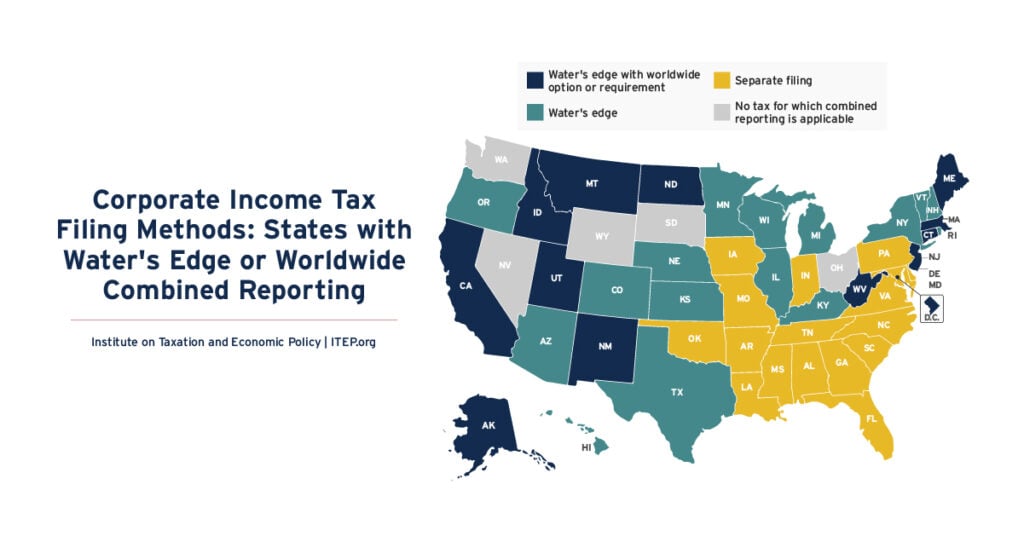
The purpose of state corporate income taxes is to tax the profit, or net income, an incorporated business earns in each state. Ascertaining the state where profits are earned is, however, complicated for companies that conduct business in multiple jurisdictions. Twenty-eight states plus D.C. now require a limited version of combined reporting called “water’s edge” […]
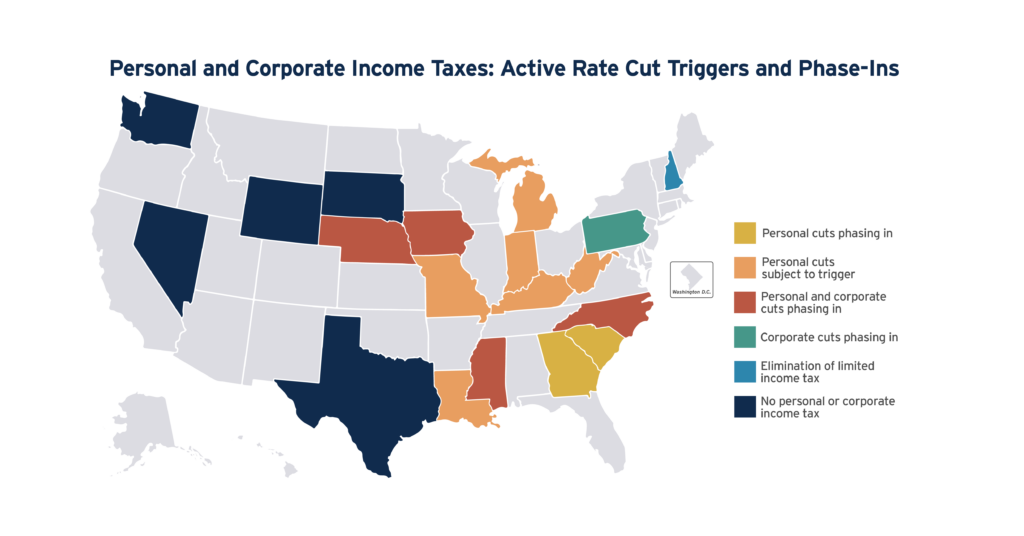
In recent years, lawmakers have been quick to push for phased-in tax cuts or cuts attached to trigger mechanisms. These policy tools push the implementation of tax cuts outside of the current budget window with a predetermined phase-in schedule or a mathematical formula tied to state revenue trends.
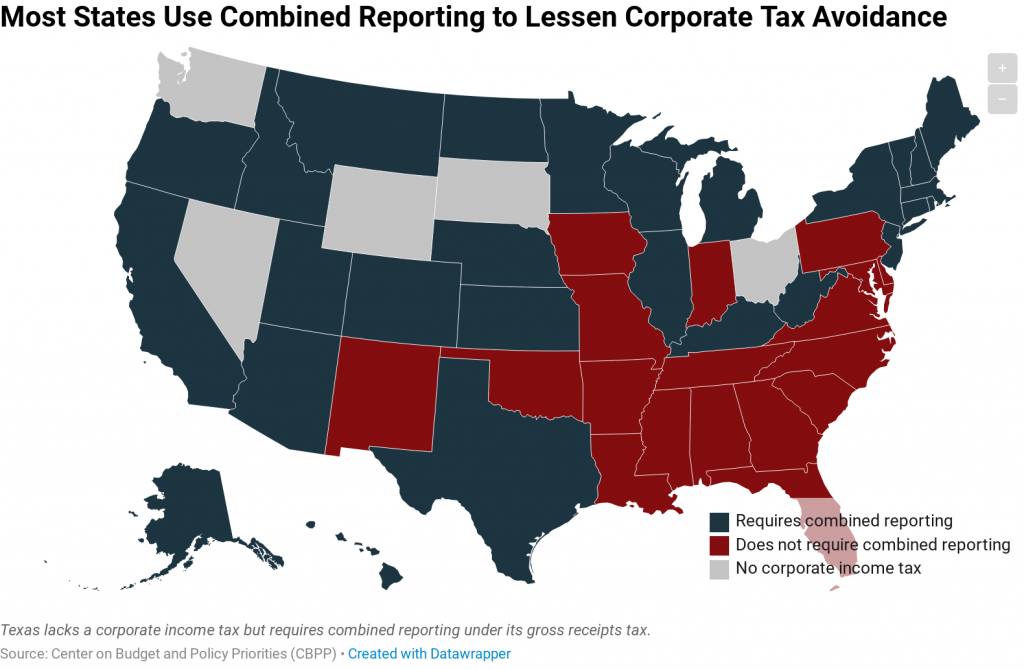
"Combined reporting" lessens the effectiveness of a tax avoidance scheme known as income shifting, in which large multi-state corporations dubiously claim that their income was earned in states with little or no corporate income tax.
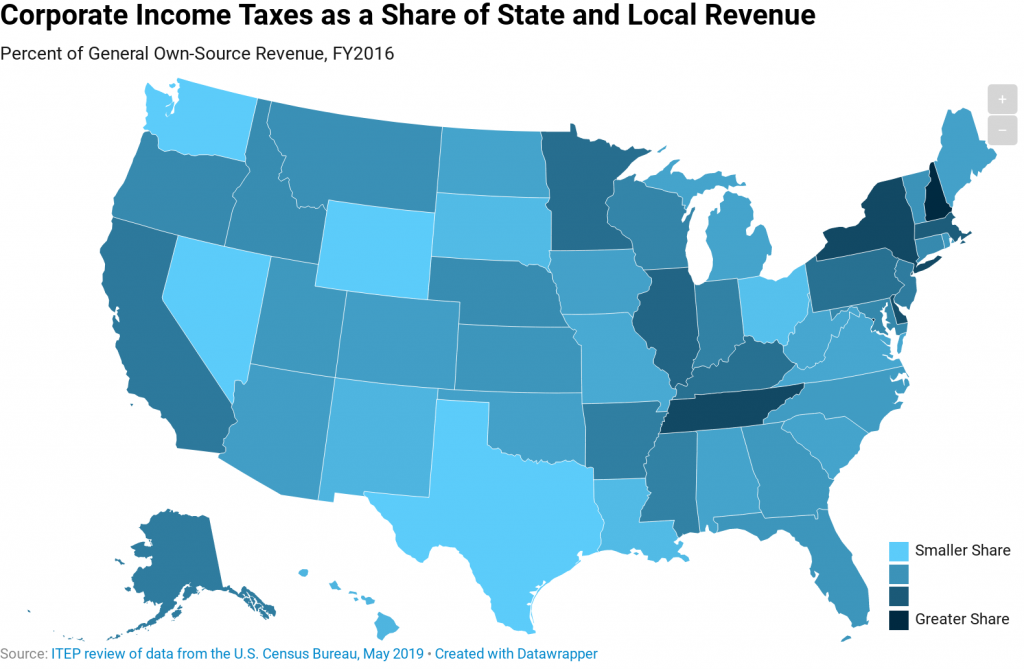
Corporate income taxes are an important source of revenue for state governments and ensure that profitable corporations benefiting from public services pay toward the maintenance of those services.
