Idaho
Download PDF
State and local tax shares of family income
| Top 20% | |||||||
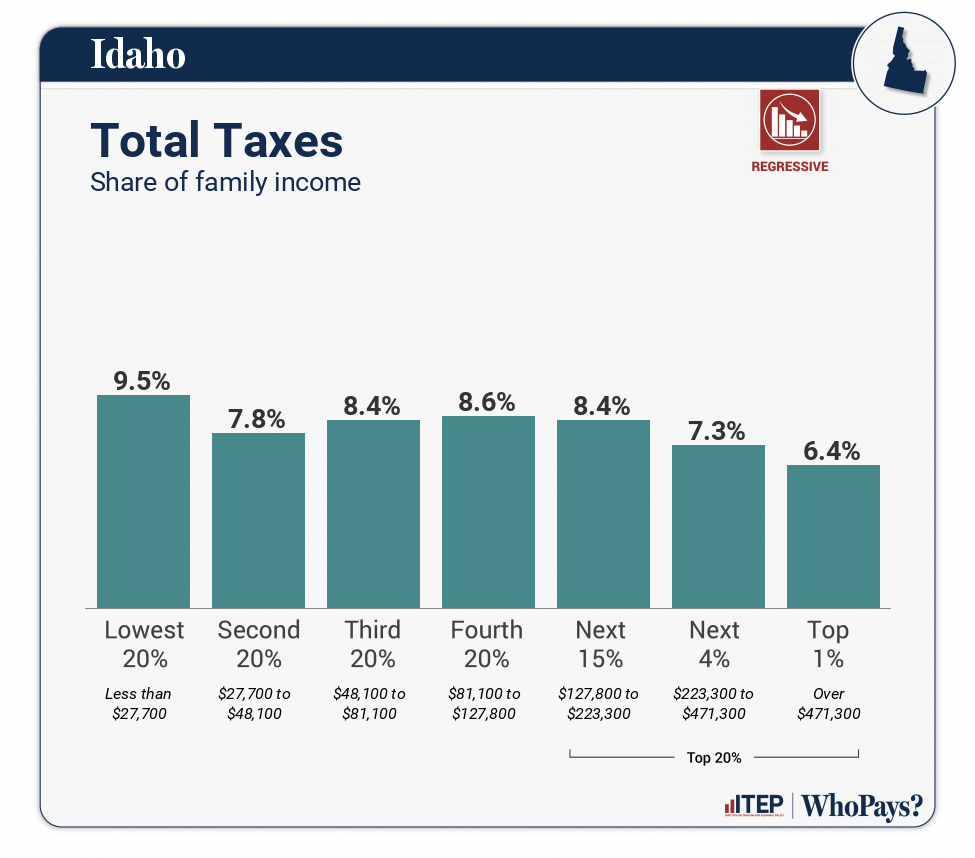
| Income Group | Lowest 20% | Second 20% | Middle 20% | Fourth 20% | Next 15% | Next 4% | Top 1% |
| Income Range | Less than $27,700 | $27,700 to $48,100 | $48,100 to $81,100 | $81,100 to $127,800 | $127,800 to $223,300 | $223,300 to $471,300 | Over $471,300 |
| Average Income in Group | $14,500 | $37,300 | $62,400 | $103,100 | $157,800 | $315,600 | $741,500 |
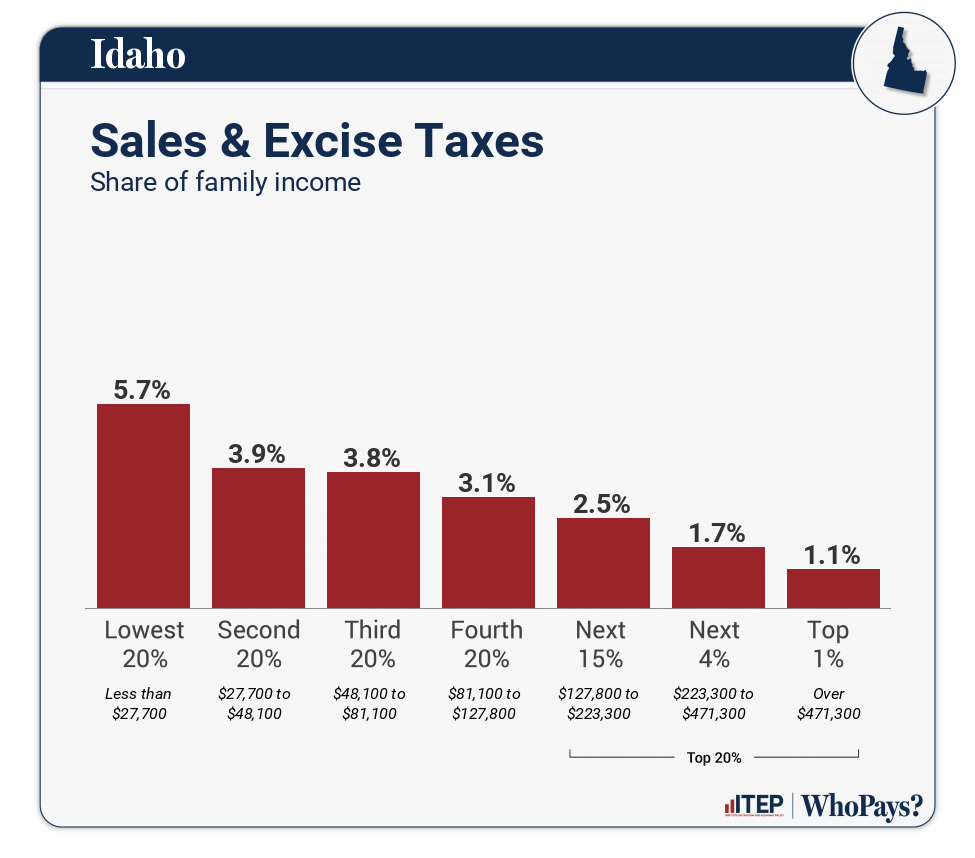
| Sales & Excise Taxes | 5.7% | 3.9% | 3.8% | 3.1% | 2.5% | 1.7% | 1.1% |
| General Sales–Individuals | 3.5% | 2.3% | 2.3% | 2% | 1.6% | 1% | 0.5% |
| Other Sales & Excise–Ind | 1.1% | 0.7% | 0.6% | 0.4% | 0.3% | 0.2% | 0.1% |
| Sales & Excise–Business | 1.1% | 0.8% | 0.8% | 0.7% | 0.6% | 0.6% | 0.5% |
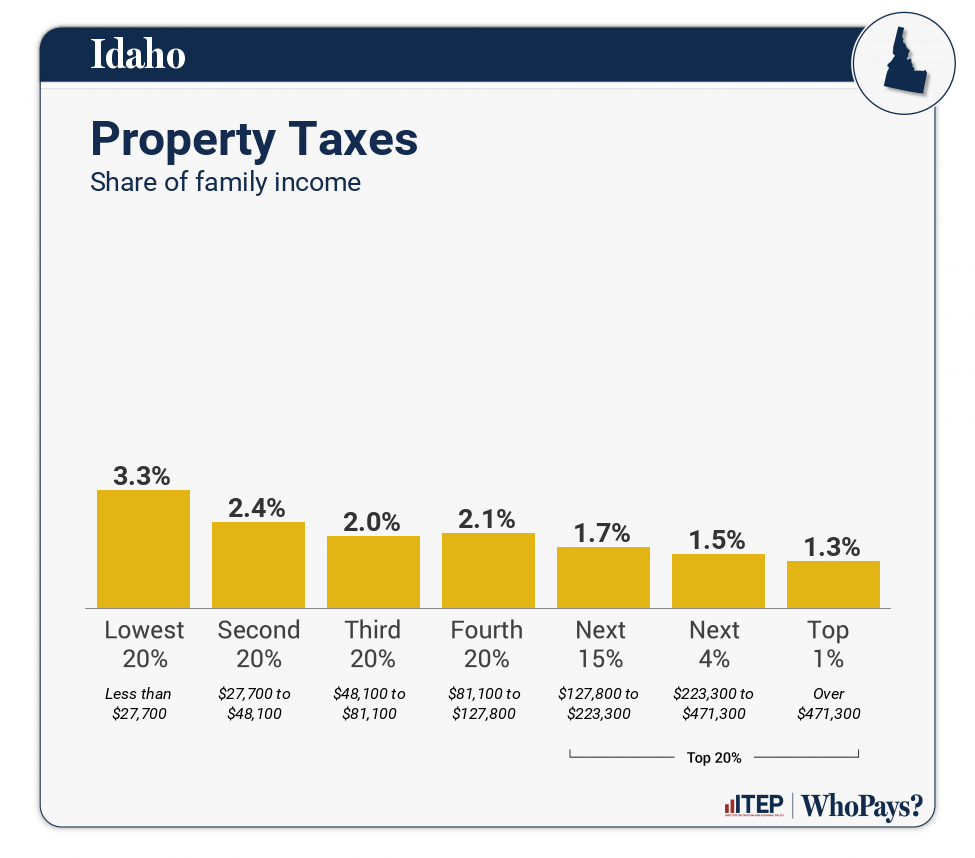
| Property Taxes | 3.3% | 2.4% | 2% | 2.1% | 1.7% | 1.5% | 1.3% |
| Home, Rent, Car–Individuals | 2.7% | 1.9% | 1.4% | 1.6% | 1.3% | 0.8% | 0.5% |
| Other Property Taxes | 0.6% | 0.5% | 0.6% | 0.5% | 0.4% | 0.7% | 0.8% |
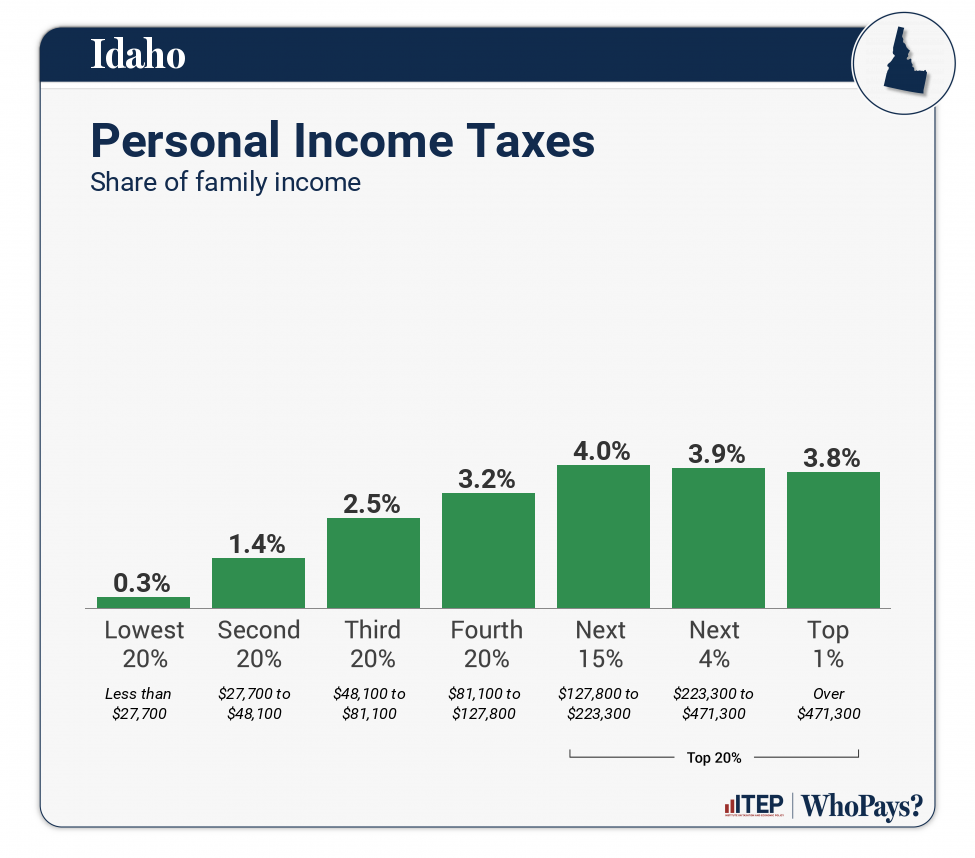
| Income Taxes | 0.3% | 1.5% | 2.5% | 3.3% | 4.1% | 4% | 3.9% |
| Personal Income Taxes | 0.3% | 1.4% | 2.5% | 3.2% | 4% | 3.9% | 3.8% |
| Corporate Income Taxes | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0.1% |
| Other Taxes | 0.2% | 0.1% | 0.1% | 0.1% | 0.1% | 0.1% | 0.1% |
| TOTAL TAXES | 9.5% | 7.8% | 8.4% | 8.6% | 8.4% | 7.3% | 6.4% |
| Individual figures may not sum to totals due to rounding. | |||||||
ITEP Tax Inequality Index
ITEP’s Tax Inequality Index measures the effects of each state’s tax system on income inequality. According to this measure, Idaho has the 36th most regressive state and local tax system in the country. Income disparities are larger in Idaho after state and local taxes are collected than before. (See Appendix B for state-by-state rankings and the report methodology for additional detail.)
Tax features driving the data in Idaho
|
Requires combined reporting for the corporate income tax; some foreign tax haven income is partially taxed through GILTI inclusion
Refundable income tax credit to offset the impact of its sales tax on groceries
Provides a Child Tax Credit (CTC)
Property tax homestead exemption
|
|
|
No property tax “circuit breaker” credit for low-income, non-senior taxpayers
Offers 60 percent exclusion for gains from sales of certain Idaho-based property
Nonrefundable Child Tax Credit (CTC) is limited in reach
State and local sales tax bases include groceries
Does not levy a tax on estates or inheritances
Personal income tax uses a flat rate
No Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC)
|