
Recent Work by ITEP
Trump Megabill Will Encourage Dynastic Wealth Hoarding by Further Weakening the Estate Tax
May 15, 2025 • By Jon Whiten

The tax and spending megabill signed into law by President Trump on July 4 will cut nearly $200 billion from food assistance, affecting tens of millions adults and children, while providing an estate tax cut costing roughly the same amount to a few thousand people who will leave behind more than $7 million to their heirs.
House Tax Bill Enlists the Wealthy to Spread Private School Vouchers
May 15, 2025 • By Carl Davis

The House tax plan cuts charitable giving tax incentives for donors to most nonprofit groups while roughly tripling the incentive available to donors to groups that fund private K-12 school vouchers. The bill would also allow private school voucher donors to avoid capital gains tax on their gifts of corporate stock, creating a profitable tax shelter for wealthy people who agree to help funnel public funds into private schools. The bill would reduce federal tax revenue by $23.2 billion over the next 10 years as currently drafted, or by $67 billion over the next 10 years if it is extended…
State Rundown 5/15: State Tax Debates Carry On in the Midst of Chaotic Federal Tax Landscape
May 15, 2025 • By ITEP Staff

Even as most major headlines have been about the ever-changing landscape of federal tax policy, the latest “ideas of the week," and now the House tax bill, state tax policy continues to be a priority for lawmakers.
Trump’s Proposed Higher Tax Rate on the Richest Taxpayers Would Affect Very Little of Their Income
May 10, 2025 • By Carl Davis, Steve Wamhoff
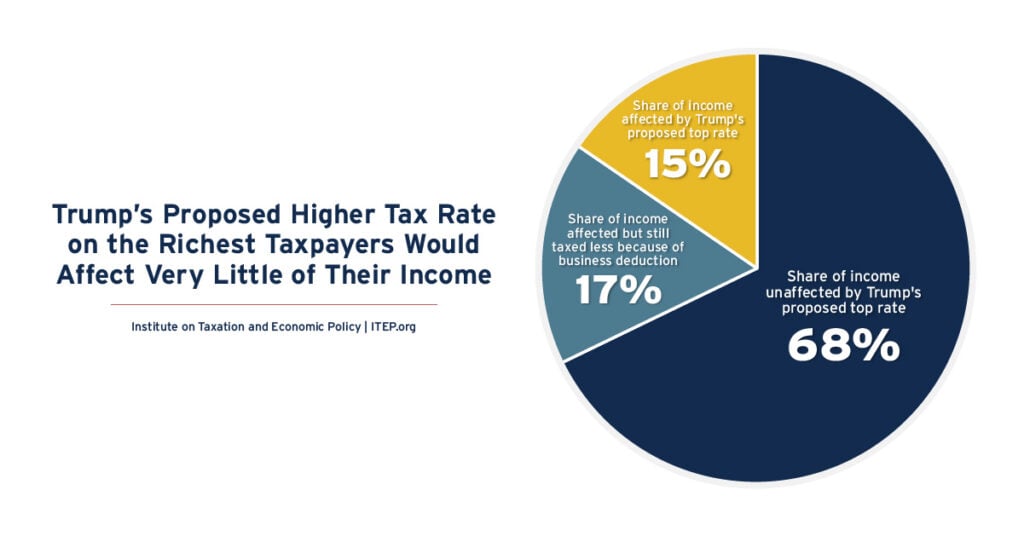
President Donald Trump has proposed allowing the top rate to revert from 37 percent to 39.6 percent for taxable income greater than $5 million for married couples and $2.5 million for unmarried taxpayers. But many other special breaks in the tax code would ensure that most income of very well-off people would never be subject to Trump’s 39.6 percent tax rate.
State Rundown 5/7: As Budget Season Heats Up, Tax Proposals Are Getting Serious
May 7, 2025 • By ITEP Staff
With spring in full bloom ,many state lawmakers are reaching tax policy agreements. Out west, lawmakers in North Dakota and Texas have moved major property tax cuts. Meanwhile, in the east and south, Vermont appears likely to pass an expansion to its Child Tax Credit and Earned Income Tax Credit, and South Carolina lawmakers are aiming to make deep, drastic cuts to the state’s income tax.
What Corporations Have to Gain from the Gutting of the IRS
May 7, 2025 • By Matthew Gardner, Spandan Marasini, Steve Wamhoff

Seven huge corporations recently announced that in 2024 they were allowed to collectively keep $1.4 billion in tax breaks from previous years that they had publicly admitted would likely be found illegal if investigated – all because the tax authorities were unable to identify and disallow them before the statute of limitations ran out.

The final budget adopted by the Maryland General Assembly shows progress in advancing tax equity in the state while boosting state revenues to address the state’s budget deficit. To help close a $3.3 billion budget deficit, Maryland legislators enacted much-needed tax reforms and progressive revenue raisers that help meet the state’s needs while making the […]
America Has Left the Building: U.S. Loses from Our Global Tax Policy Choices, Others Could Gain
May 5, 2025 • By Amy Hanauer

Countries that once looked to the U.S. for direction on tax policy have concluded they need to form alliances without us. If so, it will often be to the benefit of other people around the globe and to the deficit of U.S. communities.

Want to know more about the tax and spending megabill that President Trump recently signed into law? We've got you covered.
State Rundown 5/1: State Tax Debates Wrapping Up, and Just Beginning
May 1, 2025 • By ITEP Staff

The rampant uncertainty this year extends far beyond the national economy and federal policy, as many state legislatures are declaring their tax and budget debates finished, and just getting started, sometimes in the same breath.
