
Recent Work by ITEP
Gaps in Sales Tax Collection Linger at Amazon.com and Among Other E-Retailers
July 1, 2019 • By Carl Davis
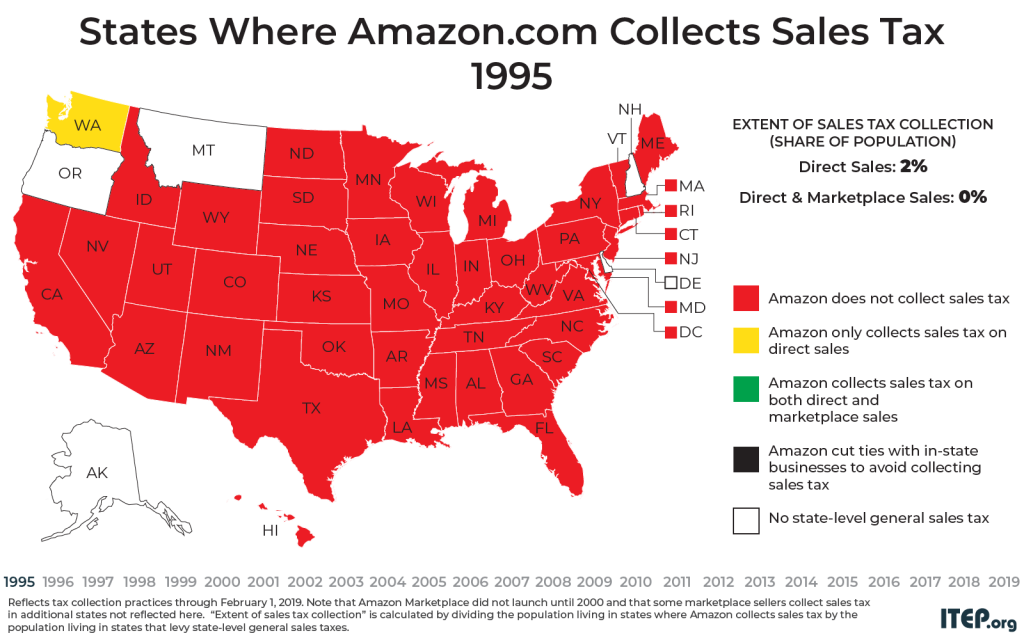
The last few years have brought big changes to sales tax collection for purchases made at Amazon.com and other e-retail websites. As recently as 2011, Amazon was only collecting sales tax on its direct sales in five states – a fact that gave the company a competitive edge over brick and mortar stores during a critical time in its growth. Today, Amazon is collecting state-level sales taxes on all its direct sales, but it still usually fails to collect sales tax on the large volume of sales it makes through the “Amazon Marketplace.” This points to a broader problem in…
Why Trump Administration’s Plan to Index Capital Gains to Inflation Is Just Another Giveaway to the Wealthy
June 28, 2019 • By Steve Wamhoff

The White House is reported to be planning to unilaterally adjust the way capital gains are assessed to benefit the wealthiest Americans. The proposal would adjust capital gains for inflation, reducing taxes disproportionately for the wealthiest households who own most assets by limiting their taxable gains to those above and beyond the inflation rate.
State Rundown 6/27: States Look at Raising Incomes at the Bottom, Taxes at the Top
June 27, 2019 • By ITEP Staff

Low-income working families got good news and bad news this week, as Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) enhancements passed in California and advanced in Oregon, while minimum wage increases failed in Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, and Wisconsin. Meanwhile, the momentum for taxing wealth and the very rich continued to grow, as more one-percenters called for enacting progressive taxes, and Inequality.org held a star-studded conference on why and how to do so.

A summary of ITEP reports, analyses and blogs this month.
Wealth Tax Is Supported by Basically Everyone Who Is Not a Politician
June 27, 2019 • By Steve Wamhoff

A February survey found that 61 percent of registered voters supported a wealth tax proposal, including 51 percent of Republican voters. And it’s not just the non-rich wanting to tax the very rich. A June survey found that 60 percent of millionaires support the idea.
Gas Taxes Rise in a Dozen States, Including an Historic Increase in Illinois
June 27, 2019 • By Carl Davis
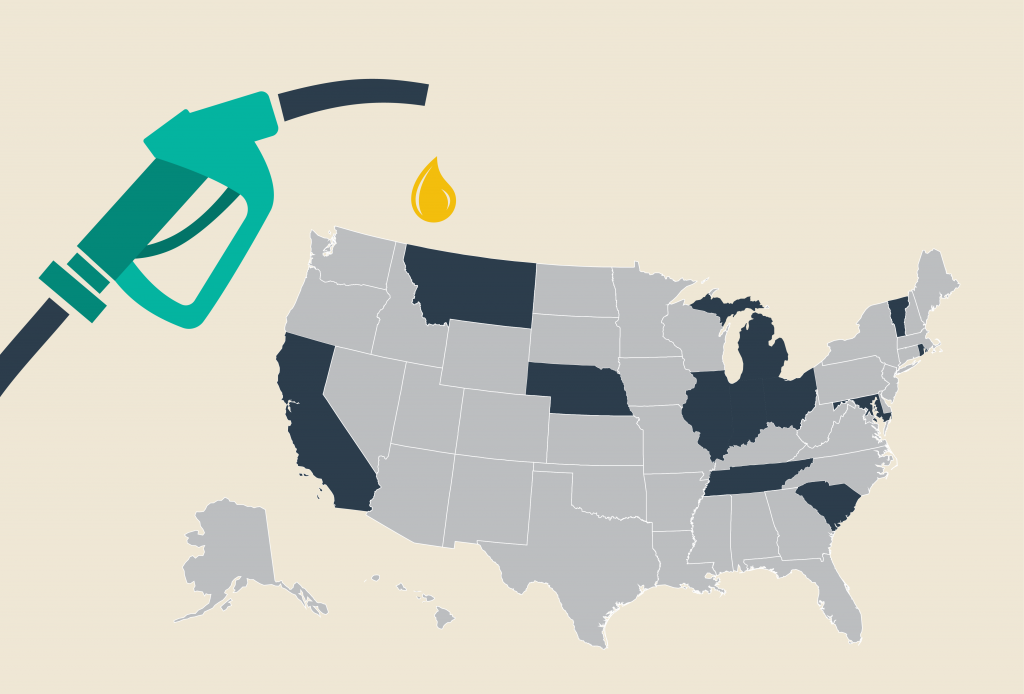
On July 1, 12 states will boost their gasoline taxes and 11 will boost their diesel taxes. The reasons for these increases vary, but they’re generally intended to fund maintenance and improvement of our nation’s transportation infrastructure–a job at which Congress has not excelled in recent years.
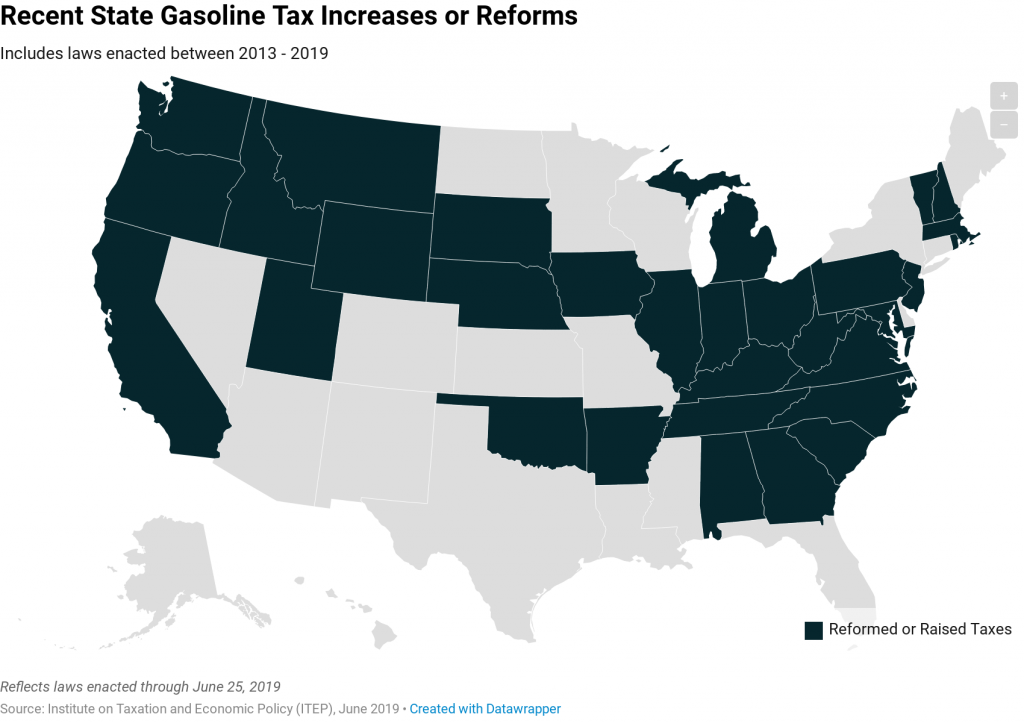
Gas taxes are the most important revenue source that states have available to pay for transportation infrastructure. In recent years, state lawmakers across the country have increasingly agreed that gas taxes must be increased to fund the maintenance and improvement of their infrastructure networks.
Ohio now enjoys the distinction of being the 30th state to raise or reform its gas tax this decade, and the third state to do so this year, under a bill signed into law by Gov. Mike DeWine. While state tax policy can be a contentious topic, there has been a remarkable level of agreement on the gasoline tax. Increasingly, state lawmakers are deciding that outdated gas taxes need to be raised and reformed to fund infrastructure projects that are vital to their economies. These actions are helping reverse losses in gas tax purchasing power caused by rising construction costs…
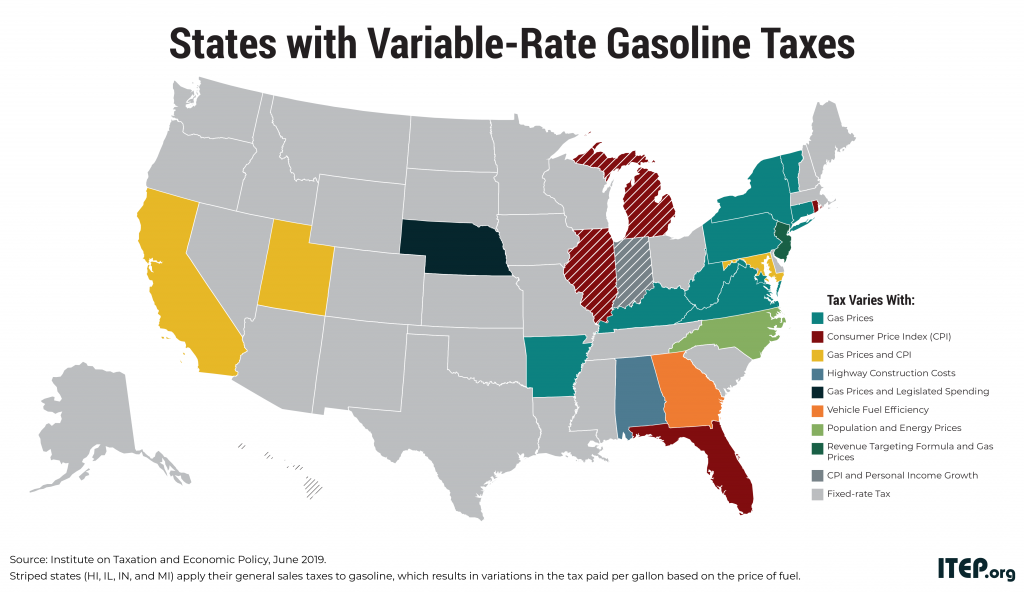
The flawed design of federal and state gasoline taxes has made it exceedingly difficult to raise adequate funds to maintain the nation’s transportation infrastructure. Twenty-eight states and the federal government levy fixed-rate gas taxes where the tax rate does not change even when the cost of infrastructure materials rises or when drivers purchase more fuel-efficient vehicles and pay less in gas tax. The federal government’s 18.4-cent gas tax, for example, has not increased in over 25 years. Many states have waited a decade or more since last raising their own gas tax rates.
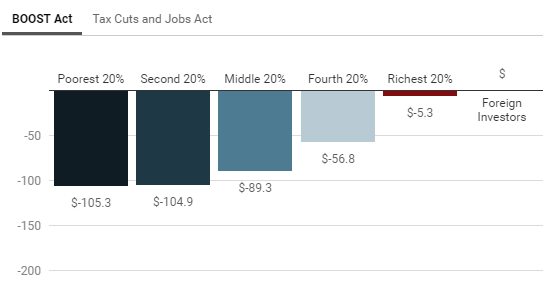
A refundable tax credit proposed by Rep. Rashida Tlaib (D-MI) would be more expansive than other recent tax credit proposals, new estimates from ITEP show. Rep. Tlaib’s proposal, unlike others, does not require households to work to receive the benefit.
