
District of Columbia

Refundable tax credits were a big part of state tax policy conversations this year. In 2025, nine states improved or created Child Tax Credits or Earned Income Tax Credits.
State Rundown 7/24: States Begin Preparing for Federal Megabill Fallout
July 24, 2025 • By ITEP Staff

All eyes in statehouses in recent weeks have been on federal budget negotiations, and now that the “megabill” has passed, they are focused in on their own budgets in search of ways to cope with the enormous consequences coming their way. All states will see fewer federal dollars flowing through their coffers, higher needs due […]
How Will the Trump Megabill Change Americans’ Taxes in 2026?
July 22, 2025 • By Steve Wamhoff, Michael Ettlinger, Carl Davis, Jon Whiten

The megabill will raise taxes on the poorest 40 percent of Americans, barely cut them for the middle 20 percent, and cut them tremendously for the wealthiest Americans next year.
Sales Tax Holidays Miss the Mark When it Comes to Effective Sales Tax Reform
July 17, 2025 • By Miles Trinidad

Sales tax holidays are often marketed as relief for everyday families, but they do little to address the deeper inequities of regressive sales taxes. In 2025, 18 states offer these holidays at a collective cost of $1.3 billion.
States Should Move Quickly to Chart Their Own Course on SALT Deductions
July 17, 2025 • By Dylan Grundman O'Neill, Nick Johnson

While a federal SALT cap is hotly debated, capping deductibility at $10,000 was an unambiguously good idea at the state level. States would be smart to stick with the current cap or, better yet, go even farther and repeal SALT deductions outright. Going along with a higher federal SALT cap would double down on a regressive tax cut that will mostly benefit a small number of relatively wealthy state residents and cost states significant revenue.
Anti-Tax Revolts Backfire: What We’ve Learned from 50 Years of Property Tax Limits
July 15, 2025 • By Rita Jefferson

Across-the-board property tax cuts create less fair local tax systems in the long run. State legislators and local governments should prioritize the residents who can least afford their property taxes, not the residents and businesses who can.
How Much Would Every Family in Every State Get if the Megabill’s Tax Cuts Given to the Rich Had Instead Been Evenly Divided?
July 14, 2025 • By Michael Ettlinger
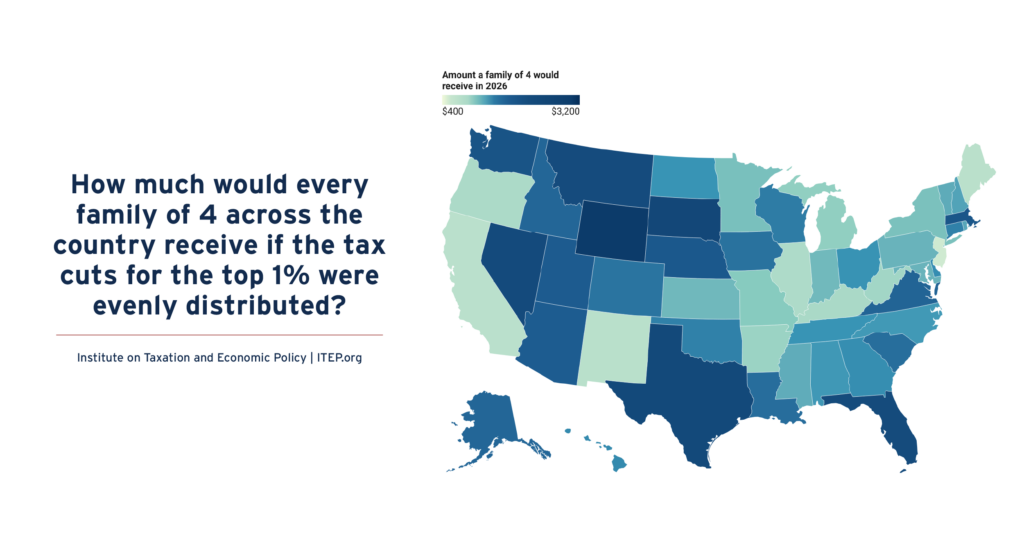
If instead of giving $117 billion to the richest 1 percent, that money had been evenly divided among all Americans, we'd each get $343 - or nearly $1,400 for a family of four.
Analysis of Tax Provisions in the Trump Megabill as Signed into Law: National and State Level Estimates
July 7, 2025 • By Steve Wamhoff, Carl Davis, Joe Hughes, Jessica Vela

President Trump has signed into law the tax and spending “megabill” that largely favors the richest taxpayers and provides working-class Americans with relatively small tax cuts that will in many cases be more than offset by Trump's tariffs.
Trump Megabill Will Give $117 Billion in Tax Cuts to the Top 1% in 2026. How Much In Your State?
June 30, 2025 • By Michael Ettlinger

The predominant feature of the tax and spending bill working its way through Congress is a massive tax cut for the richest 1 percent — a $114 billion benefit to the wealthiest people in the country in 2026 alone.
How Much Do the Top 1% in Each State Get from the Trump Megabill?
June 30, 2025 • By Carl Davis

The Senate tax bill under debate right now would bring very large tax cuts to very high-income people. In total, the richest 1 percent would receive $114 billion in tax cuts next year alone. That would amount to nearly $61,000 for each of these affluent households.

State legislatures are enjoying a relatively quiet period right now, though it is merely a temporary calm before the storm of the federal tax and budget debate begins raging again.

As the Washington, D.C. region heads toward a likely recession, local policymakers will need to look to new revenue sources to help lessen the pain. In D.C., lawmakers ought to adopt a simple reform that would raise substantial revenue and make the District’s business tax system fairer.
State Rundown 6/5: States Wrap Sessions, Some Prepare for Fiscal Uncertainty
June 5, 2025 • By ITEP Staff

States use the final hours of their legislative sessions to address deficits and preserve revenue in preparation for the times ahead.
Analysis of Tax Provisions in the House Reconciliation Bill: National and State Level Estimates
May 22, 2025 • By Carl Davis, Jessica Vela, Joe Hughes, Steve Wamhoff

The poorest fifth of Americans would receive 1 percent of the House reconciliation bill's net tax cuts in 2026 while the richest fifth of Americans would receive two-thirds of the tax cuts. The richest 5 percent alone would receive a little less than half of the net tax cuts that year.

Want to know more about the tax and spending megabill that President Trump recently signed into law? We've got you covered.
IRS Cooperation with ICE Will Damage Public Trust, Putting Tax Revenues in Jeopardy
April 10, 2025 • By Marco Guzman

Attempts by the Department of Homeland Security to secure private information from the IRS on people who file taxes with an Individual Taxpayer Identification Number is a violation of federal privacy laws that protect taxpayers. It is also a change that could seriously damage public trust in the IRS, which could jeopardize billions of dollars in tax payments by hardworking immigrant families.
Sharp Turn in Federal Policy Brings Significant Risks for State Tax Revenues
April 9, 2025 • By Carl Davis

Summary The new presidential administration and Congress have indicated that they intend to bring about a dramatic federal retreat in funding for health care, food assistance, education, and other services that will push more of the responsibility for providing these essential services to the states. Meeting these new obligations would be a challenging task for […]
State Rundown 4/3: Amidst Tariff Uncertainty, State Lawmakers Talk Taxes
April 3, 2025 • By ITEP Staff

While all eyes are on the Trump administration’s tariffs on foreign imports, state lawmakers are moving forward with a mix of deep, regressive tax cuts and progressive revenue raisers.
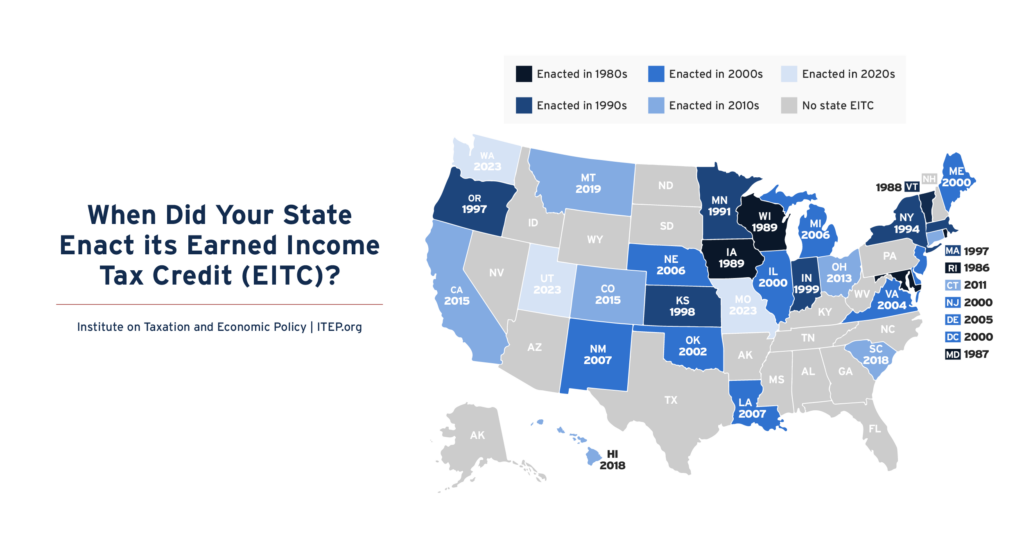
The Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) supports millions of workers and families and continues to grow in states and localities across the country. Today, 31 states plus the District of Columbia and Puerto Rico offer EITCs. Local EITCs can also now be found in Montgomery County, Maryland, New York City, and San Francisco, where they benefited 700,000 households in 2023.

This week, we celebrate 50 years of the federal Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) and the impact it's had on millions of workers and families. In 2023 alone, the latest year of available data, the federal EITC alongside the refundable portion of the Child Tax Credit lifted 6.4 million people and 3.4 million children out of poverty.

The U.S. needs a tax code that is more adequate, meaning any major tax legislation should increase revenue, not reduce it. The U.S. also needs a tax code that is more progressive, meaning any significant tax legislation should require more, not less, from those most able to pay.
A Revenue Impact Analysis of the Educational Choice for Children Act of 2025
March 18, 2025 • By Carl Davis

The Educational Choice for Children Act of 2025 would provide donors to nonprofit groups that distribute private K-12 school vouchers with a dollar-for-dollar federal tax credit in exchange for their contributions. In total, the ECCA would reduce federal and state tax revenues by $10.6 billion in 2026 and by $136.3 billion over the next 10 years. Federal tax revenues would decline by $134 billion over 10 years while state revenues would decline by $2.3 billion.
State Rundown 3/6: In the Shadow of Chaotic Federal Policymaking States Seek to Tax the Top, Cut Taxes
March 6, 2025 • By ITEP Staff

Proposals from governors in both New Jersey and Wisconsin include provisions to tax high-income earners. Meanwhile, several major tax proposals are advancing in the great plains, with Iowa considering a major cut to unemployment taxes, North Dakota advancing new benefits for private schools, and Wyoming cutting property taxes. The District of Columbia is facing a more than a $1 billion revenue shortfall over the next three years, compared to previous estimates, and a mild recession due in large part to the layoffs of federal workers.
Below is a list of tax expenditure reports published in the states.
Testimony: ITEP’s Matt Gardner Discusses How to Improve Maryland’s Tax Code at House Ways & Means Committee Hearing
February 27, 2025
ITEP Senior Fellow Matt Gardner submitted the written testimony below to Maryland’s House Ways & Means Committee on February 20, 2025. Video of his oral testimony is at the bottom of this post. Thank you for the opportunity to submit written testimony. My name is Matthew Gardner. I am a senior fellow at the Institute […]
