
Reports
Fairness Matters: A Chart Book on Who Pays State and Local Taxes
April 11, 2024 • By ITEP Staff

State and local tax codes can do a lot to reduce inequality. But they add to the nation’s growing income inequality problem when they capture a greater share of income from low- or moderate-income taxpayers. These regressive tax codes also result in higher tax rates on communities of color, further worsening racial income and wealth divides.

America's tax system is just barely progressive, and not nearly as progressive as many suggest or as progressive as it could be. There is plenty of room for lawmakers to improve the progressivity of the tax code to combat economic, wealth, and racial inequality.
Revenue-Raising Proposals in President Biden’s Fiscal Year 2025 Budget Plan
March 12, 2024 • By Steve Wamhoff

President Biden’s most recent budget plan includes proposals that would raise more than $5 trillion from high-income individuals and corporations over a decade. Like the budget plan he submitted to Congress last year, it would partly reverse the Trump tax cuts for corporations and high-income individuals, clamp down on corporate tax avoidance, and require the wealthiest individuals to pay taxes on their capital gains income just as they are required to for other types of income, among other reforms.
Corporate Tax Avoidance in the First Five Years of the Trump Tax Law
February 29, 2024 • By Matthew Gardner, Spandan Marasini, Steve Wamhoff

The Trump tax law overhaul cut the federal corporate income tax rate from 35 percent to 21 percent, but during the first five years it has been in effect, most profitable corporations paid considerably less than that.
Tax Policy to Reduce Racial Retirement Wealth Inequality
February 6, 2024 • By Brakeyshia Samms, Carl Davis

Historic and ongoing discrimination have created stark racial disparities in the US, and the racial retirement wealth gap is one such example.
Ongoing Use of Offshore Tax Havens Demonstrates the Need for the Global Minimum Tax
January 17, 2024 • By Steve Wamhoff

Key Findings To avoid taxation, American corporations use accounting gimmicks that make profits appear to be earned in foreign jurisdictions which tax corporate profits very lightly or not at all. In 2020, American corporations claimed profits in 15 of these jurisdictions that were often far too high to be possible. For example, in four jurisdictions […]
The Estate Tax is Irrelevant to More Than 99 Percent of Americans
December 7, 2023 • By Steve Wamhoff

The federal estate tax has reached historic lows. In 2019, only 8 of every 10,000 people who died left an estate large enough to trigger the tax. Legislative changes under presidents of both parties have increased the basic exemption from the estate tax over the past 20 years. This has cut the share of adults leaving behind taxable estates down from more than 2 percent to well under 1 percent.
Local Earned Income Tax Credits: How Localities Are Boosting Economic Security and Advancing Equity with EITCs
October 30, 2023 • By Andrew Boardman, Galen Hendricks, Kamolika Das

Leading localities are using refundable EITCs to boost incomes and reduce taxes for workers and families with low and moderate incomes. These local credits build on the success of EITCs at the federal and state levels, reduce economic hardship and improve the fairness of the tax code.
Supreme Corporate Tax Giveaway: Who Would Benefit from the Roberts Court Striking Down the Mandatory Repatriation Tax?
September 27, 2023 • By Matthew Gardner, Spandan Marasini

The Supreme Court is set to hear what could become one of the most important tax cases in a century. If decided broadly—with a ruling that strikes down the Mandatory Repatriation Tax for corporations, effectively making it unconstitutional to tax unrealized income—the Roberts Court’s decision in Moore v. US could stretch far beyond the plaintiffs themselves and would put in legal jeopardy many laws that prevent corporations and individuals from avoiding taxes and level the economic playing field.
Expanding the Child Tax Credit Would Advance Racial Equity in the Tax Code
August 29, 2023 • By Emma Sifre, Joe Hughes
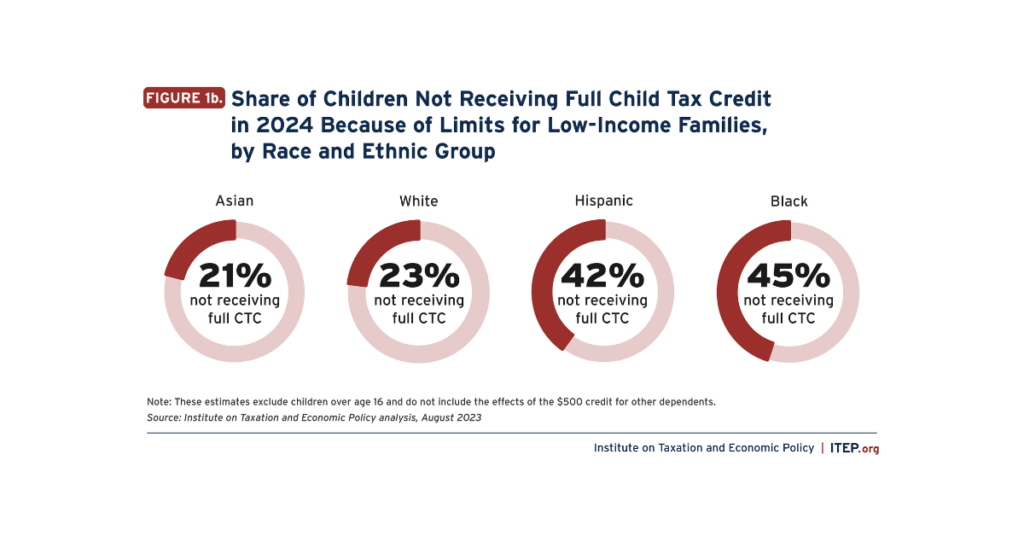
Expanding the federal Child Tax Credit to 2021 levels would help nearly 60 million children next year. It would help the lowest-income children the most and would particularly help children and families of color.
‘Fair Share Act’ Would Strengthen Medicare and Social Security Taxes
July 11, 2023 • By Joe Hughes, Steve Wamhoff

The Medicare and Social Security Fair Share Act would reform the taxes that Americans pay to finance these two important programs so that the richest 2 percent of Americans pay these taxes on most of their income the way that middle-class taxpayers already do.
Corporations Reap Billions in Tax Breaks Under ‘Bonus Depreciation’
June 29, 2023 • By Matthew Gardner, Steve Wamhoff

Since TCJA expanded tax breaks for “accelerated depreciation” starting in 2018, it has reduced taxes by nearly $67 billion for the 25 profitable corporations that benefited the most. Congress is now looking at extending this policy.
Preventing an Overload: How Property Tax Circuit Breakers Promote Housing Affordability
May 11, 2023 • By Brakeyshia Samms, Carl Davis

Circuit breaker credits are the most effective tool available to promote property tax affordability. These policies prevent a property tax “overload” by crediting back property taxes that go beyond a certain share of income. Circuit breakers intervene to ensure that property taxes do not swallow up an unreasonable portion of qualifying households’ budgets.
Extending Temporary Provisions of the 2017 Trump Tax Law: National and State-by-State Estimates
May 4, 2023 • By Joe Hughes, Matthew Gardner, Steve Wamhoff
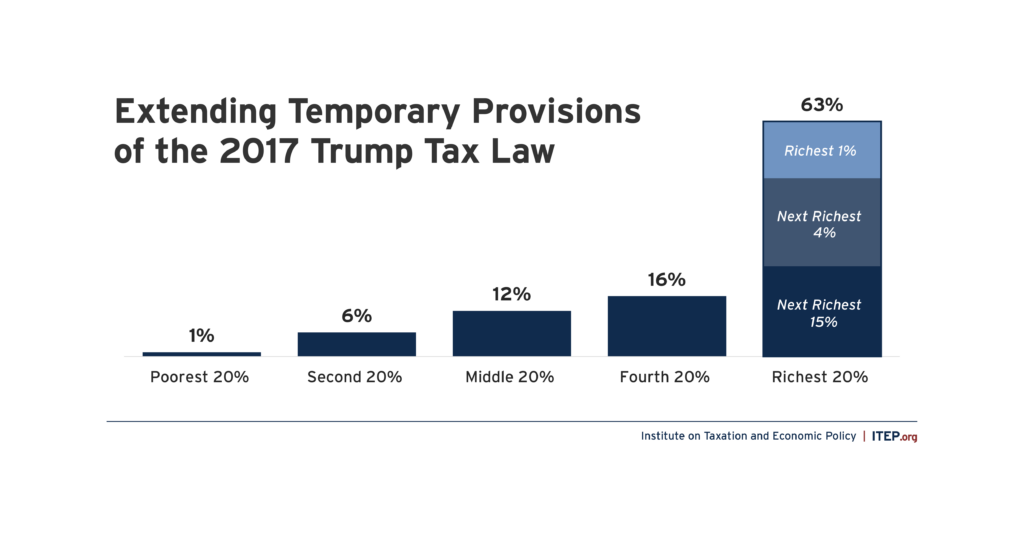
The push by Congressional Republicans to make the provisions of the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act permanent would cost nearly $300 billion in the first year and deliver the bulk of the tax benefits to the wealthiest Americans.

State governments provide a wide array of tax subsidies to their older residents. But too many of these carveouts focus on predominately wealthy and white seniors, all while the cost climbs.
Effects of President Biden’s Proposal to Expand the Child Tax Credit
March 16, 2023 • By Joe Hughes

In his latest budget proposal, President Biden proposes enhancing the Child Tax Credit (CTC) based on the temporary credit that was in effect for 2021 as part of the American Rescue Plan Act. In this report we analyze how that proposal would help children and families.
Revenue-Raising Proposals in President Biden’s Fiscal Year 2024 Budget Plan
March 10, 2023 • By Steve Wamhoff

President Biden’s latest budget proposal includes trillions of dollars of new revenue that would be paid by the richest Americans, both directly through increases in personal income, Medicare and estate taxes, and indirectly through increases in corporate income taxes.
State Child Tax Credits and Child Poverty: A 50-State Analysis
November 16, 2022 • By Aidan Davis

Regardless of future Child Tax Credit developments at the federal level, state policies can supplement the federal credit to deliver additional benefits to children and families. State credits can be specifically tailored to meet the needs of local populations while also producing long-term benefits for society as a whole

More than one in four dollars of wealth in the U.S. is held by a tiny fraction of households with net worth over $30 million. Nationally, we estimate that wealth over $30 million per household will reach $26 trillion in 2022 with roughly one-fifth of that amount ($4.5 trillion) held by billionaires.

While the Inflation Reduction Act's corporate minimum tax is a huge improvement in our tax system, implementing the global corporate minimum tax would improve it much more. And if other governments implement the global minimum tax, the United States will have an even stronger interest in joining them to ensure that new revenue collected from American corporations flows to the U.S. rather than to other countries.
National and State-by-State Estimates of Two Approaches to Expanding the Child Tax Credit
September 7, 2022 • By Emma Sifre, Joe Hughes, Steve Wamhoff

The Romney Child Tax Credit plan would leave a quarter of children worse off compared to current law and help half as many low-income children as the 2021 expansion of the credit.
Creating Racially and Economically Equitable Tax Policy in the South
June 21, 2022 • By Kamolika Das

The South's negative outcomes on measures of wellbeing are the result of a century and a half of policy choices. Lawmakers have many options available to make concrete improvements to tax policy that would raise more revenue, do so equitably, and generate resources that could improve schools, healthcare, social services, infrastructure, and other public resources.
Revenue-Raising Proposals in President Biden’s Fiscal Year 2023 Budget Plan
April 26, 2022 • By Steve Wamhoff

President Biden's latest budget plan includes proposals that would raise $2.5 trillion in new revenue. While many of these reforms appeared in his previous budget, some of them are brand new, such as his proposal to prevent basis-shifting in partnerships and his Billionaires Minimum Income Tax.
What the Biden Administration Can Do on Its Own, Without Congress, to Fix the Tax Code
March 25, 2022 • By Steve Wamhoff

The Biden administration has several options to address tax reform even when Congress is unable or unwilling to help.
State-by-State Estimates of Sen. Rick Scott’s “Skin in the Game” Proposal
March 7, 2022 • By Steve Wamhoff
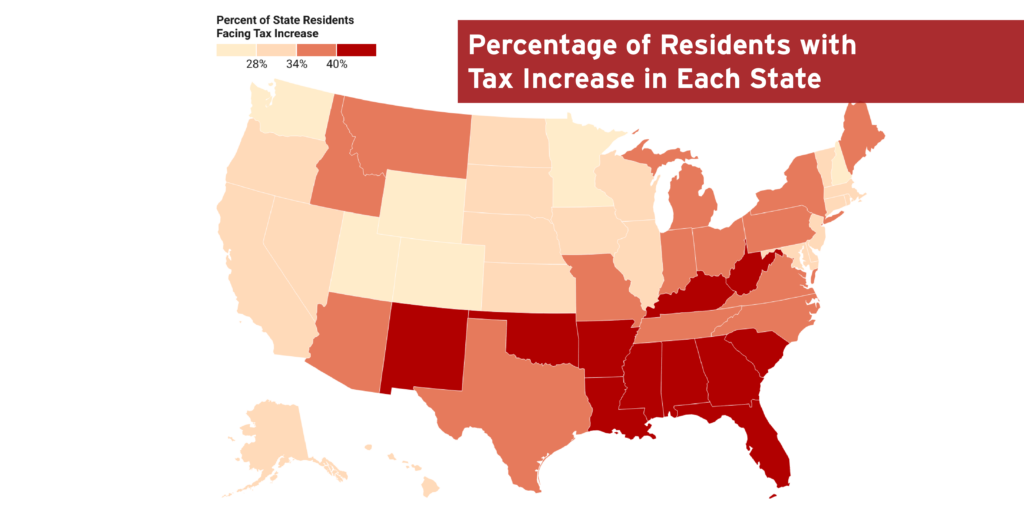
A proposal from Sen. Rick Scott would increase taxes for more than 35% of Americans, with the poorest fifth of Americans paying 34% of the tax increase.
