
Recent Work
2162 items
New Legislation Would Close Significant Offshore Loopholes in the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act
June 6, 2018 • By Richard Phillips

One simple rule should drive the nation’s international tax policies: tax the offshore profits of American companies the same way their domestic profits are taxed. The latest legislation to approach that ideal is the Per-Country Minimum Act (H.R. 6015), from Rep. Peter DeFazio (D-OR). The DeFazio bill closes the loophole that allows corporations to use foreign tax credits to shelter profits in tax havens from U.S. taxes. No other bill addresses this.
The New International Corporate Tax Rules: Problems and Solutions
June 6, 2018 • By Steve Wamhoff

The nation’s corporate tax system has been dysfunctional for decades. Unfortunately, the recently enacted Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) fails to solve fundamental problems facing the corporate tax and, in some ways, makes these problems even worse.
State Rundown 6/1: Time Is Ripe for Closer Look at Intergovernmental Relations
June 1, 2018 • By ITEP Staff

This week, Virginia lawmakers overcame their budget impasse and approved an expansion of Medicaid, North Carolina's behind closed doors budget debate appears to be wrapping up, and Vermont's special session continues in the wake of the governor's vetoes of the state budget and accompanying tax bills. New research highlighted in our What We're Reading section shows that both corporate income tax cuts and business tax subsidies contribute to wider economic inequality. And the possible reconstitution of a federal commission on intergovernmental relations could not come soon enough, as other headlines this week include a state-to-local shift in school funding, governments…
ITEP’s Senior Policy Analyst Richard Phillips Remarks at Facebook Shareholders Meeting in Favor of Tax Principles Resolution
May 31, 2018 • By Richard Phillips

Read the Remarks in PDF Listen to Webcast of Shareholders Meeting (Richard’s remarks begin at 21:20) My name is Richard Phillips and I am here to present Item 8 on behalf of the AFL-CIO Office of Investments. This proposal requests that the board articulate a set of responsible global tax principles that ensure the company […]
Facebook Facing Shareholder Scrutiny for Its Offshore Tax Avoidance
May 30, 2018 • By Richard Phillips

In advance of its annual shareholders meeting on May 31, Facebook was confronted with a shareholder resolution asking it to endorse a set of principles to guide its tax policy and to ensure that such principles consider the impact of its tax strategies on local economies and public services. The resolution is a signal from a group of concerned shareholders that Facebook’s tax avoidance hurts its reputation, the communities in which it operates, and creates financial risks to the company’s shareholders.
As IRS Prepares to Act, Red-State Taxpayers Profit from Use of SALT “Workaround Credits”
May 24, 2018 • By Carl Davis

A new ITEP report explains the close parallels between the new workaround credits and existing state tax credits, including those benefiting private schools. The report comes the same day that the IRS and Treasury Department announced they would seek new regulations related to these tax credits. It notes that the SALT workarounds are emblematic of a broader weakness with the federal charitable deduction. And it cautions regulators to avoid a “narrow fix” that will only address the newest SALT workarounds (which, so far, have only been enacted in blue states) without also addressing other abuses of the deduction, which have…
New Legislation Would End Tax Incentives to Move Jobs and Profits Offshore
May 24, 2018 • By Richard Phillips

New legislation introduced today, the No Tax Breaks for Outsourcing Act, by Rep. Lloyd Doggett (D-TX) and Sen. Sheldon Whitehouse (D-RI) would help repair the damage to the international tax code wrought by the new Trump-GOP tax law and move toward a system where U.S. corporations can’t reap tax benefits from shifting jobs and profits offshore.
State Rundown 5/23: Special Sessions Abound Amid Budget Vetoes, Stalemates, Federal Tax Bill
May 23, 2018 • By ITEP Staff

This week the governors of Louisiana and Minnesota both vetoed budget bills, leading to another special session in Louisiana and unanswered questions in Minnesota, and Missouri legislators managed to push through a tax shift bill just before adjourning their regular session and heading right into a special session to impeach their governor. Wisconsin and Wyoming localities are both looking at ways to raise revenues as state funding drops. And our What We're Reading section contains helpful pieces on changing demographics, the effects of wealth inequality on families with children, and the impacts of the Supreme Court sports gambling and online…
SALT/Charitable Workaround Credits Require a Broad Fix, Not a Narrow One
May 23, 2018 • By Carl Davis

The federal Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) enacted last year temporarily capped deductions for state and local tax (SALT) payments at $10,000 per year. The cap, which expires at the end of 2025, disproportionately impacts taxpayers in higher-income states and in states and localities more reliant on income or property taxes, as opposed to sales taxes. Increasingly, lawmakers in those states who feel their residents were unfairly targeted by the federal law are debating and enacting tax credits that can help some of their residents circumvent this cap.
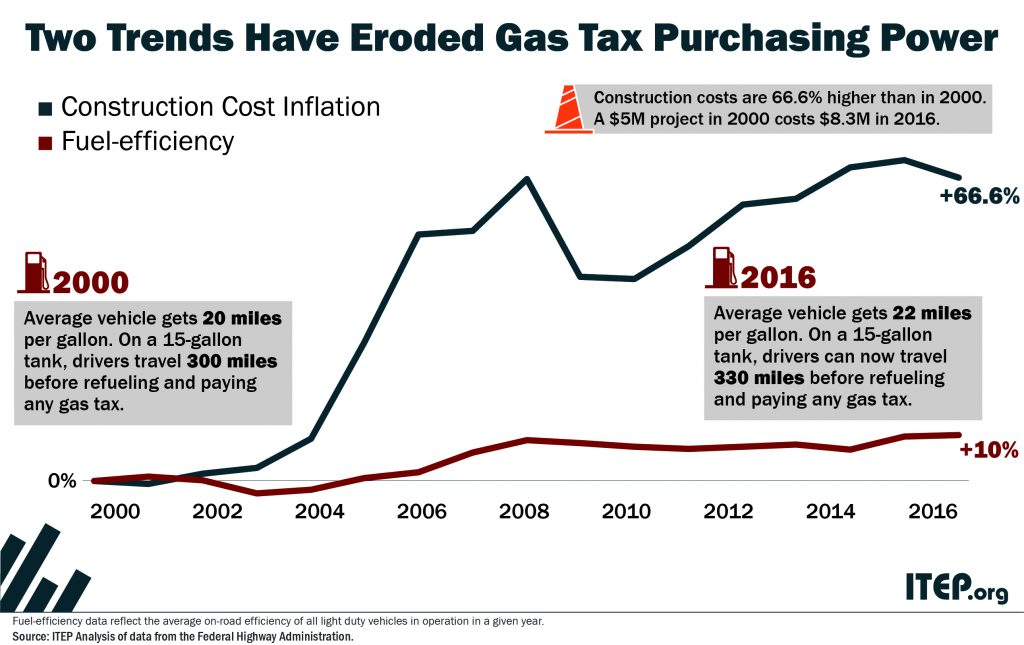
An updated version of this blog was published in April 2019. State tax policy can be a contentious topic, but in recent years there has been a remarkable level of agreement on one tax in particular: the gasoline tax. Increasingly, state lawmakers are deciding that outdated gas taxes need to be raised and reformed to fund infrastructure projects that are vital to their economies.
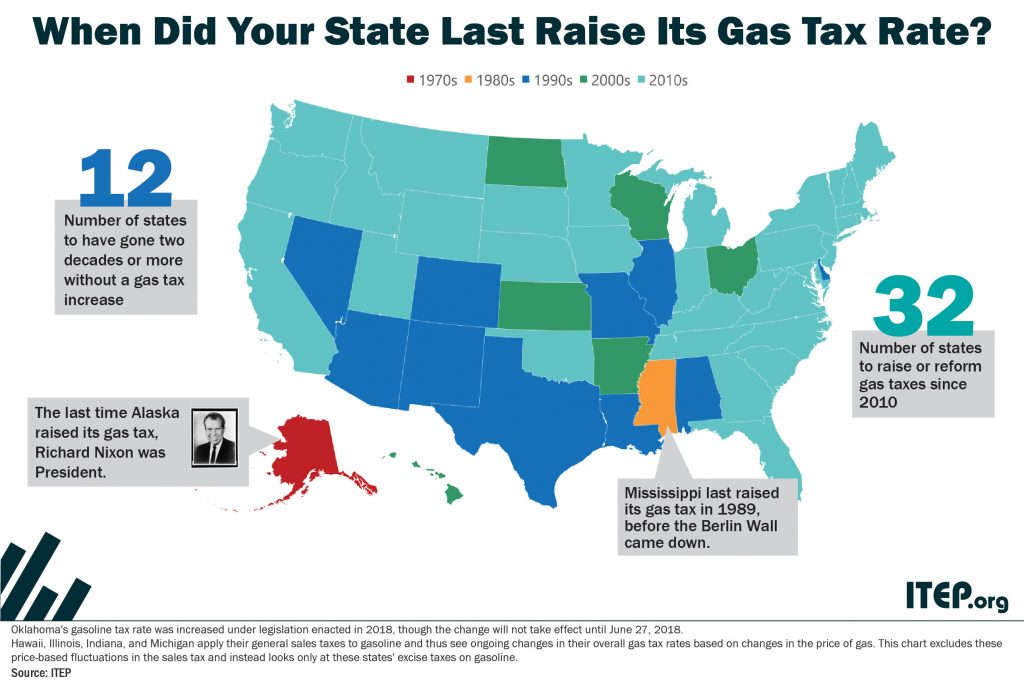
Many state governments are struggling to repair and expand their transportation infrastructure because they are attempting to cover the rising cost of asphalt, machinery, and other construction materials with fixed-rate gasoline taxes that are rarely increased.

New Jersey’s new governor, Phil Murphy campaigned on a promise to raise state income taxes on millionaires, a proposal that is supported by 70 percent of the state and was, until recently, backed by New Jersey’s Senate President, Steve Sweeney. In recent months, Sweeney changed his position on the proposed millionaires tax and called for an increase in New Jersey’s corporate tax instead. The idea of hiking taxes on corporations is not a bad one, particularly since corporations received a windfall from the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act. But Sweeney’s new opposition to an income tax hike for the state’s…
State Rundown 5/17: Don’t Bet on Legal Sports Betting Solving State Budget Woes
May 17, 2018 • By ITEP Staff

This week the U.S. Supreme Court opened the door to legal sports gambling in the states (see our What We're Reading section), which will surely be a hot topic in state legislative chambers, but most states currently have more pressing matters before them. The teacher pay crisis made news in North Carolina, Alabama, and nationally. Louisiana, Oregon, and Vermont lawmakers are headed for special sessions over tax and budget issues. And several other states have recently reached or are very near the end of their legislative sessions.
Why Proponents of the Trump-GOP Tax Law Can’t Get their Story Straight
May 16, 2018 • By Steve Wamhoff

If you listened closely to today’s House Ways and Means Committee hearing on the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), you could sense that the witnesses speaking in favor of the new tax law were not 100 percent on the same page. This has been apparent ever since the law was enacted at the end of last year. The economists who speak in favor of the law (including Douglas Holtz-Eakin at today’s hearing) tend to focus on other indicators of its success. They know that the talk of bonuses and raises is nothing more than a desperate corporate PR campaign…
There Is No Evidence That the New Tax Law Is Growing Our Economy or Creating Jobs
May 15, 2018 • By Steve Wamhoff

The House Ways and Means Committee will hold a hearing on the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) Wednesday. Proponents of the law likely will use the occasion to tout its alleged economic benefits and argue that its temporary provisions should be made permanent. The title of the hearing is “Growing Our Economy and Creating Jobs,” but there is little evidence that the law does either of these things.
