
SALT

A new IRS proposal could once again allow wealthy business owners to use state charitable tax credits–including tax credits for donating to support private and religious K-12 schools–to dodge the federal government’s $10,000 cap on state and local tax (SALT) deductions.
ITEP Comments and Recommendations on REG-107431-19
January 29, 2020 • By Carl Davis
Comments regarding the possibility that owners of passthrough businesses may be able to circumvent the $10,000 SALT deduction cap of section 164(b)(6) by recharacterizing the nondeductible portion of their state and local income tax payments as deductible expenses associated with carrying on a trade or business.
House Democrats’ Latest Bill on SALT Deductions Would Mean Bigger Tax Cuts for the Rich
December 11, 2019 • By Steve Wamhoff
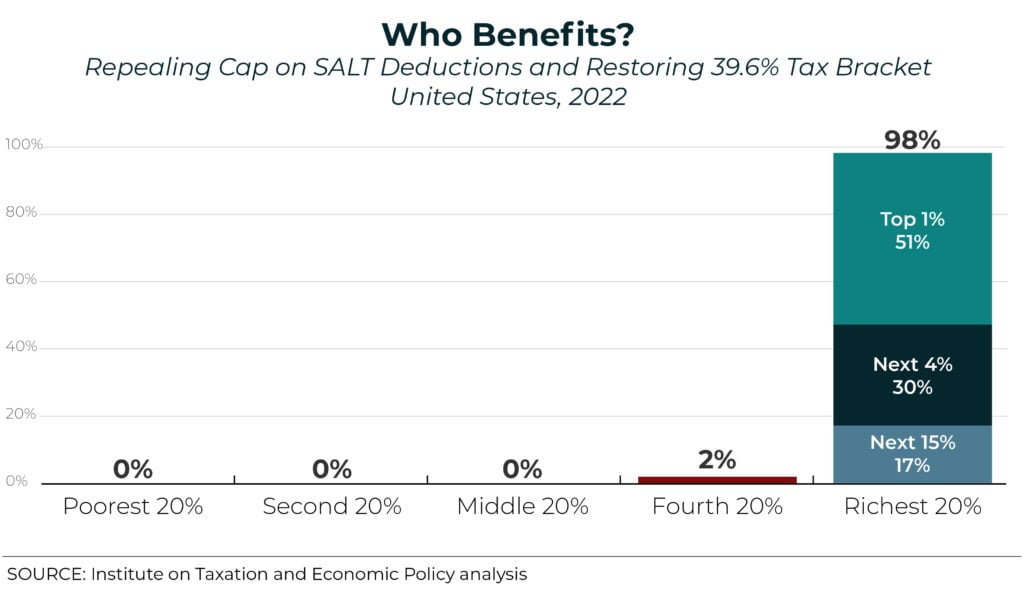
ITEP estimates show that if the House Democrats' proposal was in effect in 2022, it would have a net cost of $81 billion in that year alone. The estimates also show that 51 percent of the benefits would go to the richest 1 percent of taxpayers in the U.S. Clearly, lawmakers concerned about the SALT cap need to go back to the drawing board.
Press-Republican: Cuomo Loses Opening Round in Fight Against New Tax Law
October 6, 2019
The Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy, a national think tank, projected in late 2017 that more than 70 percent of New York taxpayers would end up paying less in federal taxes as a result of the code revisions. Cuomo, though, has maintained the capping of the SALT deduction would motivate some wealthy earners to […]
CNBC: New York Judge Dismisses Blue State Suit Over SALT Tax Deductions
September 30, 2019
Whether the final rule will ultimately deter people from donating to these funds remains to be seen. “If you’re really passionate about private school vouchers in Georgia, you donate and you still get 100% of your donation back,” Carl Davis, research director at the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy, told CNBC earlier. “You just […]
IRS’s SALT Workaround Regulations Should be Strengthened, Not Rejected
August 13, 2019 • By Carl Davis

Lawmakers are seeking to achieve a backdoor repeal of the $10,000 cap on deductions for state and local taxes paid (SALT) by invalidating recent IRS regulations that cracked down on schemes that let taxpayers dodge the cap. If successful, their efforts would drain tens of billions of dollars from federal coffers each year, with the vast majority of the benefits going to the nation’s wealthiest families.
What to Watch for When the IRS Releases Its SALT Workaround Regulations
April 1, 2019 • By Carl Davis

The Treasury Department and IRS last summer proposed regulations that would make it more difficult for taxpayers to avoid the $10,000 cap on deductions for state and local taxes (SALT). Now, likely days away from the unveiling of the final version of IRS regulations on SALT cap workarounds, Carl Davis recaps the finer points ITEP will be watching for when the regulations become public.

On Monday a group of Senators and Representatives from the Northeast announced their latest proposal to repeal the cap on deductions for state and local taxes (SALT), this time offsetting the costs by restoring the top personal income tax rate to 39.6 percent. This is an improvement over previous proposals to repeal the cap on SALT deductions without offsetting the costs at all. But the new approach does not improve our tax system overall. Instead, it trades one tax cut for the rich (a lower top income tax rate) for another (repeal of the cap on SALT deductions).
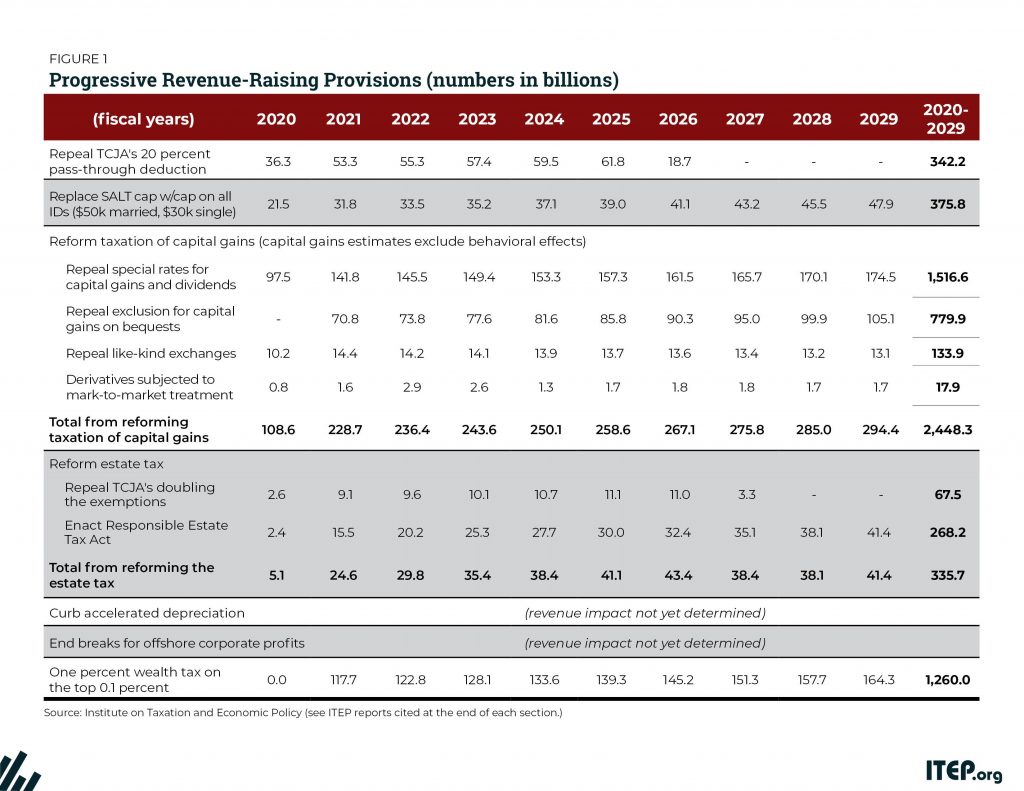
America has long needed a more equitable tax code that raises enough revenue to invest in building shared prosperity. The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), enacted at the end of 2017, moved the federal tax code in the opposite direction, reducing revenue by $1.9 trillion over a decade, opening new loopholes, and providing its most significant benefits to the well-off. The law cut taxes on the wealthy directly by reducing their personal income taxes and estate taxes, and indirectly by reducing corporate taxes.

The cap on federal tax deductions for state and local taxes (SALT) that is in effect now under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) is a flawed provision but repealing it outright would be costly and provide a windfall to the rich. Congress should consider replacing the SALT cap with a different type of limit on deductions that would avoid both of these outcomes. Using the ITEP microsimulation tax model, this report provides revenue estimates and distributional estimates for several such options, assuming they would be in effect in 2019.
