
Reports
The Case for Extending State-Level Child Tax Credits to Those Left Out: A 50-State Analysis
April 17, 2019 • By Aidan Davis, Meg Wiehe

As of 2017, 11.5 million children in the United States were living in poverty. A national, fully-refundable Child Tax Credit (CTC) would effectively address persistently high child poverty rates at the national and state levels. The federal CTC in its current form falls short of achieving this goal due to its earnings requirement and lack of full refundability. Fortunately, states have options to make state-level improvements in the absence of federal policy change. A state-level CTC is a tool that states can employ to remedy inequalities created by the current structure of the federal CTC. State-level CTCs would significantly reduce…
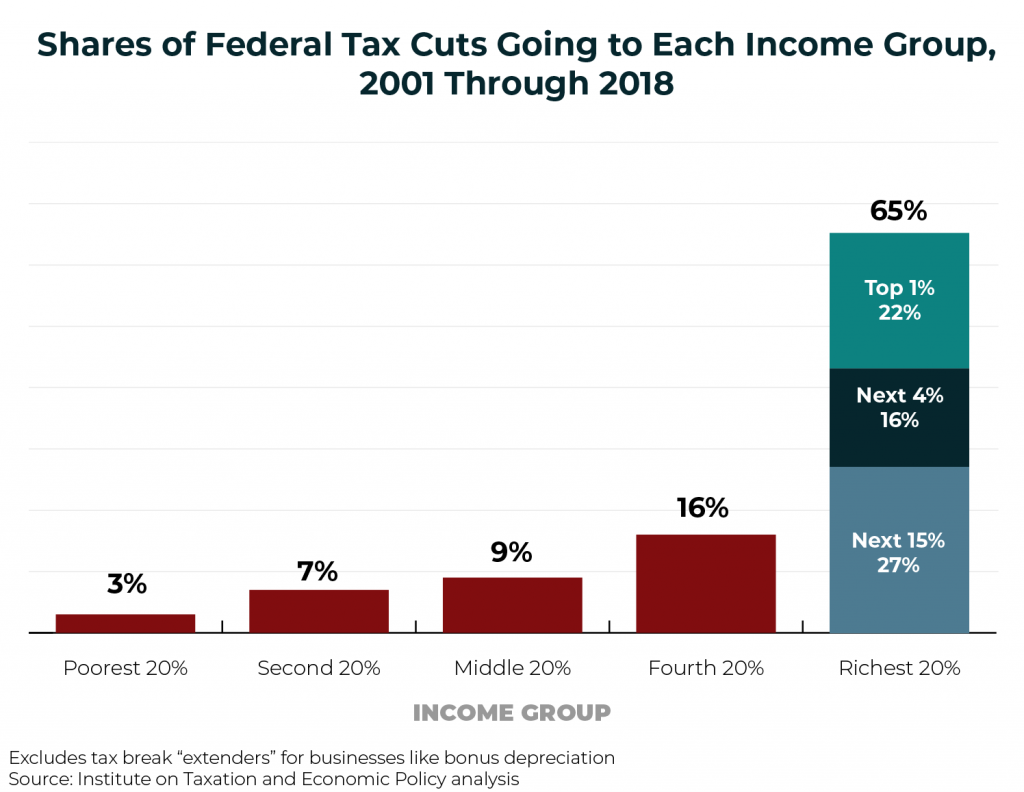
Income inequality is a national challenge. And inadequate federal revenue is a challenge that the nation will eventually have to reckon with. This chart book makes a strong case for why federal lawmakers should seriously consider progressive revenue-raising options.
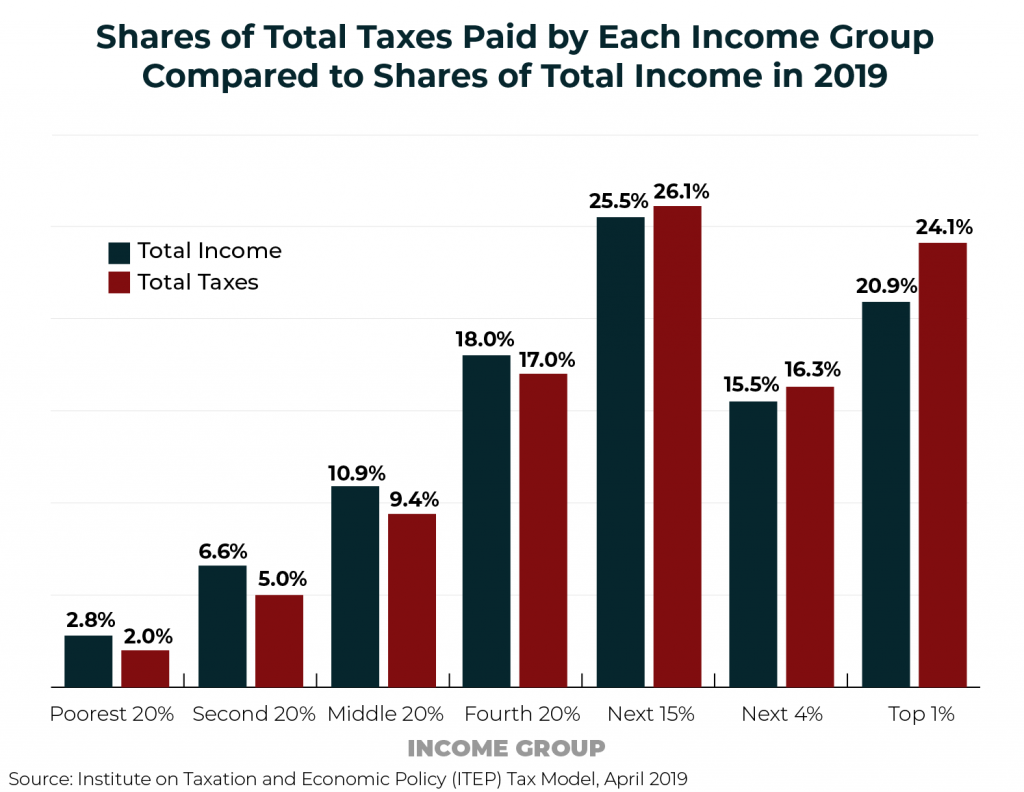
For years, Americans have been told that the rich are paying a highly disproportionate share of the nation’s taxes. Claims to that effect often focus on just one tax, the federal personal income tax, which is indeed progressive overall. But when the nation’s tax system is viewed in its entirety, it becomes clear that the reality is very different. Despite their enormous incomes and wealth, the nation’s richest taxpayers are paying a share of overall taxes that slightly exceeds their share of income.
Corporate Tax Avoidance Remains Rampant Under New Tax Law
April 11, 2019 • By Lorena Roque, Matthew Gardner, Steve Wamhoff

For decades, profitable Fortune 500 companies have been able to manipulate the tax system to avoid paying even a dime in tax on billions of dollars in U.S. profits. This ITEP report provides the first comprehensive look at how the new corporate tax laws that took effect after the passage of the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act affects the scale of corporate tax avoidance.
Fairness Matters: A Chart Book on Who Pays State and Local Taxes
March 6, 2019 • By ITEP Staff
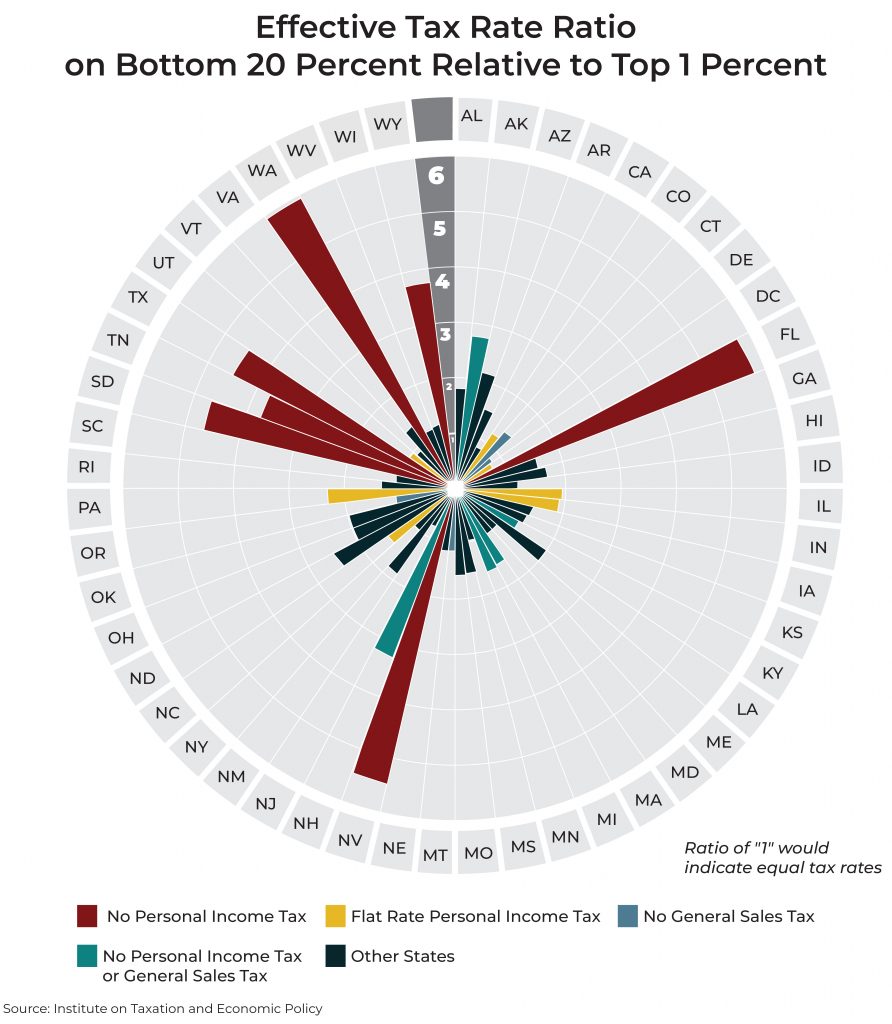
There is significant room for improvement in state and local tax codes. State tax codes are filled with top-heavy exemptions and deductions and often fail to tax higher incomes at higher rates. States and localities have come to rely too heavily on regressive sales taxes that fail to reflect the modern economy. And overall tax collections are often inadequate in the short-run and unsustainable in the long-run. These types of shortcomings provide compelling reason to pursue state and local tax reforms to make these systems more equitable, adequate, and sustainable.
The Illusion of Race-Neutral Tax Policy
February 14, 2019 • By Alan Essig, Carl Davis, Jenice Robinson, Meg Wiehe, Misha Hill, Steve Wamhoff
It is well known that the bulk of the federal tax cuts flowed to the highest-earning households, who received the largest tax cut both in terms of real dollars and also as a share of income. But as our analysis with Prosperity Now reveals, solely examining the tax law in the context of class misses a bigger-picture story about how the nation’s public policies not only perpetuate widening income and wealth inequality, they also preserve historic and current injustices that continue to allow white communities to build wealth while denying the same level of opportunity (and often suppressing it) to…
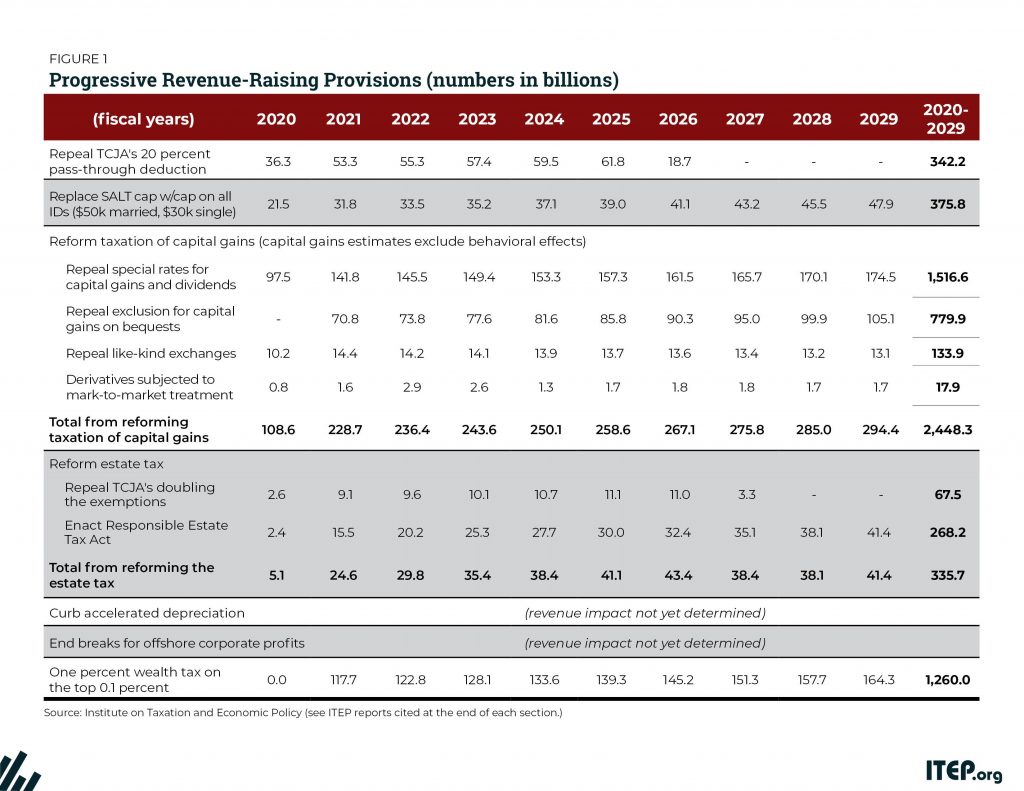
America has long needed a more equitable tax code that raises enough revenue to invest in building shared prosperity. The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), enacted at the end of 2017, moved the federal tax code in the opposite direction, reducing revenue by $1.9 trillion over a decade, opening new loopholes, and providing its most significant benefits to the well-off. The law cut taxes on the wealthy directly by reducing their personal income taxes and estate taxes, and indirectly by reducing corporate taxes.
Congress Should Reduce, Not Expand, Tax Breaks for Capital Gains
February 1, 2019 • By Steve Wamhoff
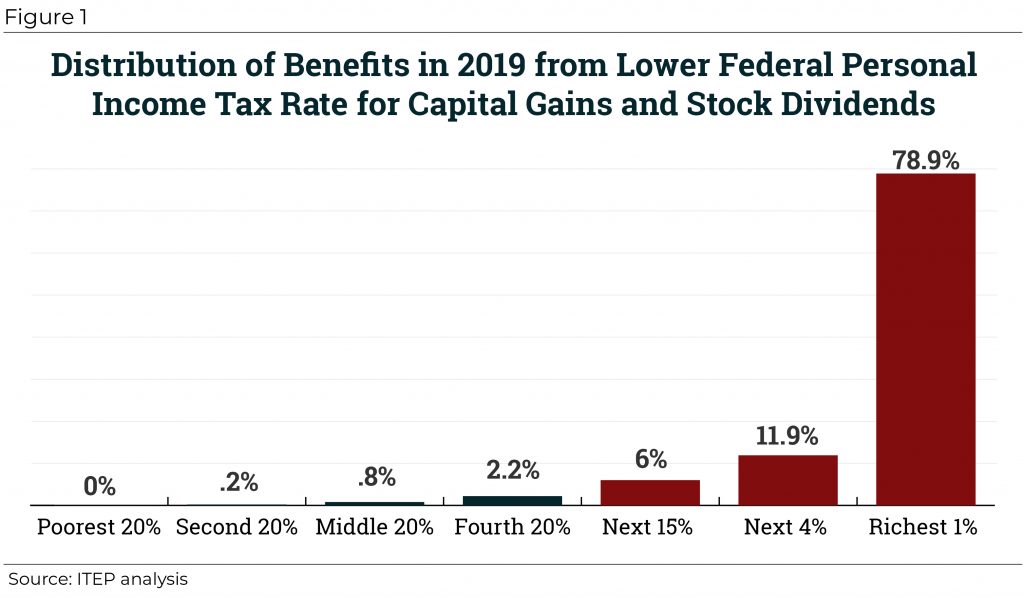
Even though income derived from capital gains receives a special lower tax rate and is therefore undertaxed, some proponents of lower taxes on the wealthy claim that capital gains are overtaxed due to the effects of inflation. But existing tax breaks for capital gains more than compensate for any problem related to inflation. Congress should repeal or restrict special tax provisions for capital gains rather than creating even more breaks.

A federal wealth tax on the richest 0.1 percent of Americans is a viable approach for Congress to raise revenue and is one of the few approaches that could truly address rising inequality. As this report explains, an annual federal tax of only 1 percent on the portion of any taxpayer’s net worth exceeding the threshold for belonging to the wealthiest 0.1 percent (likely to be about $32.2 million in 2020) could raise $1.3 trillion over a decade.

State policy toward cannabis is evolving rapidly. While much of the debate around legalization has rightly focused on potential health and criminal justice impacts, legalization also has revenue implications for state and local governments that choose to regulate and tax cannabis sales. This report describes the various options for structuring state and local taxes on cannabis and identifies approaches currently in use. It also undertakes an in-depth exploration of state cannabis tax revenue performance and offers a glimpse into what may lie ahead for these taxes.
A Simple Fix for a $17 Billion Loophole: How States Can Reclaim Revenue Lost to Tax Havens
January 17, 2019 • By Richard Phillips

Enacting Worldwide Combined Reporting or Complete Reporting in all states, this report calculates, would increase state tax revenue by $17.04 billion dollars. Of that total, $2.85 billion would be raised through domestic Combined Reporting improvements, and $14.19 billion would be raised by addressing offshore tax dodging (see Table 1). Enacting Combined Reporting and including known tax havens would result in $7.75 billion in annual tax revenue, $4.9 billion from income booked offshore.

New and returning policymakers have a tremendous opportunity to improve their constituents’ lives and their states’ economies through tax policy. This report distills the findings of “Who Pays?” into policy recommendations that can serve as a guide to new lawmakers, advocates, and others seeking to improve their state’s tax codes. It explains the importance of favoring taxes on income and wealth over taxes on consumption, the value of certain targeted tax benefits for families living in poverty, the need to abandon ineffective, unnecessary tax subsidies for high-income households, and the promise of bold new options for improving the regressive distributional…
The Federal Estate Tax: An Important Progressive Revenue Source
December 6, 2018 • By ITEP Staff

For years, wealth and income inequality have been widening at a troubling pace. One study estimated that the wealthiest 1 percent of Americans held 42 percent of the nation’s wealth in 2012, up from 28 percent in 1989. Lawmakers have exacerbated this trend by dramatically cutting federal taxes on inherited wealth, most recently by doubling the estate tax exemption as part of the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act. Further, lawmakers have done little to stop aggressive accounting schemes designed to avoid the estate tax altogether. This report explains how the percentage of estates subject to the federal estate tax…
The Failure of Expensing and Other Depreciation Tax Breaks
November 19, 2018 • By Richard Phillips, Steve Wamhoff

Congress permitted full expensing only for five years, which will encourage businesses to speed up investments they would have made later. Republicans in Congress have discussed making the expensing provision permanent. This report argues that Congress should move in the other direction and repeal not just the full expensing provision but even some of the permanent accelerated depreciation breaks in the tax code, for several reasons.

The cap on federal tax deductions for state and local taxes (SALT) that is in effect now under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) is a flawed provision but repealing it outright would be costly and provide a windfall to the rich. Congress should consider replacing the SALT cap with a different type of limit on deductions that would avoid both of these outcomes. Using the ITEP microsimulation tax model, this report provides revenue estimates and distributional estimates for several such options, assuming they would be in effect in 2019.
Low Tax for Whom? Indiana is a “Low Tax State” Overall, But Not for Families Living in Poverty
October 17, 2018 • By ITEP Staff
Indiana’s tax system has vastly different impacts on taxpayers at different income levels. For instance, the lowest-income 20 percent of Hoosiers contribute 12.8 percent of their income in state and local taxes — considerably more than any other income group in the state. For low-income families, Indiana is far from being a low tax state; in fact, it is the eighth highest-tax state in the country for low-income families.
Low Tax for Whom? Oklahoma is a “Low Tax State” Overall, But Not for Families Living in Poverty
October 17, 2018 • By ITEP Staff
Oklahoma’s tax system has vastly different impacts on taxpayers at different income levels. For instance, the lowest-income 20 percent of Oklahomans contribute 13.2 percent of their income in state and local taxes — considerably more than any other income group in the state. For low-income families, Oklahoma is far from being a low tax state; in fact, it is the fifth highest-tax state in the country for low-income families.
Low Tax for Whom? Florida is a “Low Tax State” Overall, But Not for Families Living in Poverty
October 17, 2018 • By ITEP Staff
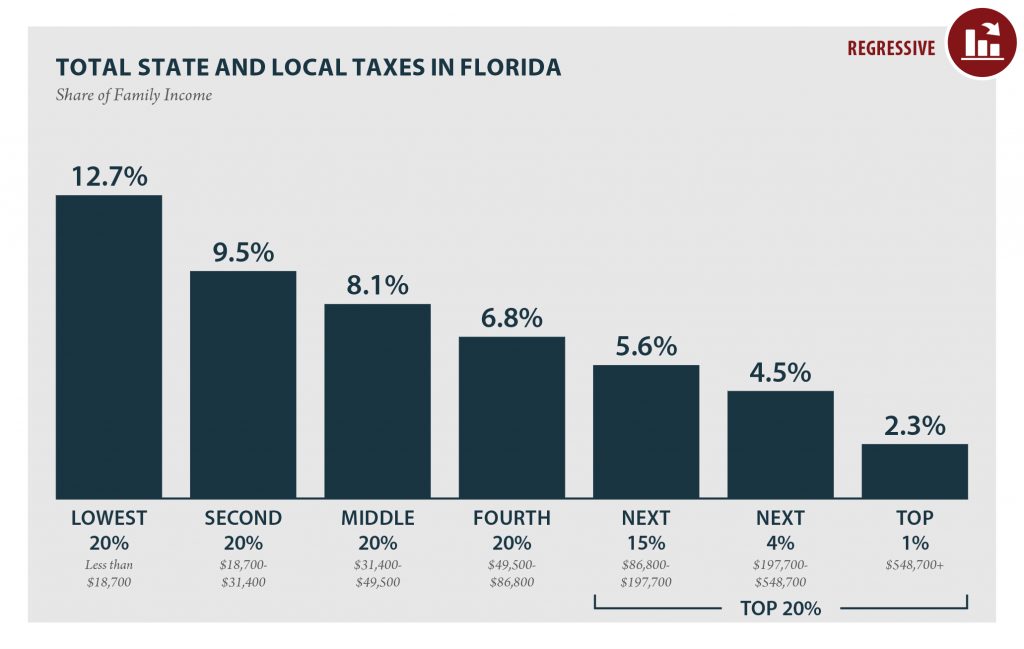
Florida’s tax system has vastly different impacts on taxpayers at different income levels. For instance, the lowest-income 20 percent of Floridians contribute 12.7 percent of their income in state and local taxes — considerably more than any other income group in the state. For low-income families, Florida is far from being a low tax state; in fact, it is the ninth highest-tax state in the country for low-income families.
ITEP Comments and Recommendations on Proposed Section 170 Regulation (REG-112176-18)
October 11, 2018 • By Carl Davis
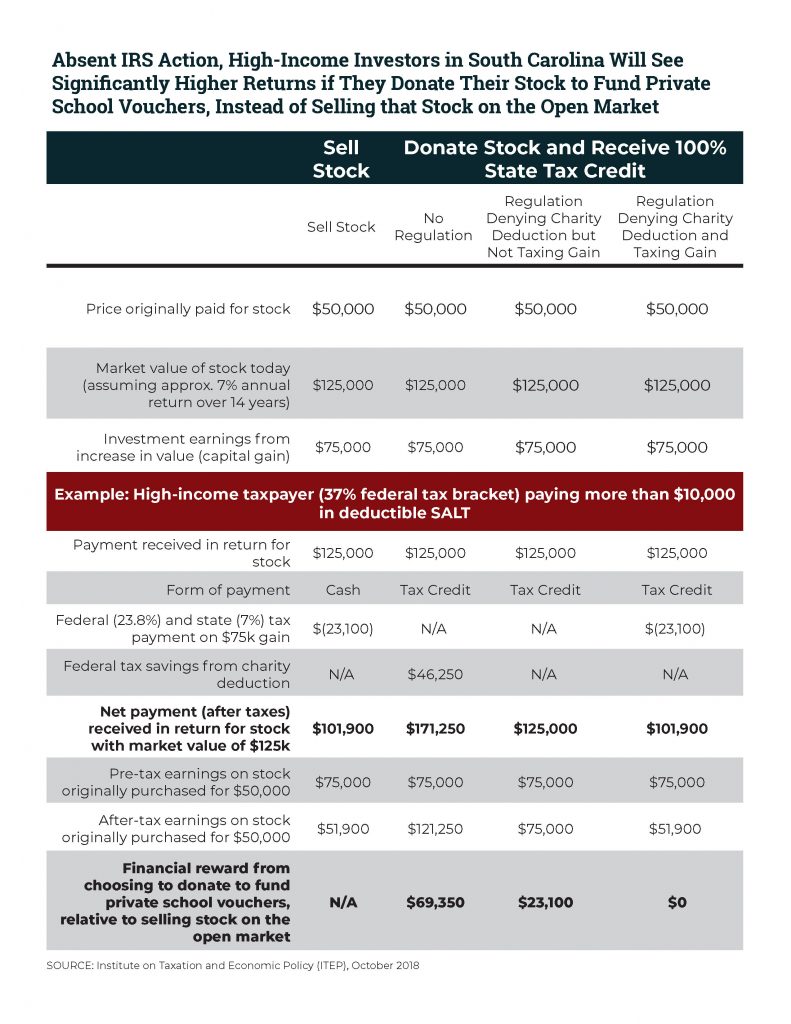
The IRS recently proposed a commonsense improvement to the federal charitable deduction. If finalized, the regulation would prevent not just the newest workarounds to the $10,000 deduction for state and local taxes (SALT), but also a longer-running tax shelter abused by wealthy donors to private K-12 school voucher programs. ITEP has submitted official comments outlining four key recommendations related to the proposed regulation.
Race, Wealth and Taxes: How the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act Supercharges the Racial Wealth Divide
October 11, 2018 • By Meg Wiehe
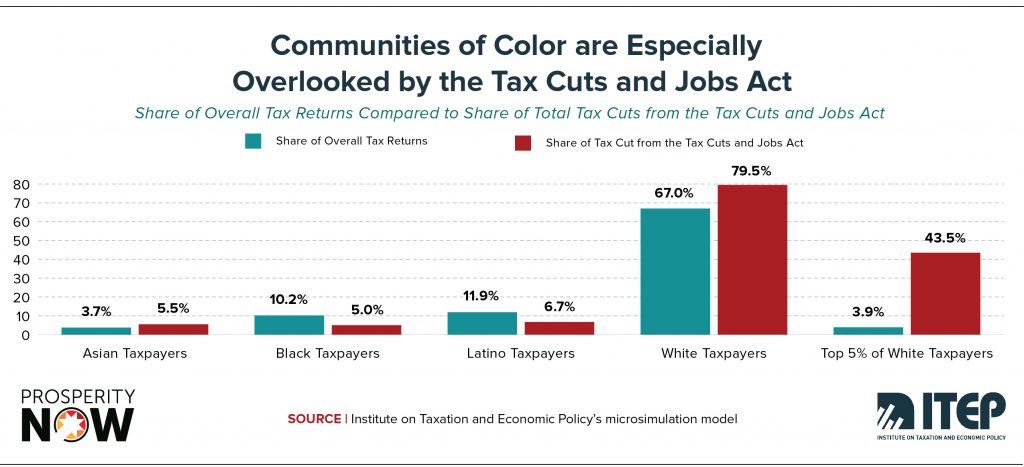
A newly released report by Prosperity Now and the Institution on Taxation and Economic Policy, Race, Wealth and Taxes: How the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act Supercharges the Racial Wealth Divide, finds that the TCJA not only adds unnecessary fuel to the growing problem of overall economic inequality, but also supercharges an already massive racial wealth divide to an alarming extent.
State Tax Codes as Poverty Fighting Tools: 2018 Update on Four Key Policies in All 50 States
September 17, 2018 • By Aidan Davis, Misha Hill

This report presents a comprehensive overview of anti-poverty tax policies, surveys tax policy decisions made in the states in 2018, and offers recommendations that every state should consider to help families rise out of poverty. States can jumpstart their anti-poverty efforts by enacting one or more of four proven and effective tax strategies to reduce the share of taxes paid by low- and moderate-income families: state Earned Income Tax Credits, property tax circuit breakers, targeted low-income credits, and child-related tax credits.
ITEP Testimony “Regarding the Final Report of the Arkansas Tax Reform and Relief Legislative Task Force”
August 23, 2018 • By Lisa Christensen Gee
Read the testimony in PDF WRITTEN TESTIMONY SUBMITTED TO: THE ARKANSAS TAX REFORM AND RELIEF TASK FORCE Lisa Christensen Gree, Senior State Tax Policy Analyst Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy Regarding the Final Report of the Arkansas Tax Reform and Relief Legislative Task Force August 22, 2018 Thank you for the opportunity to submit these […]
Rep. Shuster’s Mixed Bag: Doubling the Gas Tax before Repealing It Entirely
July 24, 2018 • By Carl Davis
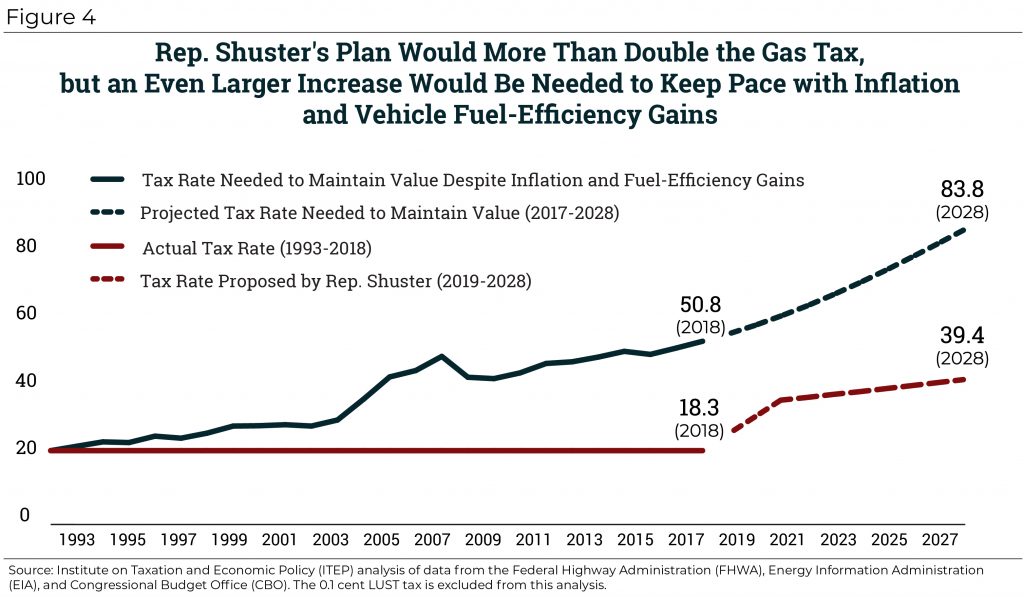
This article examines the good aspects of Rep. Shuster’s infrastructure funding plan (a higher gas tax that is indexed to inflation), the bad (a flawed indexing formula and eventual gas tax repeal), and the downright ugly (tying the hands of a funding commission before their work even begins and refusing to ask more of high-income households).
Understanding and Fixing the New International Corporate Tax System
July 17, 2018 • By Richard Phillips

The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) radically changed the international tax system. It slashed taxes on corporate income, both domestic and foreign. It encouraged U.S. multinational corporations to shift jobs, profits, and tangible property abroad, and keep intangibles home. This report describes the new international tax system—and its many gaps—and also provides a road map for how to fix these gaps and surveys recent legislative approaches.
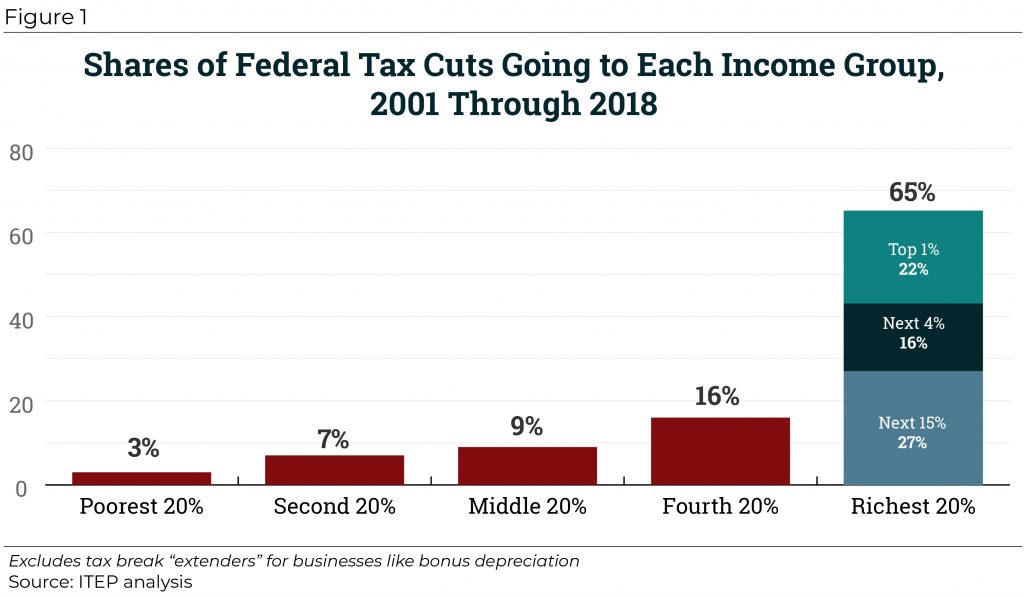
Since 2000, tax cuts have reduced federal revenue by trillions of dollars and disproportionately benefited well-off households. From 2001 through 2018, significant federal tax changes have reduced revenue by $5.1 trillion, with nearly two-thirds of that flowing to the richest fifth of Americans.
