
Kentucky
State Tax Watch 2026
March 9, 2026 • By ITEP Staff

ITEP tracks tax discussions in legislatures across the country and uses our unique data capacity to analyze the revenue, distributional, and racial and ethnic impacts of many of these proposals. State Tax Watch offers the latest news and movement from each state.
State Rundown 1/7: New Year, New Opportunities for Progressive Revenue
January 7, 2026 • By ITEP Staff

As we kick off a new year, several states are facing revenue shortfalls. Some lawmakers are approaching the challenge with sustainable and equitable solutions.
Kentucky Center for Economic Policy: In New Poll, Kentuckians Say Income Tax Cuts Aren’t Helping
January 5, 2026
Kentucky’s legislative leaders have made reducing the state’s individual income tax rate their top priority in recent years. Lawmakers have repeatedly acted on that, reducing the rate several times and costing the state billions annually that could have been invested in kids and families. Read more.
Kentucky Center for Economic Policy: A State Budget for an Affordable Kentucky: Preview of the 2026–2028 Budget of the Commonwealth
December 17, 2025
The Kentucky General Assembly will perform its most important job — crafting a two-year state budget that funds education, health, social services and other critical needs. But unlike recent years, when pandemic-era stimulus created robust revenue growth, lawmakers are now facing a serious budget crunch due to the loss of federal funds, a weakening economy […]
Kentucky Center for Economic Policy: Building a Kentucky Workers Can Afford
December 2, 2025
The working class drives prosperity, and it’s time for an agenda in Frankfort that puts them first. From the state’s rural counties to our biggest cities, it’s Kentuckians—whether white, Black or brown—who make it all go. Supported by the right policies, ones that reward their efforts and prioritize their concerns, more Kentuckians could work in […]
Re-Examining 529 Plans: Stopping State Subsidies to Private Schools After New Trump Tax Law
November 20, 2025 • By Miles Trinidad, Nick Johnson

The 2025 federal tax law risks making 529 plans more costly for states by increasing tax avoidance and allowing wealthy families to use these funds for private and religious K-12 schools.
State Rundown 11/13: States Tackle Impending Deficits, Pennsylvania Secures an EITC
November 13, 2025 • By ITEP Staff

Revenue forecasts look increasingly grim as states anticipate shortfalls due to the slowing economy and impacts of the new federal tax law.
Kentucky Center for Economic Policy: State and Federal Tax Cuts of the Last Decade Are Giving an Enormous Windfall to the Wealthiest Kentuckians
November 12, 2025
In 2026, Kentucky’s richest 5% will receive $3.4 billion from tax cuts enacted over the last decade. That’s revenue no longer available to meet people’s needs. Kentucky workers, meanwhile, are facing stagnant and inadequate wages and a growing cost of living crisis that will get worse if state budget cuts are enacted. Read more.
The 5 Biggest State Tax Cuts for Millionaires this Year
October 16, 2025 • By Dylan Grundman O'Neill, Aidan Davis

Some states continue to hand out huge tax cuts to millionaires. The five largest tax cuts this year will cost states a total of $2.2 billion per year once fully implemented.
State Tax Action in 2025: Amid Uncertainty, Tax Cuts and New Revenue
July 28, 2025 • By Aidan Davis, Neva Butkus, Marco Guzman

Federal policy choices on tariffs, taxes, and spending cuts will be deeply felt by all states, which will have less money available to fund key priorities. This year some states raised revenue to ensure that their coffers were well-funded, some proceeded with warranted caution, and many others passed large regressive tax cuts that pile on to the massive tax cuts the wealthiest just received under the federal megabill.
State Rundown 7/24: States Begin Preparing for Federal Megabill Fallout
July 24, 2025 • By ITEP Staff

All eyes in statehouses in recent weeks have been on federal budget negotiations, and now that the “megabill” has passed, they are focused in on their own budgets in search of ways to cope with the enormous consequences coming their way. All states will see fewer federal dollars flowing through their coffers, higher needs due […]
How Much Would Every Family in Every State Get if the Megabill’s Tax Cuts Given to the Rich Had Instead Been Evenly Divided?
July 14, 2025 • By Michael Ettlinger
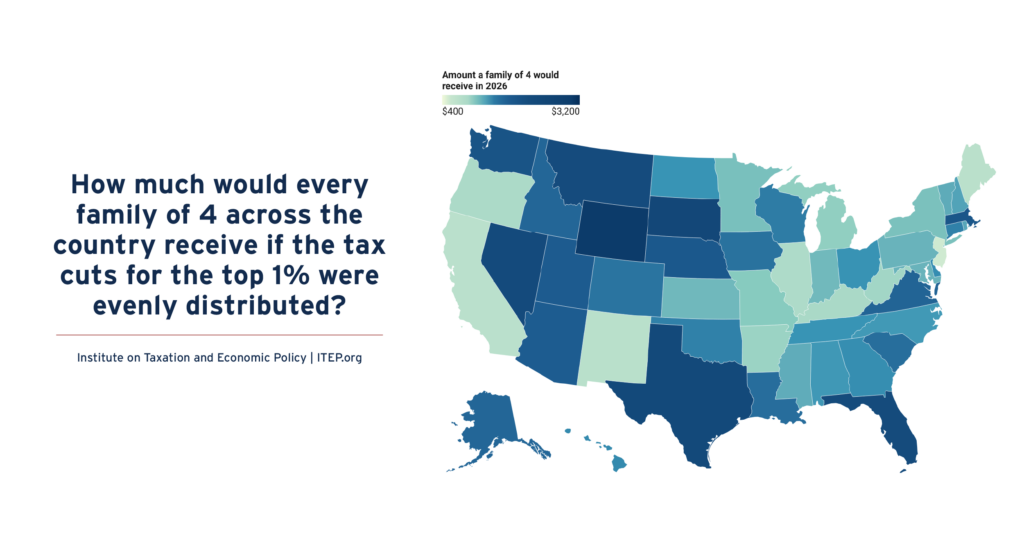
If instead of giving $117 billion to the richest 1 percent, that money had been evenly divided among all Americans, we'd each get $343 - or nearly $1,400 for a family of four.
Analysis of Tax Provisions in the Trump Megabill as Signed into Law: National and State Level Estimates
July 7, 2025 • By Steve Wamhoff, Carl Davis, Joe Hughes, Jessica Vela

President Trump has signed into law the tax and spending “megabill” that largely favors the richest taxpayers and provides working-class Americans with relatively small tax cuts that will in many cases be more than offset by Trump's tariffs.
Megabill Takes Cap Off Unprecedented Private School Voucher Tax Credit, Potentially Raising Cost by Tens of Billions Relative to Earlier Version
July 2, 2025 • By Carl Davis

It is clear that this tax credit has the potential to come with an enormous cost if private school groups are successful in convincing their supporters to participate. In these times of very high debt and deficits, this is reason for all of us to be uneasy.
Trump Megabill Will Give $117 Billion in Tax Cuts to the Top 1% in 2026. How Much In Your State?
June 30, 2025 • By Michael Ettlinger

The predominant feature of the tax and spending bill working its way through Congress is a massive tax cut for the richest 1 percent — a $114 billion benefit to the wealthiest people in the country in 2026 alone.
How Much Do the Top 1% in Each State Get from the Trump Megabill?
June 30, 2025 • By Carl Davis

The Senate tax bill under debate right now would bring very large tax cuts to very high-income people. In total, the richest 1 percent would receive $114 billion in tax cuts next year alone. That would amount to nearly $61,000 for each of these affluent households.
The ‘Big, Beautiful’ Bill Creates a $5 Billion Tax Shelter for Private School Donors
June 9, 2025 • By Amy Hanauer

On May 22, Congress passed the House reconciliation bill or “One Big Beautiful Bill Act” by a one-vote margin. The bill’s dozens of destructive tax provisions would supercharge inequality and force devastating cuts to health and food aid that have been bedrocks of the American safety net since the 1960s.
Kentucky Center for Economic Policy: Program Cuts and Tariff Costs Will Leave Many Kentucky Families Worse Off, Even with Modest Tax Cuts
June 4, 2025
On Thursday, May 22nd, the House of Representatives passed its major tax and spending legislation, which included last-minute revisions that made it even more favorable for the wealthy.
Analysis of Tax Provisions in the House Reconciliation Bill: National and State Level Estimates
May 22, 2025 • By Carl Davis, Jessica Vela, Joe Hughes, Steve Wamhoff

The poorest fifth of Americans would receive 1 percent of the House reconciliation bill's net tax cuts in 2026 while the richest fifth of Americans would receive two-thirds of the tax cuts. The richest 5 percent alone would receive a little less than half of the net tax cuts that year.

Want to know more about the tax and spending megabill that President Trump recently signed into law? We've got you covered.
IRS Cooperation with ICE Will Damage Public Trust, Putting Tax Revenues in Jeopardy
April 10, 2025 • By Marco Guzman

Attempts by the Department of Homeland Security to secure private information from the IRS on people who file taxes with an Individual Taxpayer Identification Number is a violation of federal privacy laws that protect taxpayers. It is also a change that could seriously damage public trust in the IRS, which could jeopardize billions of dollars in tax payments by hardworking immigrant families.
Associated Press: Mississippi and Kentucky Aim to End Personal Income Taxes
April 6, 2025
About 45 years have passed since a U.S. state last eliminated its income tax on wages and salaries. But with recent actions in Mississippi and Kentucky, two states now are on a path to do so, if their economies keep growing. Read more.
State Rundown 3/12: Last-Minute Tax Cut Mayhem and New Progressive Revenue Raisers
March 12, 2025 • By ITEP Staff

A bevy of tax cut proposals sprung to life this week while others were signed into law. In Kentucky, lawmakers are working to make it easier for the legislature to enact income and business tax cuts. The governor in Idaho signed into law a personal and corporate income tax cut.
Below is a list of tax expenditure reports published in the states.
In the face of immense uncertainty around looming federal tax and budget decisions, many of which could threaten state budgets, state lawmakers have an opportunity to show up for their constituents by raising and protecting the revenue needed to fund shared priorities. Lawmakers have a choice: advance tax policies that improve equity and help communities thrive, or push tax policies that disproportionately benefit the wealthy, drain funding for critical public services, and make it harder for most families to get ahead.
