
New York
Trickle-Down Dries Up: States without personal income taxes lag behind states with the highest top tax rates
October 26, 2017 • By Carl Davis, Nick Buffie

Lawmakers who support reducing or eliminating state personal income taxes typically claim that doing so will spur economic growth. Often, this claim is accompanied by the assertion that states without income taxes are booming, and that their success could be replicated by any state that abandons its income tax. To help evaluate these arguments, this study compares the economic performance of the nine states without broad-based personal income taxes to their mirror opposites—the nine states levying the highest top marginal personal income tax rates throughout the last decade.
New York Times: U.S. and Europe May Collide on Taxing Apple and Amazon
October 13, 2017
The rulings on Amazon and Apple — which those companies are disputing — are byproducts of a race among governments to lure corporate giants to their shores in the hunt for new sources of revenue. That cutthroat competition is the reason that 73 percent of Fortune 500 companies have a subsidiary in a low-tax haven, […]
State Rundown 10/13: Soda Taxes, Business Subsidies, and Gas Taxes Considered in Several States
October 13, 2017 • By ITEP Staff

A comprehensive tax study is underway in Arkansas this week as other states hone in on more specific issues. Soda taxes hit setbacks in Illinois and Michigan, business tax subsidies faced scrutiny in Iowa and Missouri, and gas tax update efforts are underway in Mississippi and North Dakota.
50-State Analysis: GOP-Trump Tax Proposal Would Give the Store Away to the Wealthy, Exacerbate the Income Divide
October 4, 2017 • By Alan Essig
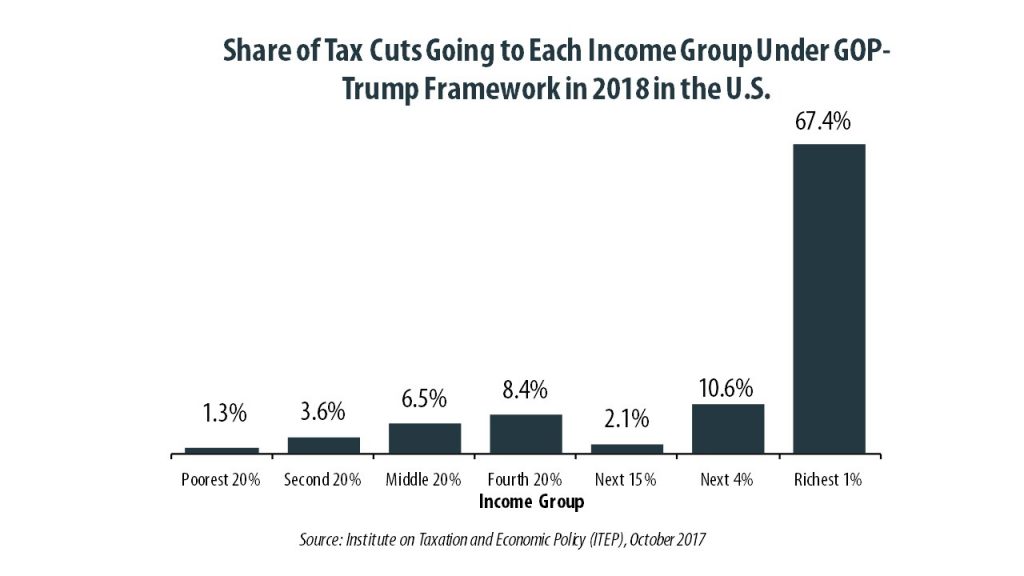
A 50-state analysis of the GOP tax framework reveals the top 1 percent of taxpayers would receive a substantial tax cut while middle- and upper-middle-income taxpayers in many states would pay more, the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy said today. The GOP continues to tout its tax plan as “beneficial to the middle class.” […]
Benefits of GOP-Trump Framework Tilted Toward the Richest Taxpayers in Each State
October 4, 2017 • By Steve Wamhoff
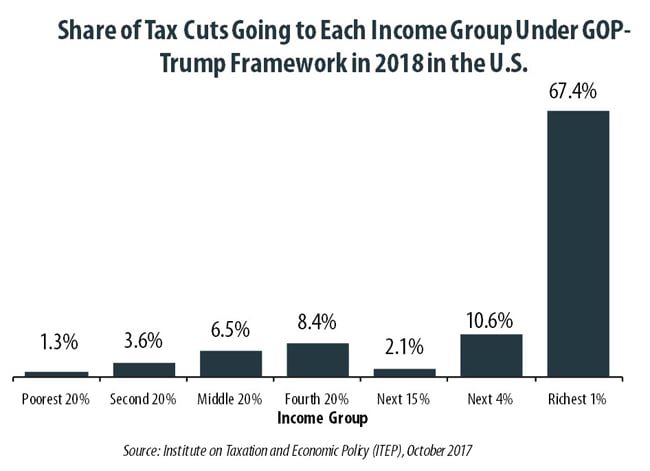
The “tax reform framework” released by the Trump administration and Congressional Republican leaders on September 27 would affect states differently, but every state would see its richest residents grow richer if it is enacted. In all but a handful of states, at least half of the tax cuts would flow to the richest one percent of residents if the framework took effect.
GOP-Trump Tax Framework Would Provide Richest One Percent in New York with 84.0 Percent of the State’s Tax Cuts
October 4, 2017 • By ITEP Staff
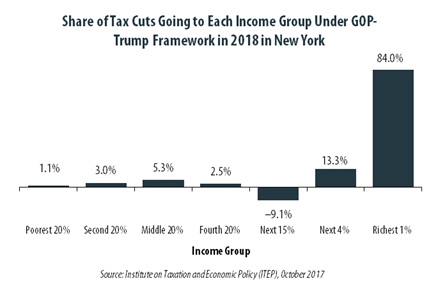
The “tax reform framework” released by the Trump administration and congressional Republican leaders on September 27 would not benefit everyone in New York equally. The richest one percent of New York residents would receive 84.0 percent of the tax cuts within the state under the framework in 2018. These households are projected to have an income of at least $872,200 next year. The framework would provide them an average tax cut of $103,660 in 2018, which would increase their income by an average of 3.2 percent.
New York Times: Will a Corporate Tax Holiday Give Workers Anything to Cheer?
September 26, 2017
Apple alone is sitting on an overseas stash of almost $260 billion, according to Bloomberg, while Microsoft has more than $120 billion parked abroad. The pharmaceutical giant Pfizer does not regularly disclose how much of its offshore profits are stored in foreign tax havens, but the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy estimates that at […]
New York Times: Nothing Is Too Strange for Cities Wooing Amazon to Build There
September 25, 2017
Tax policy experts are more skeptical of Amazon’s bidding process and how much cities stand to benefit. “Why are they doing this whole dog and pony show? Amazon wants something for nothing,” said Matthew Gardner, a senior fellow at the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy, a nonpartisan think tank. “They would like a package […]
State Rundown 9/25: No Rest for the Weary as State Tax and Budget Debates Wind Down, Ramp Up
September 25, 2017 • By ITEP Staff

Last week, Wisconsin leaders finally came to agreement on a state budget, while their peers in Connecticut appear to be close behind them. Iowa lawmakers avoided a special session with a short-term fix and will have to return to their structural deficit issues next session, as will those in Louisiana who will face a $1 billion shortfall. Meanwhile, District of Columbia leaders have already resumed meeting and discussing tax and budget issues there.
Astonishingly, tax policies in virtually every state make it harder for those living in poverty to make ends meet. When all the taxes imposed by state and local governments are taken into account, every state imposes higher effective tax rates on poor families than on the richest taxpayers.

State lawmakers seeking to make residential property taxes more affordable have two broad options: across-the-board tax cuts for taxpayers at all income levels, such as a homestead exemption or a tax cap, and targeted tax breaks that are given only to particular groups of low- and middle-income taxpayers. One such targeted program to reduce property taxes is called a “circuit breaker” because it protects taxpayers from a property tax “overload” just like an electric circuit breaker: when a property tax bill exceeds a certain percentage of a taxpayer’s income, the circuit breaker reduces property taxes in excess of this “overload”…
Politifact: Will Trump’s Decision on DACA Hurt New York’s Economy?
September 10, 2017
A small part of the lost economic contribution is tax receipts. Undocumented immigrants eligible for DACA contribute more than $2 billion in state and local taxes each year, according to research from the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy. More than $140 million comes from DACA eligible immigrants in New York state. Read more
Turning Loopholes into Black Holes: Trump’s Territorial Tax Proposal Would Increase Corporate Tax Avoidance
September 6, 2017 • By Matthew Gardner, Steve Wamhoff
The problem of offshore tax avoidance by American corporations could grow much worse under President Donald Trump’s proposal to adopt a “territorial” tax system, which would exempt the offshore profits of American corporations from U.S. taxes. This change would increase the already substantial benefits American corporations obtain when they use accounting gimmicks to make their profits appear to be earned in a foreign country that has no corporate income tax or has one that is extremely low or easy to avoid.
The New York Times: Trump Tax Plan May Free Up Corporate Dollars, but Then What?
August 30, 2017
But skeptics worry that making the system airtight is impossible. “It’s an endless cat-and-mouse game,” said Matthew Gardner, senior fellow at the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy, a research group based in Washington. “What’s driving companies to engage in paper transactions is not our 35 percent tax rate,” he said, but other countries’ willingness […]
The New York Times: It’s a Myth That Corporate Tax Cuts Mean More Jobs
August 30, 2017
According to the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy, AT&T enjoyed an effective tax rate of just 8 percent between 2008 and 2015, despite recording a profit in the United States each year, by exploiting tax breaks and loopholes. (The company argues that it pays significant taxes, at a rate close to 34 percent in […]
State Rundown 8/23: Few Lingering Budget Debates Cannot Linger Much Longer
August 23, 2017 • By ITEP Staff

This week, Oklahoma lawmakers learned they'll need to enter a special session to balance their budget and that they'll likely face a lawsuit over their low funding of public education. Pennsylvania's budget stalemate is also coming to a head as the state literally runs out of funds to pay its bills. And Amazon's tax practices are in the news again as the company has been sued in South Carolina.
New York Times: Does Amazon Pay Taxes?
August 17, 2017
“If this was five years ago, the tweet would be making a very compelling point,” said Carl Davis, the research director of the left-leaning Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy. Historically, “there is no doubt that Amazon used its ability to not collect sales tax to gain a competitive advantage.” But that criticism is outdated. […]
Nearly Half of Trump’s Proposed Tax Cuts Go to People Making More than $1 Million Annually
August 17, 2017 • By ITEP Staff
A tiny fraction of the U.S. population (one-half of one percent) earns more than $1 million annually. But in 2018 this elite group would receive 48.8 percent of the tax cuts proposed by the Trump administration. A much larger group, 44.6 percent of Americans, earn less than $45,000, but would receive just 4.4 percent of the tax cuts.
In New York 57.9 Percent of Trump’s Proposed Tax Cuts Go to People Making More than $1 Million
August 17, 2017 • By ITEP Staff
A tiny fraction of the New York population (0.6 percent) earns more than $1 million annually. But this elite group would receive 57.9 percent of the tax cuts that go to New York residents under the tax proposals from the Trump administration. A much larger group, 44.8 percent of the state, earns less than $45,000, but would receive just 3.6 percent of the tax cuts.
New York Times: Questions Emerge Over What Wisconsin Must Give for Foxconn Plant
August 11, 2017
Mr. Walker, who has made promises of job creation a centerpiece of his two terms in office, has pushed lawmakers to move quickly in approving the bill, which would offer Foxconn, a producer of flat-panel display screens for televisions and other consumer electronics, close to $3 billion in state tax credits. The subsidies for the […]

This week, Rhode Island lawmakers agreed on a budget, leaving only three states – Connecticut, Pennsylvania, and Wisconsin – without complete budgets. Texas, however, remains in special session and West Virginia could go back into another special session over tax issues. And in New York City, the mayor proposes a tax on the wealthy to […]
USA Today: In Some States, Sales Tax Holidays Lose Luster
August 4, 2017
For more than a decade after New York started the modern trend in 1997, the number of states with annual sales tax holidays grew steadily. But the count peaked at 19 in 2010, and this year’s tally is one fewer than last year. The Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy estimates that states lost $300 million […]
The New York Times: Wisconsin’s Lavish Lure for Foxconn: $3 Billion in Tax Subsidies
July 28, 2017
Big companies like Foxconn possess leverage to extract concessions from state governments that smaller firms cannot, said Carl Davis, research director at the nonpartisan Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy in Washington. “This is not a comprehensive strategy for economic development,” he said. “If Wisconsin were going to offer this kind of subsidy for every […]
50-State Analysis of Trump’s Tax Outline: Poorer Taxpayers and Poorer States are Disadvantaged
July 20, 2017 • By Alan Essig
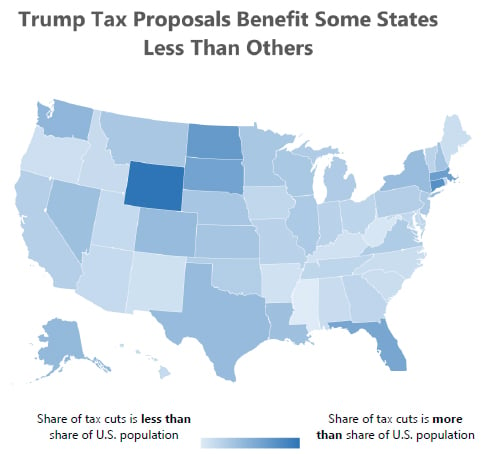
Not only would President Trump’s proposed tax plan fail to deliver on its promise of largely helping middle-class taxpayers, it also would shower a disproportionate share of the total tax cut on taxpayers in some of the richest states while southern and a few other states would receive a smaller share of the tax cut […]
Trump Tax Proposals Would Provide Richest One Percent in New York with 66.9 Percent of the State’s Tax Cuts
July 20, 2017 • By ITEP Staff
Earlier this year, the Trump administration released some broadly outlined proposals to overhaul the federal tax code. Households in New York would not benefit equally from these proposals. The richest one percent of the state’s taxpayers are projected to make an average income of $3,234,000 in 2018. They would receive 66.9 percent of the tax cuts that go to New York’s residents and would enjoy an average cut of $176,680 in 2018 alone.
