
Recent Work by ITEP

While the federal EITC provides a great deal of support for families with children, its impact is limited for those without children or who are not raising children in their homes. Childless workers under 25 and over 64 have for far too long received no benefit from the federal credit. And workers aged 25 to 64 have received very little value from the existing credit (the maximum credit is much smaller and the income limits more restrictive). The federal EITC’s meager benefits for just some childless adults lead to an inequitable outcome: the federal income tax system—which is ostensibly based…
CARES Act Helps Create $4.6 Billion Tax Cut for Health Care Companies Paying Opioid Settlements
February 12, 2021 • By Matthew Gardner

Talk about a one-two punch. A new report from the Washington Post reveals that the U.S. public is set to pay for the opioid crisis again. Already, communities across the country have paid a heavy price via the devastating public health toll. Now, it appears taxpayers will be on the hook for billions in corporate tax breaks as four pharmaceutical companies exploit a loophole in the Trump-GOP tax law and a CARES Act tax provision meant for companies facing pandemic-related profit losses.
It’s Been 10,000 Days Since the Federal Government Raised the Gas Tax
February 12, 2021 • By Carl Davis

10,000 days. More than 27 years. By next Tuesday that’s how long it will have been since the federal government last raised the gas tax. Over that time, vehicle fuel efficiency has improved by 25 percent and construction costs have grown 185 percent. And yet the federal gas tax has remained frozen at 18.3 cents per gallon, with its purchasing power shrinking by the day. The federal government has never gone this long without updating the nation’s gas tax rate.
State Rundown 2/11: Legalizing and Taxing Cannabis Becoming Increasingly Mainstream
February 11, 2021 • By ITEP Staff

This week, the governors of New Hampshire and West Virginia proposed to eliminate their states’ most progressive revenue sources and shift taxes even more heavily onto the middle- and low-income families who already pay the highest rates in both states. It was also a big week for proponents of legalizing recreational cannabis, as that movement made progress in Hawaii, Virginia, and Wisconsin.
Testimony to Washington State Legislature House Finance Committee on HB 1496
February 11, 2021 • By Dylan Grundman O'Neill

Read as PDF Following is testimony of ITEP Senior State Tax Policy Analyst Dylan Grundman O’Neill submitted to Washington State Legislature House Finance Committee in support of HB 1496. “Hello and thank you for this opportunity to testify. My name is Dylan Grundman O’Neill, and I’m a Senior State Tax Policy Analyst with the Institute […]
Details of House Democrats’ Cash Payments and Tax Credit Expansions
February 9, 2021 • By Steve Wamhoff
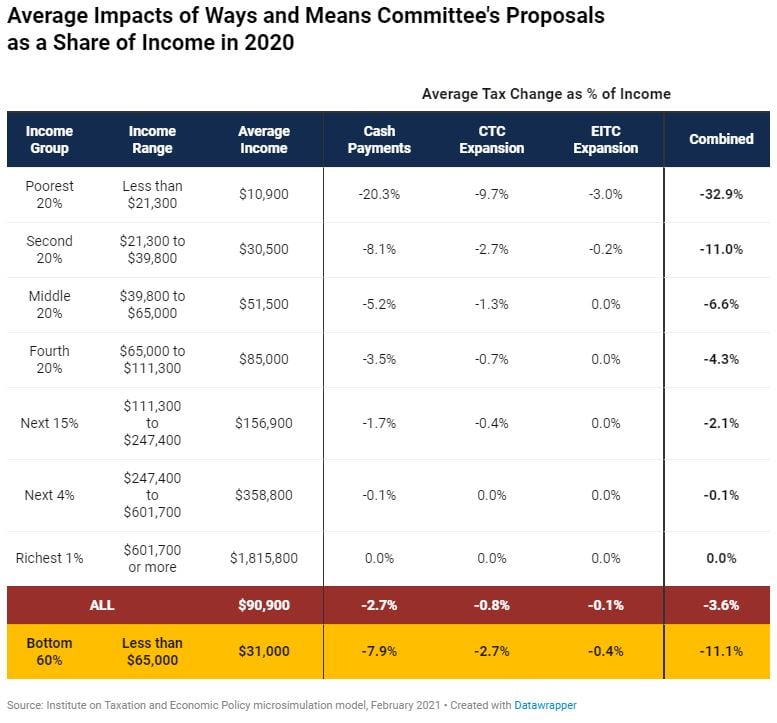
The House Ways and Means Committee published its proposal for the cash payments, tax provisions and other changes that would make up part of the $1.9 trillion COVID relief legislation that President Joe Biden called for a few weeks ago.
Does New York’s Cannabis Tax Idea Offer a Glimpse of the Future?
February 9, 2021 • By Carl Davis

Taxing cannabis won’t end New York’s budget difficulties, but a potency tax could bring New York a more sustainable stream of cannabis tax revenue than we see in most states. It could also have significant benefits for cannabis consumers.
Faulty Fact Check on Tax Breaks for the Rich and Corporations
February 5, 2021 • By Amy Hanauer

When it comes to tax policy, the details are complicated, but the story is often simple. For example, President Trump’s so-called Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) disproportionately benefits the rich. This is not controversial. Yet some opinion makers with large megaphones get lost in the details and come to conclusions that only create more confusion.
State Rundown 2/4: Some Lawmakers, Governors Rising to Occasion with Progressive Tax Proposals
February 4, 2021 • By ITEP Staff

States face shifting landscapes as they attempt to deal with both emergent and longstanding issues in their tax codes and budget structures. This is particularly evident in Oklahoma, where lawmakers must adjust to a U.S. Supreme Court decision that literally redraws state boundaries by recognizing the rights of indigenous communities, but is true in every state, and lawmakers in many of them are rising to the challenge. Read below and see our blog posted today for more on bold proposals that increase tax fairness and solidify bottom lines with needed revenue in states including Connecticut, Minnesota, New York, Pennsylvania, Vermont,…
States Are Finally Going Bold with Progressive Tax Efforts
February 4, 2021 • By Dylan Grundman O'Neill

Advocates, lawmakers, study commissions, and even governors in some states are proposing bold tax policy reforms that look beyond pandemic-induced budget shortfalls and the “K-shaped recovery” to address underlying inequities and underfunding that gave rise to them. These efforts include proposals to: end or reverse regressive tax policies like the preferential treatment of income derived from wealth over income earned through work; restore or strengthen estate and inheritance taxes to slow the concentration of wealth in ever-fewer hands; raise revenue and slow inequality with progressive income taxes; and many other ideas to right upside-down tax codes while raising the revenue…
