
Policy Briefs
Major Cash Payment and Tax Provisions in the HEROES Act
May 15, 2020 • By ITEP Staff, Meg Wiehe, Steve Wamhoff
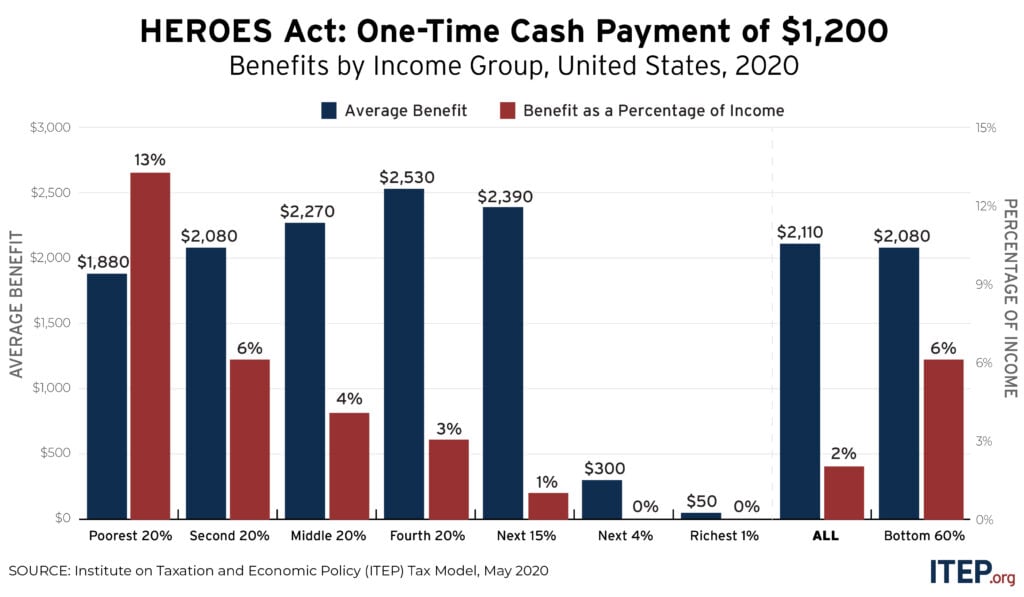
The major provisions for cash payments and tax changes in the House Democrats’ Health and Economic Recovery Omnibus Emergency Solutions (HEROES) Act would provide nearly $600 billion to individuals and households and average benefits of more than $3,000 to families in all but the highest income levels.
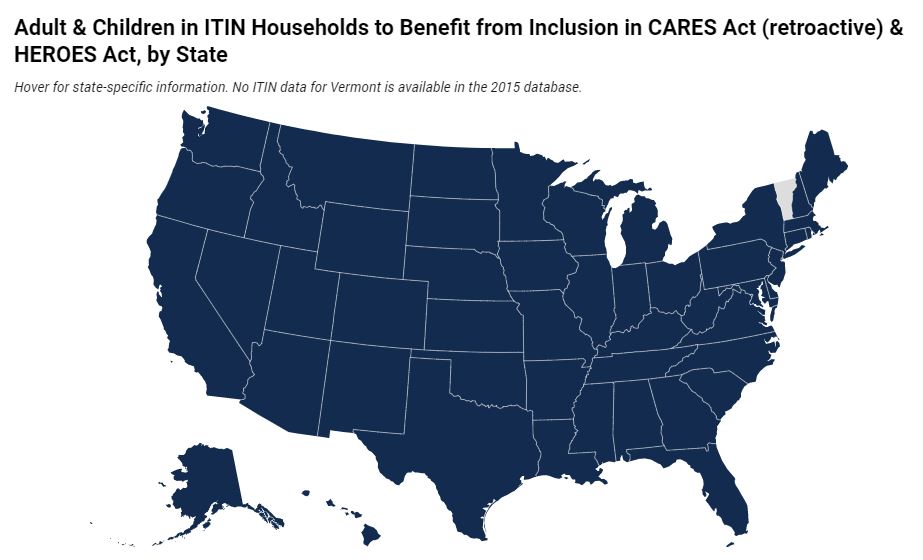
The HEROES Act, filed by the House Democrats this week, includes a new one-time payment of $1,200 per adult and child and extends the payment to ITIN filers and their families. The bill also includes a retroactive change to the CARES Act ensuring ITIN filers will also receive the initial payment under the CARES Act. ITEP estimates more than 4.3 million adults and 3.5 million children would benefit from this change.
Harris-Sanders-Markey Cash Payment Proposal Would Dwarf Checks Sent Under the CARES Act
May 8, 2020 • By Steve Wamhoff

Sens. Kamala Harris, Bernie Sanders and Edward Markey released a proposal to provide a monthly payment of $2,000 for each member of a household (including up to three dependents), with benefits phased out at income levels starting at $200,000 for married couples. The proposal is partly a response to concerns that one-time cash payments under the CARES Act, which amount to $1,200 ($2,400 for married couples) and $500 for each child under age 17, are not sufficient to help families make ends meet or boost the economy.
Opportunity Zones Bolster Investors’ Bottom Lines Rather than Economic or Racial Equity
December 12, 2019 • By Lorena Roque

This policy brief provides an overview of how opportunity zones are designed and highlights some of the flaws of the policy, including the detrimental impact opportunity zones have on communities of color.
Sales taxes are one of the most important revenue sources for state and local governments; however, they are also among the most unfair taxes, falling more heavily on low- and middle-income households. Therefore, it is important that policymakers nationwide find ways to make sales taxes more equitable while preserving this important source of funding for public services. This policy brief discusses two approaches to a less regressive sales tax: broad-based exemptions and targeted sales tax credits.
Reducing the Cost of Child Care Through State Tax Codes in 2019
September 26, 2019 • By Aidan Davis

The high cost of quality child care is a budget constraint for many working families and particularly daunting for parents who are working but earning low wages. Most families with children need one or more incomes to make ends meet which means child care expenses are an increasingly unavoidable and unaffordable expense. This policy brief examines state tax policy tools that can be used to make child care more affordable: a dependent care tax credit modeled after the federal program and a deduction for child care expenses.

State lawmakers seeking to make residential property taxes more affordable have two broad options: across-the-board tax cuts for taxpayers at all income levels, such as a homestead exemption or a tax cap, and targeted tax breaks that are given only to particular groups of low- and middle-income taxpayers. This policy brief surveys the advantages and disadvantages of the circuit breaker approach to reducing property taxes.
Boosting Incomes and Improving Tax Equity with State Earned Income Tax Credits in 2019
September 26, 2019 • By Aidan Davis

The Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) is a policy designed to bolster the incomes of low-wage workers and offset some of the taxes they pay, providing the opportunity for families struggling to afford the high cost of living to step up and out of poverty toward meaningful economic security. The federal EITC has kept millions of Americans out of poverty since its enactment in the mid-1970s. Over the past several decades, the effectiveness of the EITC has been magnified as many states have enacted and later expanded their own credits.
Promoting Greater Economic Security Through A Chicago Earned Income Tax Credit: Analyses of Six Policy Design Options
September 12, 2019 • By Lisa Christensen Gee

A new report reveals that a city-level, Chicago Earned Income Tax Credit would boost the economic security of 546,000 to 1 million of the city’s working families. ITEP produced a cost and distributional analysis of six EITC policy designs, which outlines the average after-tax income boost for families at varying income levels. The most generous policy option would increase after-tax income for more than 1 million working families with an average benefit, depending on income, ranging from $898 to $1,426 per year.

The nation’s tax policies and their role in economic inequality are front and center during this election cycle. For those interested in how the nation can move toward a fairer tax system and or more detailed information about progressive tax policy ideas, ITEP created this quick guide.
Sales Tax Holidays: An Ineffective Alternative to Real Sales Tax Reform
July 17, 2019 • By Dylan Grundman O'Neill
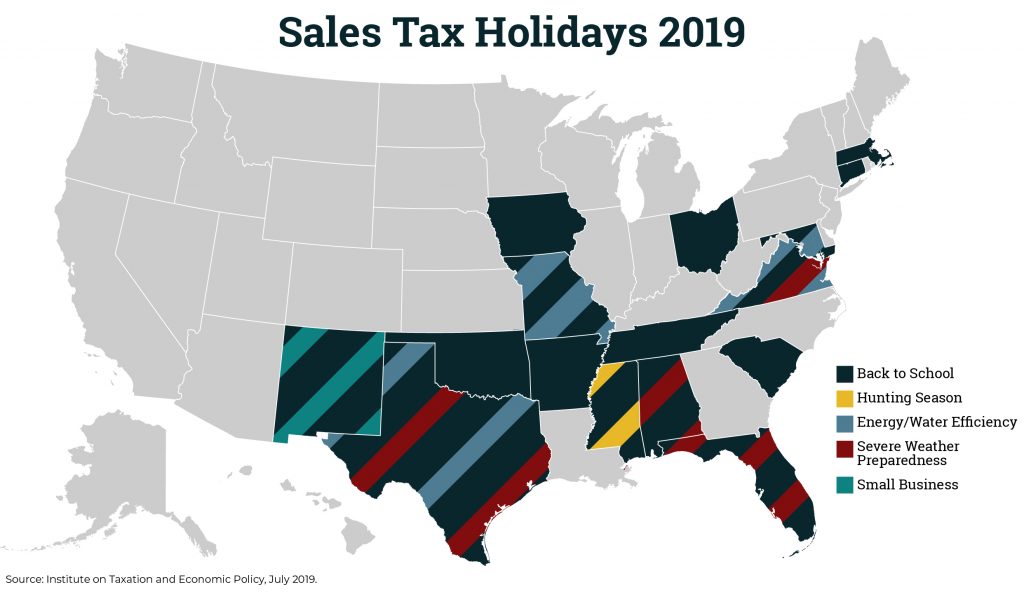
Lawmakers in many states have enacted “sales tax holidays” (16 states will hold them in 2019), to provide a temporary break on paying the tax on purchases of clothing, school supplies, and other items. While these holidays may seem to lessen the regressive impacts of the sales tax, their benefits are minimal. This policy brief looks at sales tax holidays as a tax reduction device.
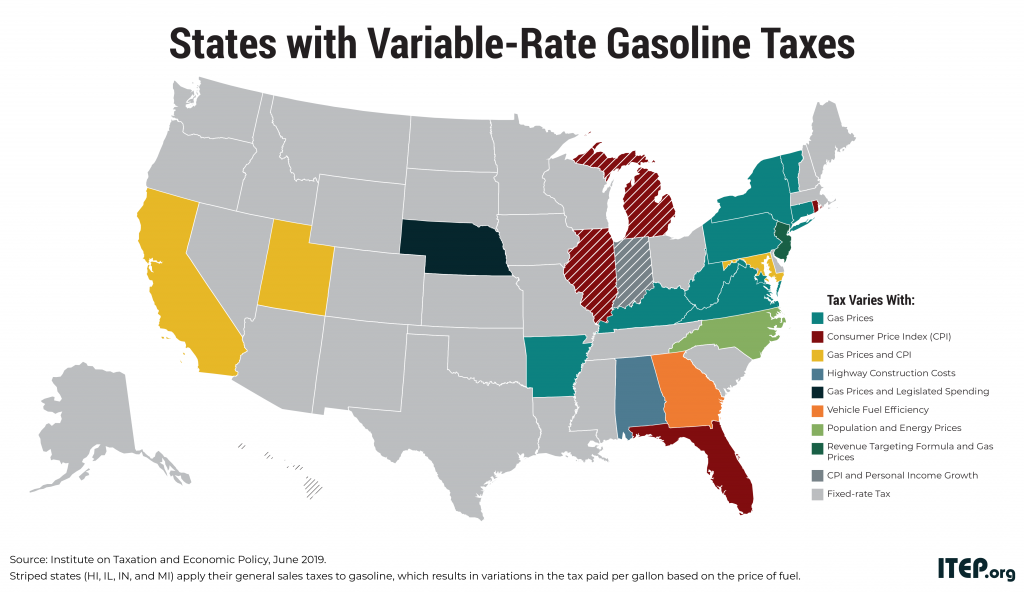
The flawed design of federal and state gasoline taxes has made it exceedingly difficult to raise adequate funds to maintain the nation’s transportation infrastructure. Twenty-eight states and the federal government levy fixed-rate gas taxes where the tax rate does not change even when the cost of infrastructure materials rises or when drivers purchase more fuel-efficient vehicles and pay less in gas tax. The federal government’s 18.4-cent gas tax, for example, has not increased in over 25 years. Many states have waited a decade or more since last raising their own gas tax rates.
Rewarding Work Through State Earned Income Tax Credits in 2018
September 17, 2018 • By ITEP Staff

The Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) is a policy designed to bolster the earnings of low-wage workers and offset some of the taxes they pay, providing the opportunity for struggling families to step up and out of poverty toward meaningful economic security. The federal EITC has kept millions of Americans out of poverty since its enactment in the mid-1970s. Over the past several decades, the effectiveness of the EITC has been magnified as many states have enacted and later expanded their own credits. The effectiveness of the EITC as an anti-poverty policy can be increased by expanding the credit at…
Reducing the Cost of Child Care Through State Tax Codes in 2018
September 17, 2018 • By Aidan Davis
Families in poverty contribute over 30 percent of their income to child care compared to about 6 percent for families at or above 200 percent of poverty. Most families with children need one or more incomes to make ends meet which means child care expenses are an increasingly unavoidable and unaffordable expense. This policy brief examines state tax policy tools that can be used to make child care more affordable: a dependent care tax credit modeled after the federal program and a deduction for child care expenses.

Sales taxes are one of the most important revenue sources for state and local governments; however, they are also among the most unfair taxes, falling more heavily on low- and middle-income households. Therefore, it is important that policymakers nationwide find ways to make sales taxes more equitable while preserving this important source of funding for public services. This policy brief discusses two approaches to a less regressive sales tax: broad-based exemptions and targeted sales tax credits.

State lawmakers seeking to make residential property taxes more affordable have two broad options: across-the-board tax cuts for taxpayers at all income levels, such as a homestead exemption or a tax cap, and targeted tax breaks that are given only to particular groups of low- and middle-income taxpayers. One such targeted program to reduce property taxes is called a “circuit breaker” because it protects taxpayers from a property tax “overload” just like an electric circuit breaker: when a property tax bill exceeds a certain percentage of a taxpayer’s income, the circuit breaker reduces property taxes in excess of this “overload”…
Sales Tax Holidays: An Ineffective Alternative to Real Sales Tax Reform
July 12, 2018 • By Dylan Grundman O'Neill
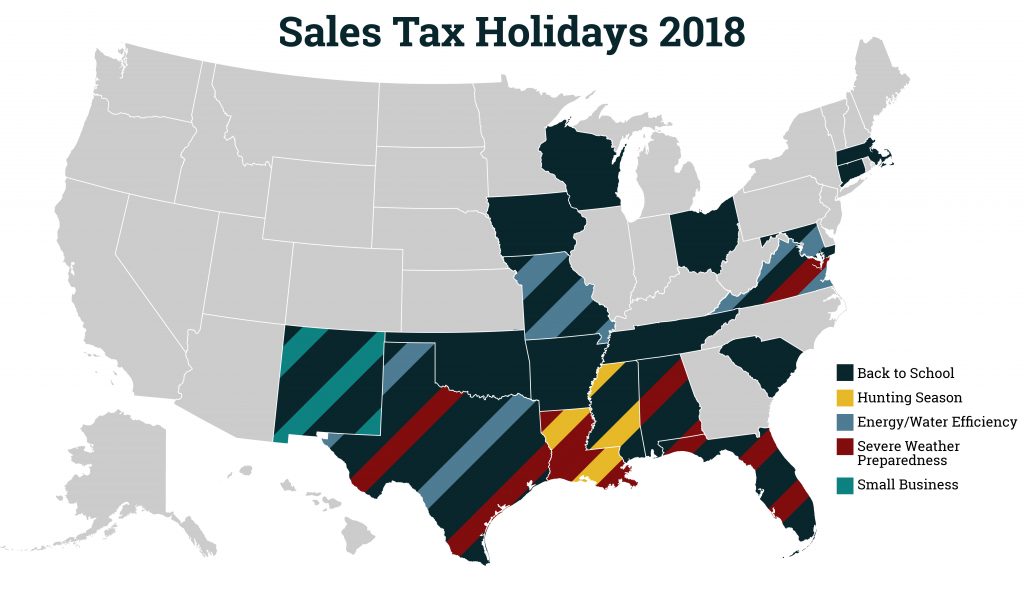
An updated version of this brief for 2019 is available here. Read this report in PDF. Overview Sales taxes are an important revenue source, composing close to half of all state tax revenues.[1] But sales taxes are also inherently regressive because the lower a family’s income, the more the family must spend on goods and […]
Lottery, Casino and other Gambling Revenue: A Fiscal Game of Chance
June 12, 2018 • By ITEP Staff

Cash-strapped, tax-averse state lawmakers continue to seek unconventional revenue-raising alternatives to the income, sales, and property taxes that form the backbone of most state tax systems. However, gambling revenues are rarely as lucrative, or as long-lasting, as supporters claim.
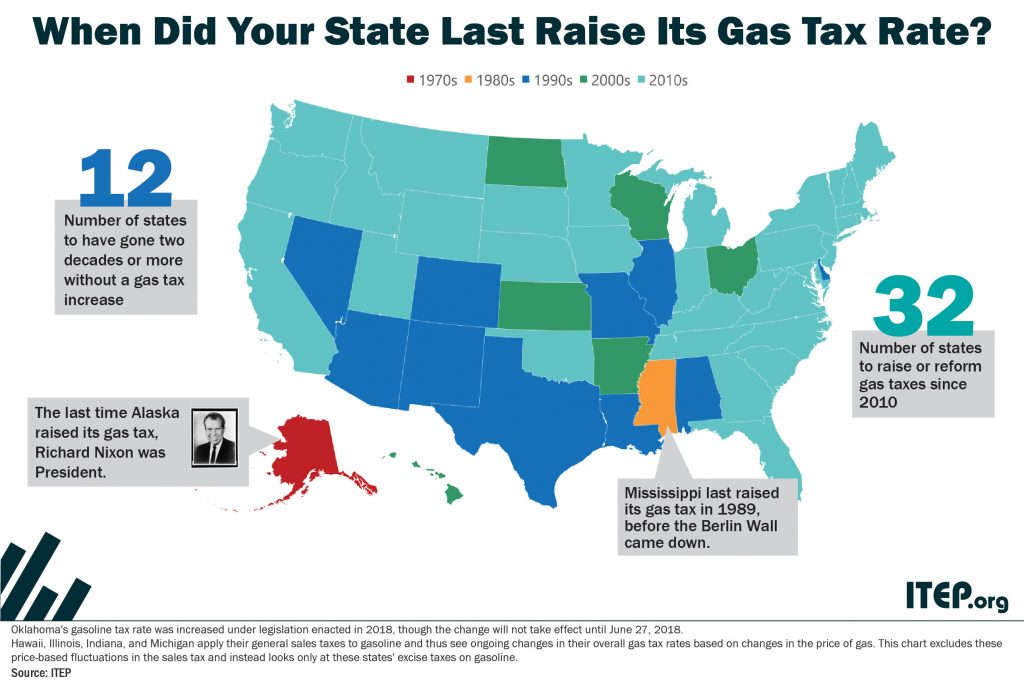
Many state governments are struggling to repair and expand their transportation infrastructure because they are attempting to cover the rising cost of asphalt, machinery, and other construction materials with fixed-rate gasoline taxes that are rarely increased.
Many Localities Are Unprepared to Collect Taxes on Online Purchases: Amazon.com and other E-Retailers Receive Tax Advantage Over Local Businesses
March 26, 2018 • By Carl Davis
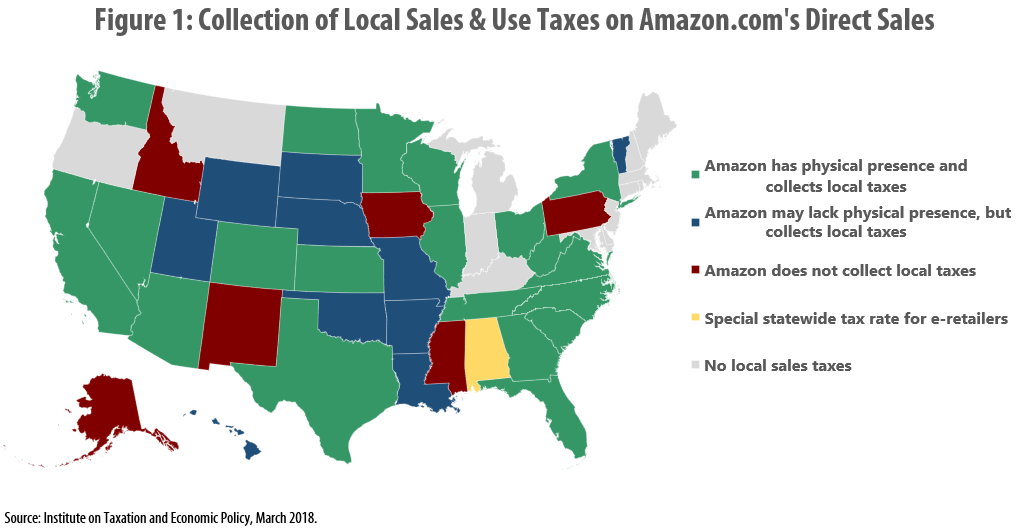
Online retailer Amazon.com made headlines last year when it began collecting every state-level sales tax on its direct sales. Savvy observers quickly noted that this change did not affect the company’s large and growing “marketplace” business, where it conducts sales in partnership with third-parties and rarely collects tax. But far fewer have noticed that even on its direct sales, Amazon is still not collecting some local-level taxes.
Preventing State Tax Subsidies for Private K-12 Education in the Wake of the New Federal 529 Law
February 23, 2018 • By Ronald Mak

This policy brief explains the federal and various state-level breaks for 529 plans and explores the potential impact that the change in federal treatment of 529 plans will have on state revenues.
What the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act Means for States – A Guide to Impacts and Options
January 26, 2018 • By ITEP Staff
The recently enacted Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) has major implications for budgets and taxes in every state, ranging from immediate to long-term, from automatic to optional, from straightforward to indirect, from certain to unknown, and from revenue positive to negative. And every state can expect reduced federal investments in shared public priorities like health care, education, public safety, and basic infrastructure, as well as a reduced federal commitment to reducing economic inequality and slowing the concentration of wealth. This report provides detail that state residents and lawmakers can use to better understand the implications of the TCJA for…
Key Lessons for States as They Determine Responses to the Federal Tax Bill
January 26, 2018 • By ITEP Staff
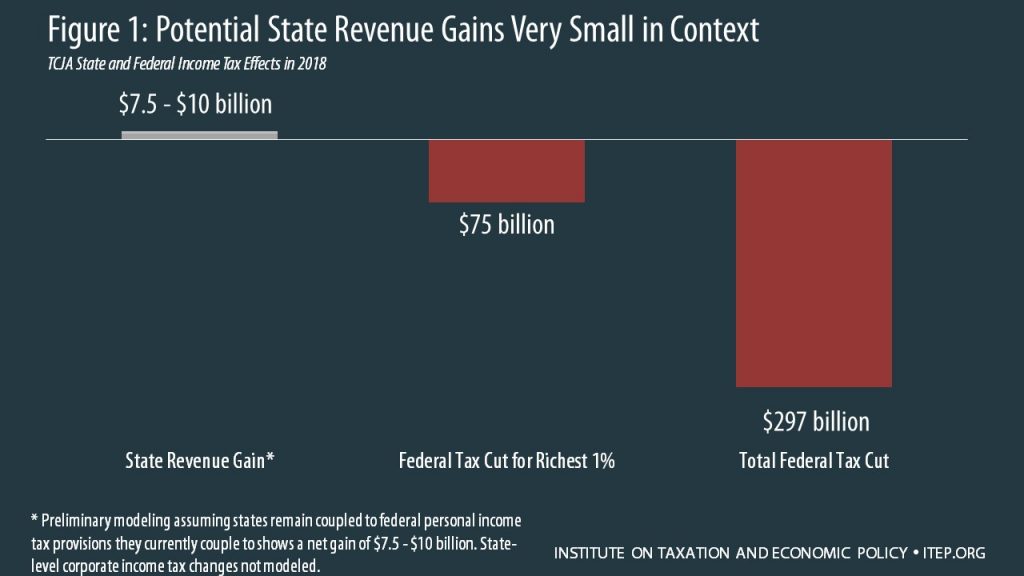
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) was enacted just weeks before many state legislatures began their sessions, leaving state lawmakers, tax officials, and the public scrambling to understand how the bill affects their states and how they should react. The TCJA has many important implications for both the fairness and adequacy of state tax codes and this report aims to summarize those implications and provide guidance on the key decisions facing state policymakers going forward.
Fact Sheet: The Consequences of Adopting a Territorial Tax System
September 18, 2017 • By Steve Wamhoff
President Trump and Republican leaders in Congress have proposed a “territorial” tax system, which would allow American corporations to pay no U.S. taxes on most profits they book offshore. This would worsen the already substantial problem of corporate tax avoidance and result in more jobs and investment leaving the U.S. Lawmakers should know some key facts about the territorial approach.
Reducing the Cost of Child Care Through State Tax Codes in 2017
September 11, 2017 • By ITEP Staff

Low- and middle-income working parents spend a significant portion of their income on child care. As the number of parents working outside of the home continues to rise, child care expenses have become an unavoidable and increasingly unaffordable expense. This policy brief examines state tax policy tools that can be used to make child care more affordable: a dependent care tax credit modeled after the federal program and a deduction for child care expenses.
