
Policy Briefs

Sales taxes are one of the most important revenue sources for state and local governments; however, they are also among the most unfair taxes, falling more heavily on low- and middle-income households. Therefore, it is important that policymakers nationwide find ways to make sales taxes more equitable while preserving this important source of funding for public services. This policy brief discusses two approaches to a less regressive sales tax: broad-based exemptions and targeted sales tax credits.
Rewarding Work Through State Earned Income Tax Credits in 2017
September 11, 2017 • By ITEP Staff
The Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) is a policy designed to bolster the earnings of low-wage workers and offset some of the taxes they pay, providing the opportunity for struggling families to step up and out of poverty toward meaningful economic security. The federal EITC has kept millions of Americans out of poverty since its enactment in the mid-1970s. Over the past several decades, the effectiveness of the EITC has been magnified as many states have enacted and later expanded their own credits.

The Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) is a policy designed to bolster the earnings of low-wage workers and offset some of the taxes they pay, providing the opportunity for struggling families to step up and out of poverty toward meaningful economic security. The federal EITC has kept millions of Americans out of poverty since its enactment in the mid-1970s. Over the past several decades, the effectiveness of the EITC has been magnified as many states have enacted and later expanded their own credits.
Sales Tax Holidays: An Ineffective Alternative to Real Sales Tax Reform
July 12, 2017 • By ITEP Staff
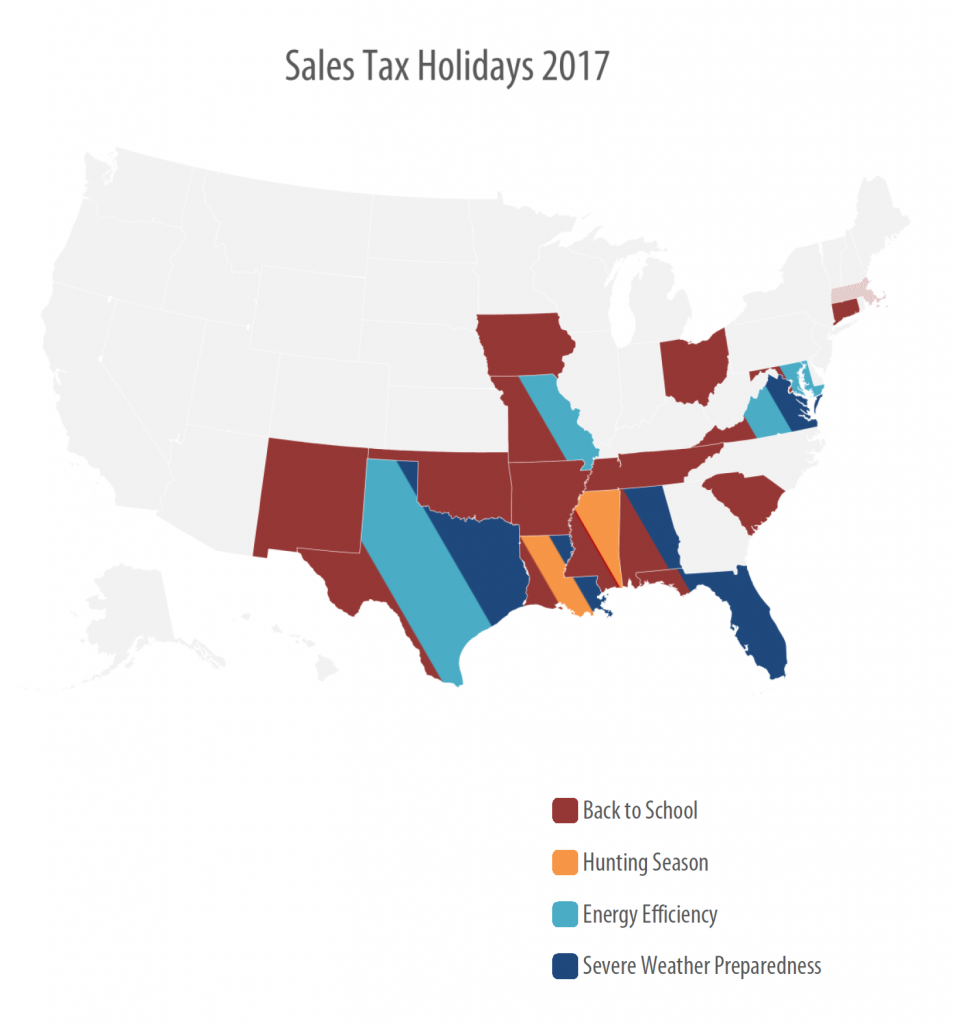
Sales taxes are an important revenue source, composing close to half of all state tax revenues. But sales taxes are also inherently regressive because the lower a family’s income, the more the family must spend on goods and services subject to the tax. Lawmakers in many states have enacted “sales tax holidays” (at least 16 states will hold them in 2017), to provide a temporary break on paying the tax on purchases of clothing, school supplies, and other items. While these holidays may seem to lessen the regressive impacts of the sales tax, their benefits are minimal. This policy brief…

Many state governments are struggling to repair and expand their transportation infrastructure because they are attempting to cover the rising cost of asphalt, machinery, and other construction materials with fixed-rate gasoline taxes that are rarely increased.

The flawed design of federal and state gasoline taxes has made it exceedingly difficult to raise adequate funds to maintain the nation’s transportation infrastructure. Thirty states and the federal government levy fixed-rate gas taxes where the tax rate does not change even when the cost of infrastructure materials rises or when drivers transition toward more fuel-efficient vehicles and pay less in gas tax. The federal government’s 18.4 cent gas tax, for example, has not increased in over twenty-three years. Likewise, nineteen states have waited a decade or more since last raising their own gas tax rates.
Why States That Offer the Deduction for Federal Income Taxes Paid Get It Wrong
May 1, 2017 • By Dylan Grundman O'Neill
With many states currently facing budget shortfalls—whether due to weak economic recovery after the Great Recession, struggling commodity prices, or self-inflicted tax cuts—and all states bracing for possible federal budget cuts in areas from education to health care to infrastructure, states are unlikely to be able to continue providing high-quality services to their residents without raising new revenue. In this context, states must find ways to generate additional revenue without increasing taxes on individuals and families who are already struggling to make ends meet and may bear the biggest brunt of federal funding cuts.
Combined Reporting of State Corporate Income Taxes: A Primer
February 24, 2017 • By Dylan Grundman O'Neill, Meg Wiehe
Over the past several decades, state corporate income taxes have declined markedly. One of the factors contributing to this decline has been aggressive tax avoidance on the part of large, multi-state corporations, costing states billions of dollars. The most effective approach to combating corporate tax avoidance is combined reporting, a method of taxation currently employed in more than half of the states that tax corporate income. The two most recent states to enact combined reporting are Rhode Island in 2014 and Connecticut in 2015. In several states, including Connecticut, Illinois, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Vermont, lawmakers adopted the policy after…
The federal government and many states are unable to adequately maintain the nation's transportation infrastructure in part because the gasoline taxes intended to fund infrastructure projects are often poorly designed. Thirty states and the federal government levy fixed-rate gas taxes where the tax rate does not change even when the cost of infrastructure materials rises or when drivers transition toward more fuel-efficient vehicles and pay less in gas tax. The federal government's 18.4 cent gas tax, for example, has not increased in over twenty-three years. Likewise, more than twenty states have waited a decade or more since last raising their…
Many state governments are struggling to repair and expand their transportation infrastructure because they are attempting to cover the rising cost of asphalt, machinery, and other construction materials with fixed-rate gasoline taxes that are rarely increased. The chart accompanying this brief shows (as of January 1, 2017) the number of years that have elapsed since each state's gas tax was last increased.
For much of the last century, estate and inheritance taxes have played an important role in fostering strong communities by promoting equality of opportunity and helping states adequately fund public services. While many of the taxes levied by state and local governments fall most heavily on low-income families, only the very wealthy pay estate and inheritance taxes. Changes in the federal estate tax in recent years, however, caused states to reevaluate the structure of their estate and inheritance taxes. Unfortunately, the trend of late among states has tended toward weakening or completely eliminating them. But this need not be so;…
State governments provide a wide array of tax breaks for their elderly residents. Almost every state that levies an income tax allows some form of income tax exemption or credit for citizens over age 65 that is unavailable to non-elderly taxpayers. Most states also provide special property tax breaks to the elderly. Unfortunately, too many of these breaks are poorly-targeted, unsustainable, and unfair. This policy brief surveys federal and state approaches to reducing taxes for older adults and suggests options for designing less costly and better targeted tax breaks.
Retail trade has been transformed by the Internet. As the popularity of "e-commerce" (that is, transactions conducted over the Internet) has grown, policymakers have engaged in a heated debate over how state and local sales taxes should be applied to these transactions. This debate is of critical importance for states as sales taxes comprise close to one-third of all state tax revenues and hundreds of billions of dollars in retail spending is now occurring online.
Efforts to increase taxes usually face some opposition, particularly increases to broad-based taxes such as the sales or income tax. Yet in many states, lawmakers have been able to agree on one approach to revenue-raising: the cigarette tax. Since 2002, nearly every state has enacted a cigarette tax in-crease to fund health care, discourage smoking, or to help balance state budgets. This policy brief looks at the advantages and disadvantages of cigarette taxes, and cigarette tax increases, as a source of state and local revenue.
State lawmakers seeking to make residential property taxes more affordable have two broad options: across-the-board tax cuts for taxpayers at all income levels, such as a homestead exemption or a tax cap, and targeted tax breaks that are given only to particular groups of low- and middle-income taxpayers. One such targeted program to reduce property taxes is called a "circuit breaker" because it protects taxpayers from a property tax "overload" just like an electric circuit breaker: when a property tax bill exceeds a certain percentage of a taxpayer's income, the circuit breaker reduces property taxes in excess of this "overload"…
Reducing the Cost of Child Care Through State Tax Codes
September 14, 2016 • By Aidan Davis, Meg Wiehe
Low- and middle-income working parents spend a significant portion of their income on child care. As the number of parents working outside of the home continues to rise, child care expenses have become an unavoidable and increasingly unaffordable expense. This policy brief examines state tax policy tools that can be used to make child care more affordable: a dependent care tax credit modeled after the federal program and a deduction for child care expenses.
Rewarding Work Through State Earned Income Tax Credits
September 14, 2016 • By Aidan Davis, Lisa Christensen Gee, Meg Wiehe
The Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) is a policy designed to bolster the earnings of low-wage workers and offset some of the taxes they pay, providing the opportunity for struggling families to step up and out of poverty toward meaningful economic security. The federal EITC has kept millions of Americans out of poverty since its enactment in the mid-1970s. Over the past several decades, the effectiveness of the EITC has been magnified as many states have enacted and later expanded their own credits.
Sales taxes are one of the most important revenue sources for state and local governments; however, they are also among the most unfair taxes, falling more heavily on low- and middle-income households. Therefore, it is important that policymakers nationwide find ways to make sales taxes more equitable while preserving this important source of funding for public services. This policy brief discusses two approaches to a less regressive sales tax: broad-based exemptions and targeted sales tax credits.
How State Tax Changes Affect Your Federal Taxes: A Primer on the “Federal Offset”
August 22, 2016 • By Dylan Grundman O'Neill
Read this brief in PDF here. State lawmakers frequently make claims about how proposed tax changes would affect taxpayers at different income levels. Yet too many lawmakers routinely ignore one important consequence of their tax reform proposals: the effect of state tax changes on their constituents’ federal income tax bills. Wealthier taxpayers in particular can […]
Indexing Income Taxes for Inflation: Why It Matters
August 22, 2016 • By Dylan Grundman O'Neill
Read brief in PDF here. All of us experience the effects of inflation as the price of the goods and services we buy gradually goes up over time. Fortunately, as the cost of living goes up, our incomes often tend to rise as well in order to keep pace. But many state tax systems are […]
The Folly of State Capital Gains Tax Cuts
August 17, 2016 • By Dylan Grundman O'Neill, Meg Wiehe
Read the brief in a PDF here. The federal tax system treats income from capital gains more favorably than income from work. A number of state tax systems do as well, offering tax breaks for profits realized from local investments and, in some instances, from investments around the world. As states struggle to cope with […]
Read this Policy Brief in PDF here. General sales taxes are an important revenue source for state governments, accounting for close to one-third of state tax collections nationwide. But most state sales taxes have a damaging structural flaw: they typically apply to most sales of goods, such as books and computers, but exempt most services […]
Sales Tax Holidays: An Ineffective Alternative to Real Sales Tax Reform
July 11, 2016 • By Meg Wiehe
This brief was updated July 2018 Read this Policy Brief in PDF here. Sales taxes are an important revenue source, composing close to half of all state tax revenues.[1] But sales taxes are also inherently regressive because the lower a family’s income, the more the family must spend on goods and services subject to the […]
Few state tax trends are as striking as the rapid decline of state corporate income tax revenues. As recently as 1986, state corporate income taxes equaled 0.5 percent of nationwide Gross State Product (GSP) (a measure of statewide economic activity). But in fiscal year 2013 (the last year for which data are available), state and local corporate income taxes were just 0.33 percent of nationwide GSP--representing a decline of over 30 percent.
An updated version of this report has been published with data through July 1, 2017. Read this Policy Brief in PDF form Many states’ transportation budgets are in disarray, in part because they are trying to cover the rising cost of asphalt, machinery, and other construction materials with a gasoline tax rate that is rarely […]
