
Reports
The Domestic Production Activities Deduction: Costly, Complex and Ineffective
October 26, 2017 • By Richard Phillips

When the Domestic Production Activities Deduction (DPAD) became law in 2004, proponents described it as a way to help American companies manufacture in the United States and export products abroad. In recent years, the DPAD has grown into one of the largest corporate tax expenditures, with an estimated cost of more than $15 billion in 2016 and $174 billion over the next 10 years.
Trickle-Down Dries Up: States without personal income taxes lag behind states with the highest top tax rates
October 26, 2017 • By Carl Davis, Nick Buffie

Lawmakers who support reducing or eliminating state personal income taxes typically claim that doing so will spur economic growth. Often, this claim is accompanied by the assertion that states without income taxes are booming, and that their success could be replicated by any state that abandons its income tax. To help evaluate these arguments, this study compares the economic performance of the nine states without broad-based personal income taxes to their mirror opposites—the nine states levying the highest top marginal personal income tax rates throughout the last decade.

This study explores how in 2016 Fortune 500 companies used tax haven subsidiaries to avoid paying taxes on much of their income. It reveals that tax haven use is now standard practice among the Fortune 500 and that a handful of the country’s biggest corporations benefit the most from offshore tax avoidance schemes.
Benefits of GOP-Trump Framework Tilted Toward the Richest Taxpayers in Each State
October 4, 2017 • By Steve Wamhoff
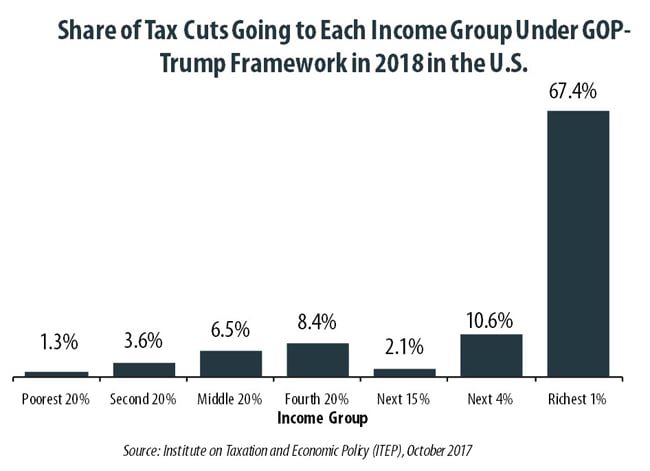
The “tax reform framework” released by the Trump administration and Congressional Republican leaders on September 27 would affect states differently, but every state would see its richest residents grow richer if it is enacted. In all but a handful of states, at least half of the tax cuts would flow to the richest one percent of residents if the framework took effect.
Astonishingly, tax policies in virtually every state make it harder for those living in poverty to make ends meet. When all the taxes imposed by state and local governments are taken into account, every state imposes higher effective tax rates on poor families than on the richest taxpayers.
Trump Proposals Would Reduce the Share of Taxes Paid by the Richest 1%, Raise It for Everyone Else
September 13, 2017 • By Steve Wamhoff
The tax proposals released by the Trump Administration in April would reduce the share of total federal, state and local taxes paid by America’s richest 1 percent while increasing the share paid by all other income groups. This clearly indicates that the tax system would be less progressive under the president’s approach.
Turning Loopholes into Black Holes: Trump’s Territorial Tax Proposal Would Increase Corporate Tax Avoidance
September 6, 2017 • By Matthew Gardner, Steve Wamhoff
The problem of offshore tax avoidance by American corporations could grow much worse under President Donald Trump’s proposal to adopt a “territorial” tax system, which would exempt the offshore profits of American corporations from U.S. taxes. This change would increase the already substantial benefits American corporations obtain when they use accounting gimmicks to make their profits appear to be earned in a foreign country that has no corporate income tax or has one that is extremely low or easy to avoid.
Nearly Half of Trump’s Proposed Tax Cuts Go to People Making More than $1 Million Annually
August 17, 2017 • By ITEP Staff
A tiny fraction of the U.S. population (one-half of one percent) earns more than $1 million annually. But in 2018 this elite group would receive 48.8 percent of the tax cuts proposed by the Trump administration. A much larger group, 44.6 percent of Americans, earn less than $45,000, but would receive just 4.4 percent of the tax cuts.
Trump’s $4.8 Trillion Tax Proposals Would Not Benefit All States or Taxpayers Equally
July 20, 2017 • By Matthew Gardner, Steve Wamhoff
The broadly outlined tax proposals released by the Trump administration would not benefit all taxpayers equally and they would not benefit all states equally either. Several states would receive a share of the total resulting tax cuts that is less than their share of the U.S. population. Of the dozen states receiving the least by this measure, seven are in the South. The others are New Mexico, Oregon, Maine, Idaho and Hawaii.
This letter outlines ITEP’s two broad objectives for meaningful federal tax reform and discusses six recommendations that would achieve them.
Trump Budget Uses Unrealistic Economic Forecast to Tee Up Tax Cuts
June 29, 2017 • By Carl Davis
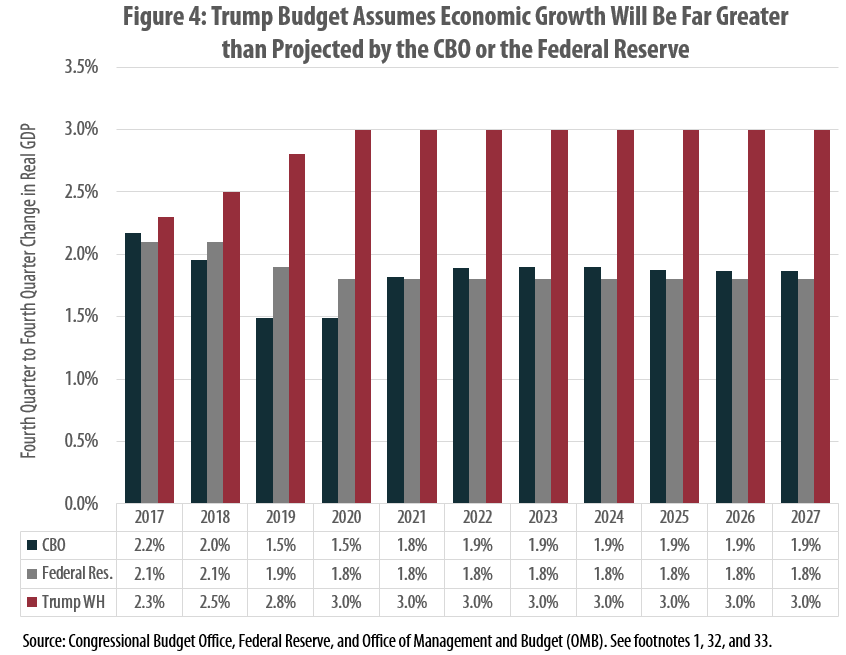
The Trump Administration recently released its proposed budget for Fiscal Year 2018. The administration claims that its proposals would reduce the deficit in nearly every year over the next decade before eventually achieving a balanced budget in 2027, but the assumptions it uses to reach this conclusion are deeply flawed. This report explains these flaws and their consequences for the debate over major federal tax changes.
Public Loss Private Gain: How School Voucher Tax Shelters Undermine Public Education
May 17, 2017 • By Carl Davis, Sasha Pudelski

One of the most important functions of government is to maintain a high-quality public education system. In many states, however, this objective is being undermined by tax policies that redirect public dollars for K-12 education toward private schools.
Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act (FATCA): A Critical Anti-Tax Evasion Tool
May 2, 2017 • By Richard Phillips
For years, a subset of the well-to-do and well-connected have been able to exploit the intricacies of our global financial system to shelter their income and investments from taxation. The U.S. government took a stand against this type of willful tax evasion with the passage of the Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act – or FATCA – enacted as part of the Hiring Incentives to Restore Employment (HIRE) Act of 2010.
If lawmakers truly want to create an environment in which economic mobility is possible for more working people, budget-busting tax cuts are the wrong way to achieve this goal. Dramatic tax giveaways would force cuts to programs that provide early education, health care, job training, affordable housing, nutrition assistance, and other vital services that promote economic mobility. Further, current tax proposals from Congress and the Trump Administration defy what most Americans would consider true reform and, instead, embrace supply-side economic theories. This policy brief outlines two sensible, broad objectives for meaningful federal tax reform and discusses six tax policies that…
3 Percent and Dropping: State Corporate Tax Avoidance in the Fortune 500, 2008 to 2015
April 27, 2017 • By Aidan Davis, Matthew Gardner, Richard Phillips
The trend is clear: states are experiencing a rapid decline in state corporate income tax revenue. Despite rebounding and even booming bottom lines for many corporations, this downward trend has become increasingly apparent in recent years. Since our last analysis of these data, in 2014, the state effective corporate tax rate paid by profitable Fortune 500 corporations has declined, dropping from 3.1 percent to 2.9 percent of their U.S. profits. A number of factors are driving this decline, including: a race to the bottom by states providing significant “incentives” for specific companies to relocate or stay put; blatant manipulation of…
State & Local Tax Contributions of Young Undocumented Immigrants (2017)
April 25, 2017 • By Meg Wiehe, Misha Hill
This report specifically examines the state and local tax contributions of undocumented immigrants who are currently enrolled or immediately eligible for DACA and the fiscal implications of various policy changes. The report includes information on the national impact (Table 1) and provides a state-by-state breakdown (Appendix 1).
Comparing the Distributional Impact of Revenue Options in Alaska
April 24, 2017 • By Aidan Davis, Carl Davis
Alaska is facing a significant budget gap because of a sharp decline in the oil tax and royalty revenue that has traditionally been relied upon to fund government. This report examines five approaches for replacing some of the oil revenue that is no longer available: enacting a broad personal income tax, state sales tax, payroll tax, investment income tax, or cutting the Permanent Fund Dividend (PFD). Any of the options examined in this report could make a meaningful contribution toward closing Alaska’s budget gap. To allow for comparisons across options, this report examines policy changes designed to generate $500 million…
State and Local Tax Contributions of Undocumented Californians: County-by- County Data
April 24, 2017 • By ITEP Staff
Public debates in California over immigrants, specifically around undocumented immigrants, often suffer from insufficient and inaccurate information about the contributions of undocumented immigrants, particularly their tax contributions at the local and state level. The fact of the matter is undocumented immigrants living in the California pay millions of dollars each year in local taxes to the counties where they live (estimated to be more than $1.5 billion) and collectively an estimated $3 billion combined in state and local taxes. A little more than half of the total state and local taxes undocumented immigrants in California pay flow to local governments.
Every year around Tax Day, ITEP updates some of its key reports to help put the nation's tax system in proper context. This year, as people around the country march to demand President Trump release his tax returns and as policymakers consider overhauling our federal tax system, these reports are especially critical. Read 10 Things You Should Know on Tax Day.
All Americans pay taxes. Most of us pay federal and state income taxes. Everyone who works pays federal payroll taxes. Everyone who buys gasoline pays federal and state gas taxes. Everyone who owns or rents a home directly or indirectly pays property taxes. Anyone who shops pays sales taxes in most states.
Profitable Fortune 500 companies in a range of economic sectors have been remarkably successful in manipulating the tax system to avoid paying even a dime in tax on billions of dollars in U.S. profits. This ITEP report examines a select, diverse group of 15 corporations' tax situations to shed light on the widespread nature of corporate tax avoidance. As a group, these companies paid no federal income tax on $21 billion in profits in 2016, and they paid almost no federal income tax on $111 billion in profits over the past five years. All but one received federal tax rebates…
The most recent data from the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) show that the United States is one of the least taxed developed nations.
U.S. Collects Smaller Share of Corporate Taxes Than Developed Country Average
April 10, 2017 • By Richard Phillips
Corporate income taxes in the United States as a share of the economy are well below the average among developed nations, according to an analysis of the most recent data from the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD). Data from the OECD show that U.S. corporate taxes as a percentage of GDP are 2.2 percent, which is 24 percent less than the 2.9 percent weighted average among the 34 other OECD countries for which data were available.
Testimony before the Alaska House Labor & Commerce Committee On House Bill 36
April 4, 2017 • By Matthew Gardner
Thank you for the opportunity to testify on the changes House Bill 36 would make to Alaska's tax treatment of pass-through income. The taxation of pass-through business entities has been a focal point of state and federal tax reform debates for over a quarter century, with a dual focus on minimizing the role of tax laws in determining the choice of business entity and on ensuring that the income of all business entities is subject to at least a minimal tax. My testimony makes two main points: 1. Alaska is one of a small number of states that do not…
Assessing the Distributional Consequences of Alaska’s House Bill 115 (Version L)
March 28, 2017 • By Carl Davis
This report contains ITEP's analysis of the distributional and revenue consequences of the revised version of House Bill 115 (Version L) as proposed on March 23, 2017. This proposal would reduce Alaska's Permanent Fund Dividend (PFD) payout and implement a personal income tax based on a modified version of Federal Adjusted Gross Income, with rates ranging from 0 to 7 percent. The analysis was produced using ITEP's Microsimulation Tax Model.
