
Recent Work
2162 items
Congress Steers Away from Entrenching So-Called Free File Program
June 6, 2019 • By Steve Wamhoff

Just before tax day in April, ITEP’s Jessica Schieder wrote that two proposals before Congress would take taxpayers in opposite directions. One was a bill passed in the House on a voice vote that included, among many other provisions, a section making permanent the “Free File” program under which private tax preparers claim to offer […]

Illinois made big news in several tax and budget areas recently, including sending a graduated income tax amendment to voters in 2020, as well as legalizing and taxing cannabis and updating gas and cigarette taxes for infrastructure improvements. Connecticut made smaller waves with sales tax reforms, a plastic bag tax, and a progressive mansion tax. Property tax credits were proposed in both Maine and New Jersey. And Nevada extended a business tax to give teachers a raise. And our What We’re Reading section is brimming with good reads on how states are doing with recovering from the Great Recession, funding…

Income inequality continues to be an undercurrent in public discourse about our economy and how working families are faring. It drove the national debate over the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, which, mounds of data reveal has exacerbated the problem. Some elected federal officials have responded to this step backward with calls for higher […]

After states implemented laws that allow taxpayers to circumvent the new $10,000 cap on deductions for state and local taxes (SALT), the IRS has proposed regulations to address this practice. It’s a safe bet the IRS will try to crack down on the newest policies that provide tax credits for donations to public education and other public services, but it remains to be seen whether new regulations will put an end to a longer-running practice of exploiting tax loopholes in some states that allow public money to be funneled to private schools.
File Under “No Surprise”: Wealthiest Taxpayers Use Offshore Tax Shelters More Than the Rest of Us, New Research Finds
June 4, 2019 • By Matthew Gardner

Tax evasion matters. It drains needed revenues from the public treasury, and saps public confidence in rules of the game. A recent Pew Research poll finds that 60 percent of Americans are bothered “a lot” by the feeling that the best-off don’t pay their fair share of taxes. And now, thanks to a new report, […]
Things Get Worse for Uber: Ride-Sharing Giant’s Taxes Under Scrutiny
June 4, 2019 • By Matthew Gardner
Since Uber’s much-hyped initial public offering last month, the news has been relentlessly bad for the scandal-plagued ride-sharing company. The company’s share price has fallen by 8 percent from its initial $45, meaning that billions of dollars of the company’s apparent value have vanished. This week the news got a little worse: Uber is under […]

From a new report comparing five major federal tax credit proposals to resources for continuing gas tax debates and the launch of ITEP's interactive library On the Map, here’s a summary of ITEP news this month.
Congressional Research Service Calls Three Strikes on the Trump Tax Cuts
May 30, 2019 • By Matthew Gardner

This new report is the most comprehensive assessment yet undertaken by the CRS, which has an unimpeachable reputation as an impartial arbiter of policy disputes. So, when it says that the TCJA doesn’t appear to have grown wages or the economy and has made our long-term budget deficits even worse, it’s a judgment that will last.

Like certain recent controversially concluded television shows, tax and budget debates can end in many ways and often receive mixed reviews. Illinois leaders, for example, ended on a cliffhanger by approving a historic constitutional amendment to create a graduated income tax in the state, whose ultimate conclusion will be crowdsourced by voters next November. Arizona’s fiscal finale fell flat with many observers due to corner-cutting on needed investments and a heavy focus on tax cuts. Texas legislators went for crowd-pleasing property tax cuts and school funding increases but left a gigantic “but how will we pay for this” plot hole…
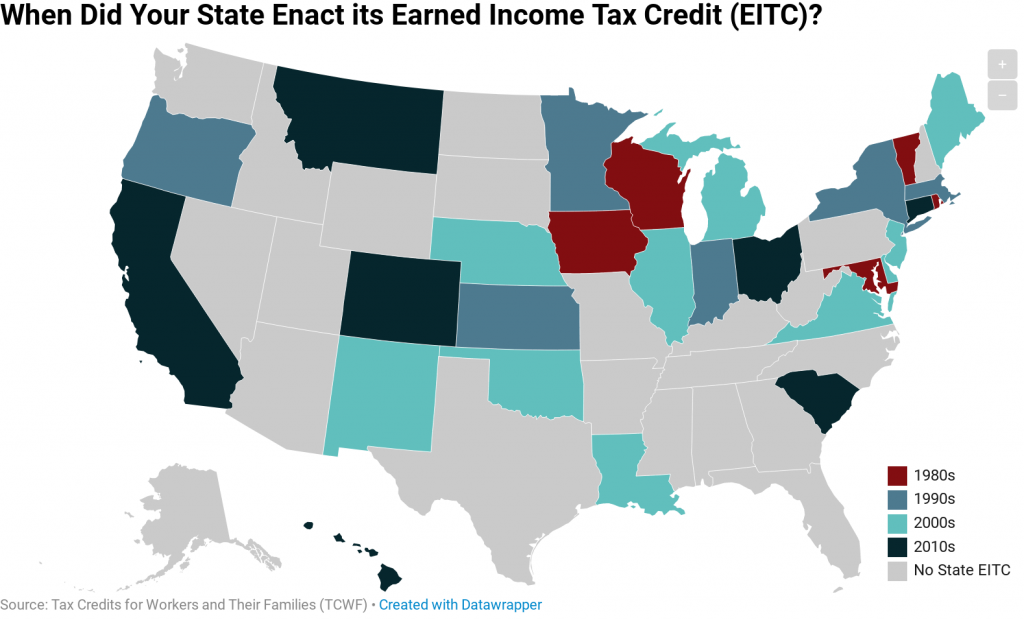
In 1986, Rhode Island became the first state to enact a tax credit patterned after the federal Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC). Since then, EITCs have become increasingly widespread at the state level with 28 states and the District of Columbia now offering them. These credits are designed to improve family economic security by bolstering […]
Unlike Trump-GOP Tax Law, There Are Tax Plans That Would Actually Deliver on Promise to Help Working People
May 24, 2019 • By Alan Essig

Using the tax code to boost the economic security of low- and moderate-income families is a proven strategy. These bold proposals would go much further than any policy currently on the books, and their approach directly contrasts with longstanding supply-side theories that call for continual tax cuts to those who are already economically faring far better than everyone else.
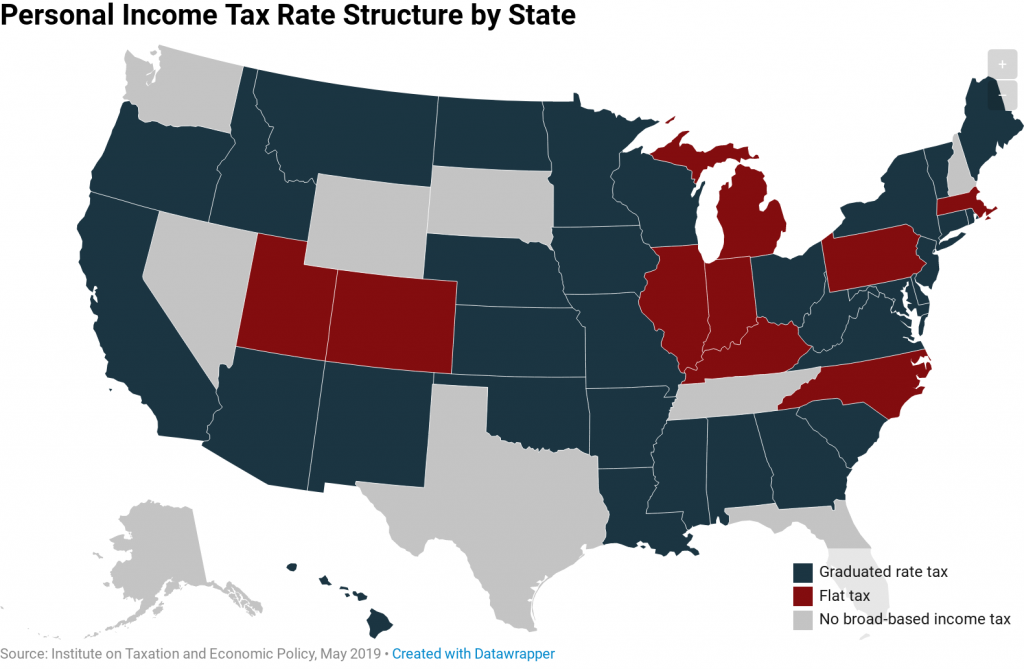
One of the most important decisions that must be made when designing a state personal income tax is whether to charge taxpayers a single flat rate on all their taxable income, or whether to levy a series of graduated rates that ask more of high-income taxpayers
State Rundown 5/22: (Some) State Lawmakers Can (Partly) Relax This Weekend
May 22, 2019 • By ITEP Staff

Lawmakers and advocates can enjoy their barbeques with only one eye on their work email this weekend in states that have essentially finished their budget debates such as Alaska, Minnesota, Nebraska, and Oklahoma, though both Alaska and Minnesota require special sessions to wrap things up. Getting to those barbeques may be a bumpy ride in Louisiana, Michigan, and other states still working to modernize outdated and inadequate gas taxes.
Proposals for Refundable Tax Credits Are Light Years from Tax Policies Enacted in Recent Years
May 22, 2019 • By Steve Wamhoff
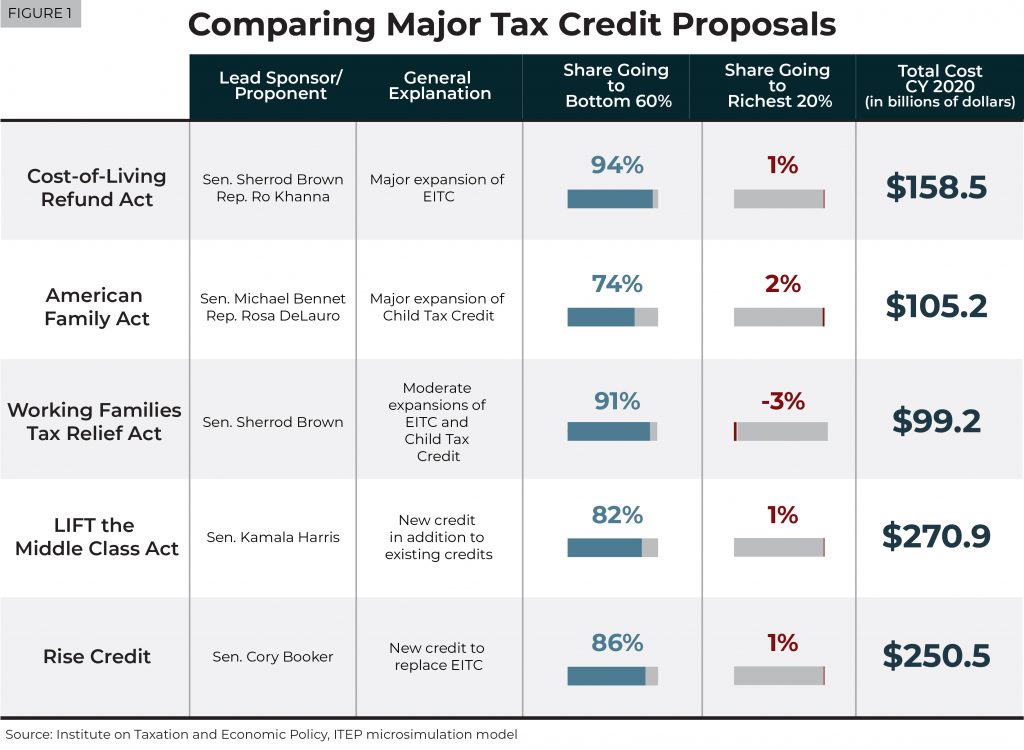
A new ITEP report examines five big proposals that have been announced this year to create or expand tax credits to address inequality and help low- and middle-income households.
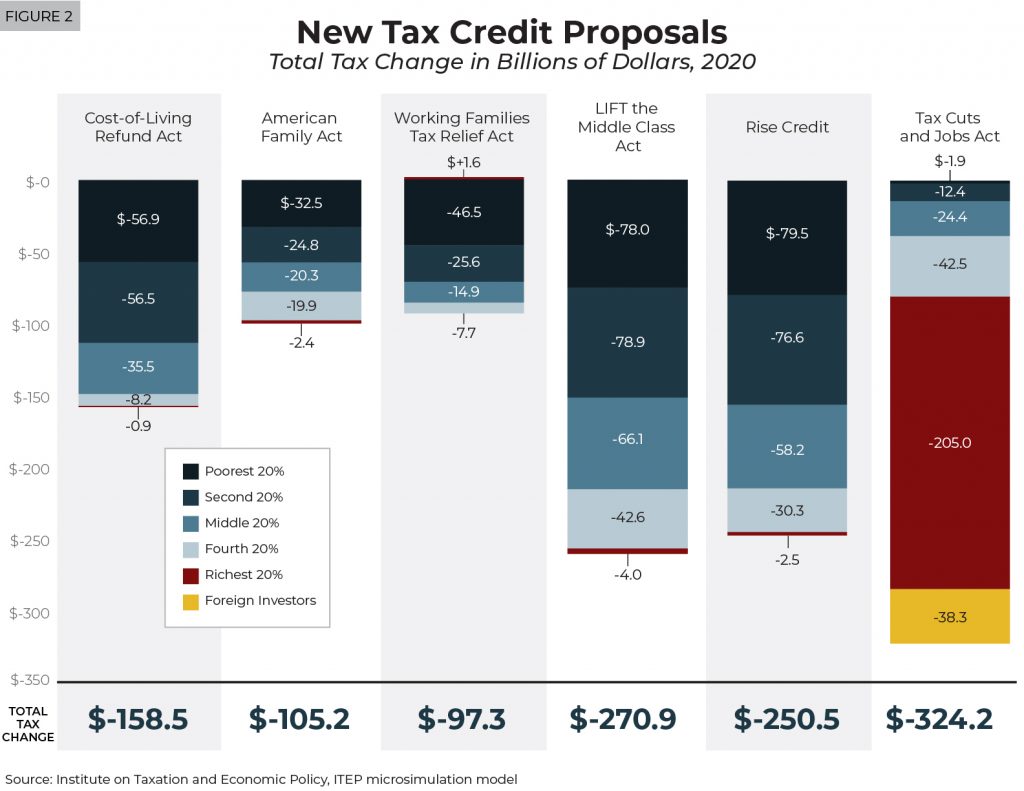
Federal lawmakers have recently announced at least five proposals to significantly expand existing tax credits or create new ones to benefit low- and moderate-income people. While these proposals vary a great deal and take different approaches, all would primarily benefit taxpayers who received only a small share of benefits from the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act.
