
Recent Work
2162 items
Presentation: NCSL Task Force on State and Local Taxation, Taxing Cannabis
May 10, 2019 • By Carl Davis

ITEP Research Director Carl Davis presented to the National Conference of State Legislatures (NCSL) Task Force on State and Local Taxation on approaches to cannabis taxation and the recent report Taxing Cannabis.
State Rundown 5/9: Illinois Moves Closer to a Progressive Income Tax
May 9, 2019 • By ITEP Staff

Lawmakers in Illinois and Ohio have advanced major tax proposals but cannot rest just yet, as they must still get past the other legislative chamber. Their counterparts in Michigan, Minnesota, Nebraska, and Oregon, meanwhile, are all at impasses over education funding, as those in Texas left their school funding disagreement unresolved at least until they reconvene...in 2021. And in an era of many states pre-empting smaller jurisdictions by revoking local decision-making powers, leaders in Colorado and Delaware made moves in the opposite direction, entrusting cities and school districts with more local control.
Proponents of Trump Tax Law Cite ITEP with Obvious Lack of Context
May 6, 2019 • By Steve Wamhoff
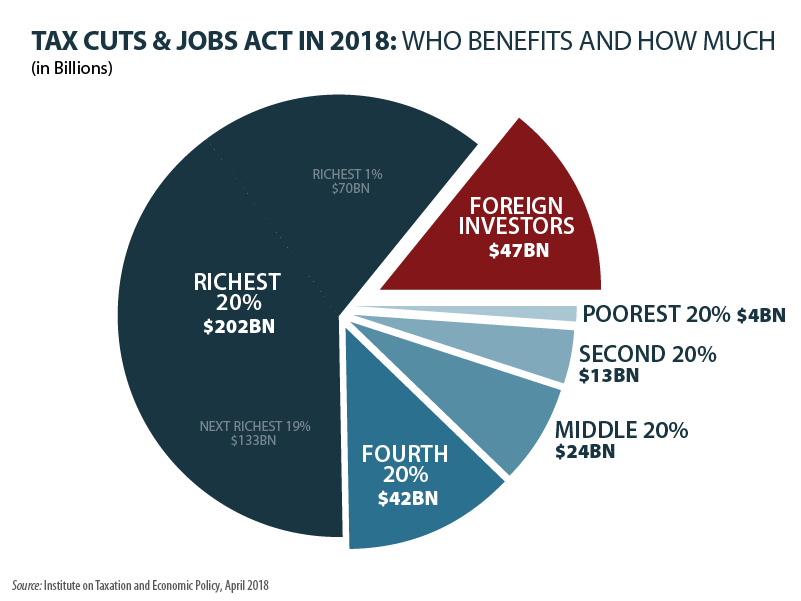
Sen. Chuck Grassley, the chairman of the Senate Finance Committee, today has an op-ed defending Trump-GOP tax law. “One of the most-covered falsehoods being spread about tax reform,” as he calls the law, “is that it’s a middle-class tax hike.” He cites ITEP’s estimates to back up his point that most people in every income group have lower taxes because of the law. As Sen. Grassley and his staff know full well, this leaves out the important point of our findings.

Teachers in North Carolina and South Carolina are walking out and rallying this week for increased education funding, teacher and staff pay, and other improvements to benefit students—if you’re unsure why be sure to check out research on the teacher shortage and pay gap under “What We’re Reading” below. Meanwhile, budget debates have recently wrapped up in Indiana, Iowa, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and Washington. And major tax debates are kicking into high gear in both Louisiana and Nebraska.
ITEP Testimony Supporting H.B. No. 7415, An Act Concerning a Surcharge on Capital Gains
April 26, 2019 • By Aidan Davis
Comments are intended to offer some perspective on the broader tax policy context in which this proposal is being considered. We find that this proposal would help to lessen long-running inequities in Connecticut’s state and local tax law that have allowed high-income taxpayers to pay lower overall effective tax rates than most low- and middle-income families.
State Rundown 4/26: Capital Gains Taxes Make Gains and Regressive Proposals Regress
April 26, 2019 • By ITEP Staff

Progressive capital gains tax proposals made news this week in Connecticut and Massachusetts, while Nebraskans came out in force to oppose a regressive tax shift, and North Carolina teachers prepare to rally over their legislature’s proclivity to cut taxes on wealthy households while underfunding schools.

From the first comprehensive look at corporate filings under the 2017 tax law to bold policy options from analysts and researchers to dramatically reduce poverty, here’s a summary of reports that ITEP released this month.

In early April, a diverse but mostly black crowd took to the streets in the Shaw neighborhood of Washington D.C. to protest T-Mobile’s decision to order Metro PCS to cease playing gogo music. This tale is a shining example of why economic investment—especially taxpayer-incentivized investment—in underserved communities is fraught with controversy. Who ultimately benefits after developers pour millions of dollars into these communities? And, as this controversy reveals, are the usually black and brown denizens of these neighborhoods and businesses that may have catered to them no longer welcome once economic development reaches a critical mass?

Tax and budget debates are now mostly complete in Alabama, Arkansas, and Colorado, but just starting or just getting interesting in several other states. Delaware and Massachusetts lawmakers, for example, are looking at progressive income tax increases on wealthy households, and New Hampshire may use a progressive tax on capital gains to simultaneously improve its upside-down tax code and invest in education. Nebraska and Texas, on the other hand, are also looking to improve school funding but plan to do so on the backs of low- and middle-income families through regressive sales tax increases. Fiscal debates are heating up in…
States Could Lift Millions of Children Out of Poverty by Enacting State-Level Child Tax Credits
April 17, 2019 • By Aidan Davis

In a new 50-state analysis, ITEP and the Center on Poverty & Social Policy at Columbia University teamed up to explain how state-level Child Tax Credits (CTCs) could lift between 2.1 and 4.5 million children out of poverty. The report outlines options that would help families who received little to no benefit from the expansion of the federal CTC included in the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act.
The Case for Extending State-Level Child Tax Credits to Those Left Out: A 50-State Analysis
April 17, 2019 • By Aidan Davis, Meg Wiehe

As of 2017, 11.5 million children in the United States were living in poverty. A national, fully-refundable Child Tax Credit (CTC) would effectively address persistently high child poverty rates at the national and state levels. The federal CTC in its current form falls short of achieving this goal due to its earnings requirement and lack of full refundability. Fortunately, states have options to make state-level improvements in the absence of federal policy change. A state-level CTC is a tool that states can employ to remedy inequalities created by the current structure of the federal CTC. State-level CTCs would significantly reduce…
For Tax Day, ITEP has released several new reports that tell a broad story about our nation’s federal, state and local tax systems, providing important details about taxes we all pay and research on the tax-paying habits of Fortune 500 corporations. And of course, we have a trove of other tax policy resources.
$4.3 Billion in Rebates, Zero-Tax Bill for 60 Profitable Corps Directly Related to Loopholes
April 12, 2019 • By Matthew Gardner

Meet the new corporate tax system, same as the old corporate tax system. That’s the inescapable conclusion of a new ITEP report assessing the taxpaying behavior of America’s most profitable corporations. The report, Corporate Tax Avoidance Remains Rampant Under New Law, released earlier this week, finds that 60 Fortune 500 corporations disclose paying zero in federal income taxes in 2018 despite enjoying large profits.
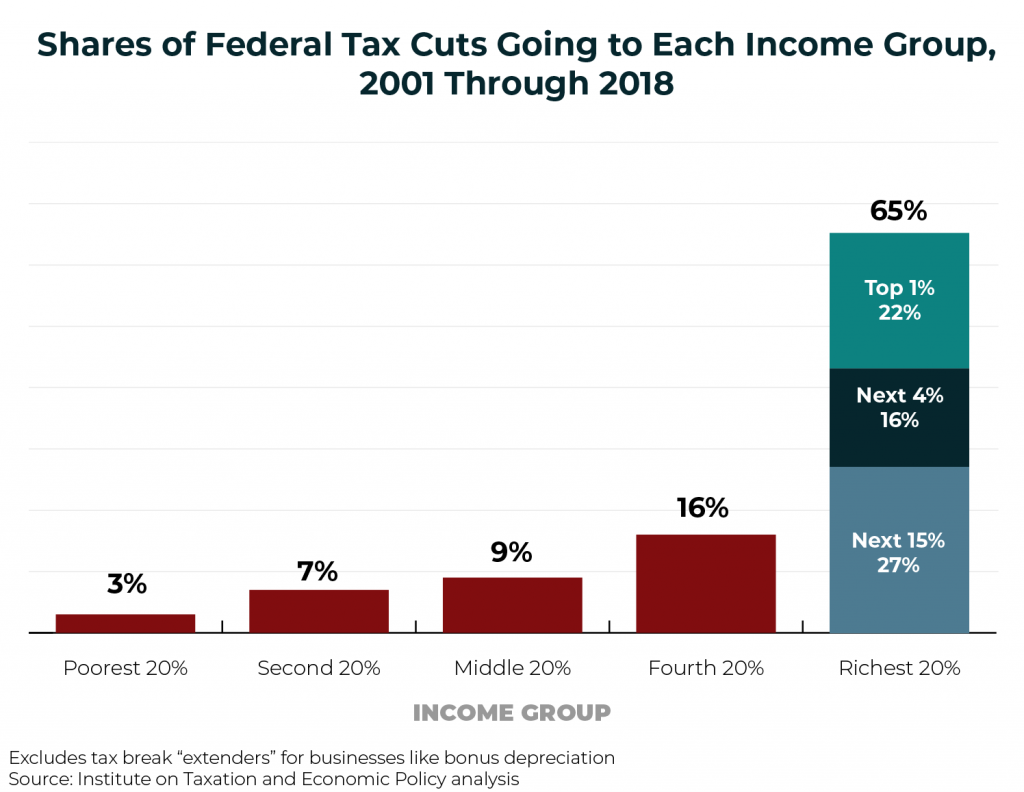
Income inequality is a national challenge. And inadequate federal revenue is a challenge that the nation will eventually have to reckon with. This chart book makes a strong case for why federal lawmakers should seriously consider progressive revenue-raising options.
The IRS Could Calculate Taxes for the Vast Majority of Taxpayers—But a Bipartisan Measure Would Ban It
April 12, 2019 • By Jessica Schieder

A proposal re-introduced this week by Sen. Elizabeth Warren (D-MA), Sen. Jeanne Shaheen (D-NH), and Rep. Brad Sherman (D-CA), The Tax Filing Simplification Act of 2019, goes a long way toward making tax filing a much more straight-forward process by broadening the IRS’s mandate.
