
District of Columbia
State Rundown 10/24: State Tax Talk Makes Like a Tree and Gets Colorful
October 24, 2019 • By ITEP Staff

As autumn brings a colorful display of foliage to many states, so too are tax proposals taking on interesting hues as states move from the summer off-season toward 2020 legislative sessions. Ohio lawmakers are blue in the face from debating and re-debating tax and budget issues there. Maryland residents again showed they can’t be called yellow-bellied when it comes to footing the bill for needed education improvements, showing their broad support for higher taxes to fund those needs even despite a hefty price tag. Alaska, Michigan, and other states are giving the green light to laws implementing their new ability…
KRWG: Analysis: 70% of NM Families With Children Will See State Income Tax Cut
October 16, 2019
Commentary: Most New Mexico families with children – 70% – will get a break on their state personal income taxes when they file their 2019 tax returns, thanks to legislation enacted in April by the state Legislature and Governor Michelle Lujan Grisham. That’s according to an analysis by the Washington, DC-based Institute on Taxation and […]
State Rundown 10/10: Always Something Old, Something New in State Tax Debates
October 10, 2019 • By ITEP Staff

Creative thinking from Pennsylvania lawmakers has helped them discover that the Wayfair ruling allowing states to collect sales tax from online retailers can also help them identify and tax corporate profits earned in their borders. Similarly, New York leaders had the vision to put bold environmental goals in place and identify a carbon price as a potential pay-for. Gubernatorial candidates in Mississippi and Kentucky showed less ingenuity, proposing tax cuts even though Mississippi is still phasing in a massive tax cut from a few years ago and Kentucky’s next election isn’t until 2020. Meanwhile, the old idea of eliminating income…
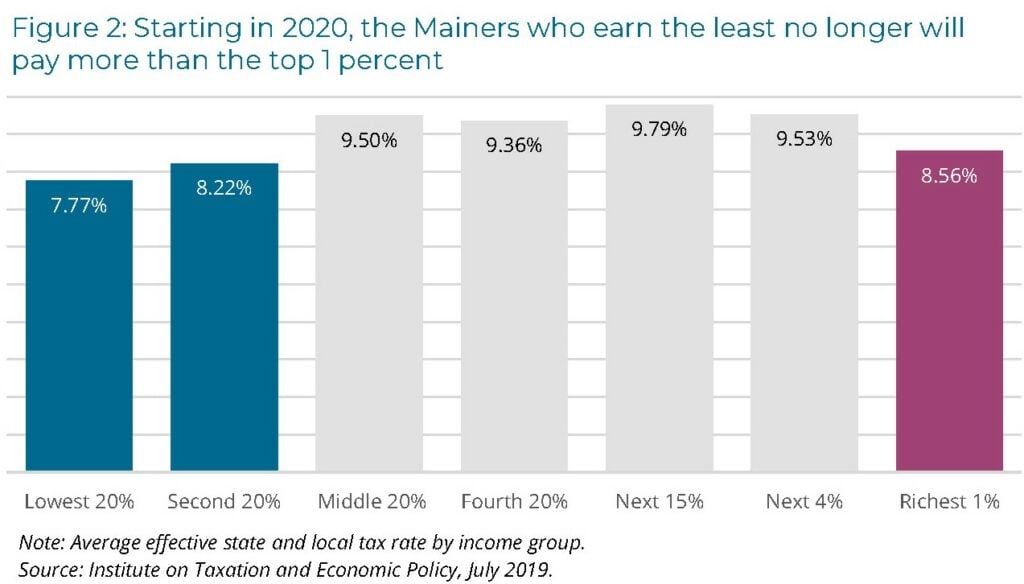
Lawmakers in Maine this year took bold steps toward making the state’s tax system fairer. Their actions demonstrate that political will can dramatically alter state tax policy landscape to improve economic well-being for low-income families while also ensuring the wealthy pay a fairer share.
State Tax Codes as Poverty Fighting Tools: 2019 Update on Four Key Policies in All 50 States
September 26, 2019 • By Aidan Davis

This report presents a comprehensive overview of anti-poverty tax policies, surveys tax policy decisions made in the states in 2019 and offers recommendations that every state should consider to help families rise out of poverty. States can jump start their anti-poverty efforts by enacting one or more of four proven and effective tax strategies to reduce the share of taxes paid by low- and moderate-income families: state Earned Income Tax Credits, property tax circuit breakers, targeted low-income credits, and child-related tax credits.
Sales taxes are one of the most important revenue sources for state and local governments; however, they are also among the most unfair taxes, falling more heavily on low- and middle-income households. Therefore, it is important that policymakers nationwide find ways to make sales taxes more equitable while preserving this important source of funding for public services. This policy brief discusses two approaches to a less regressive sales tax: broad-based exemptions and targeted sales tax credits.
Reducing the Cost of Child Care Through State Tax Codes in 2019
September 26, 2019 • By Aidan Davis

The high cost of quality child care is a budget constraint for many working families and particularly daunting for parents who are working but earning low wages. Most families with children need one or more incomes to make ends meet which means child care expenses are an increasingly unavoidable and unaffordable expense. This policy brief examines state tax policy tools that can be used to make child care more affordable: a dependent care tax credit modeled after the federal program and a deduction for child care expenses.
Boosting Incomes and Improving Tax Equity with State Earned Income Tax Credits in 2019
September 26, 2019 • By Aidan Davis

The Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) is a policy designed to bolster the incomes of low-wage workers and offset some of the taxes they pay, providing the opportunity for families struggling to afford the high cost of living to step up and out of poverty toward meaningful economic security. The federal EITC has kept millions of Americans out of poverty since its enactment in the mid-1970s. Over the past several decades, the effectiveness of the EITC has been magnified as many states have enacted and later expanded their own credits.
Promoting Greater Economic Security Through A Chicago Earned Income Tax Credit: Analyses of Six Policy Design Options
September 12, 2019 • By Lisa Christensen Gee

A new report reveals that a city-level, Chicago Earned Income Tax Credit would boost the economic security of 546,000 to 1 million of the city’s working families. ITEP produced a cost and distributional analysis of six EITC policy designs, which outlines the average after-tax income boost for families at varying income levels. The most generous policy option would increase after-tax income for more than 1 million working families with an average benefit, depending on income, ranging from $898 to $1,426 per year.
New Report: A Chicago EITC Would Benefit up to 1 Million Chicago Families
September 12, 2019 • By Lisa Christensen Gee

Media contact Report outlines policy options for Chicago Resilient Families Initiative Task Force Recommendations A new report reveals that a city-level, Chicago Earned Income Tax Credit would boost the economic security of 546,000 to 1 million of the city’s working families, the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy (ITEP) and Economic Security for Illinois said today. […]
How Tax Policy Can Help Mitigate Poverty, Address Income Inequality
September 10, 2019 • By ITEP Staff

Analysts at the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy have produced multiple recent briefs and reports that provide insight on how current and proposed tax policies affect family economic security and income inequality.
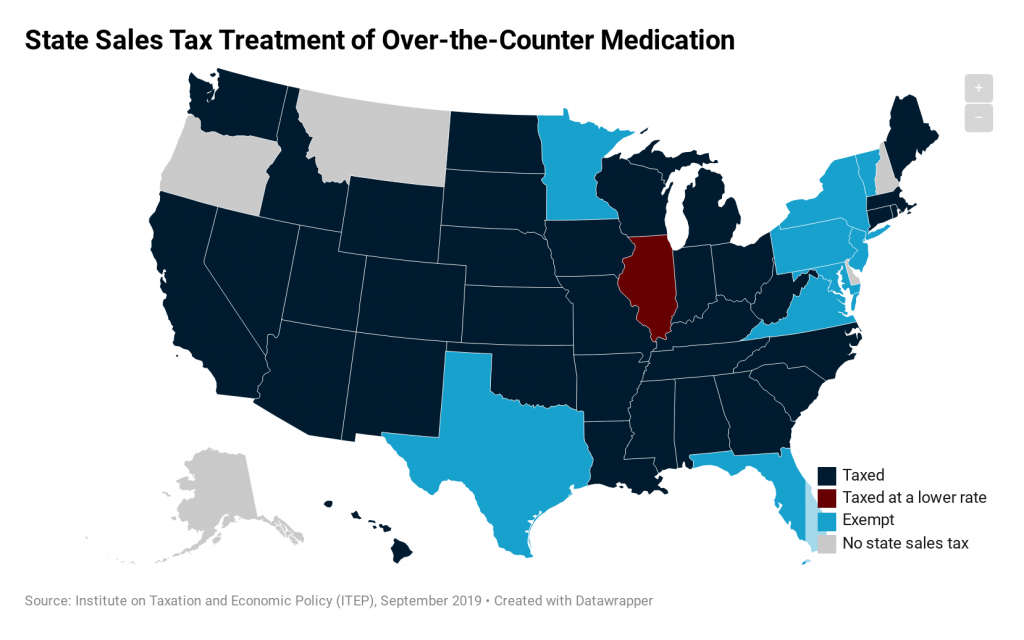
While most states levy general sales taxes on items that consumers purchase every day, those taxes often contain carveouts for some necessities such as rent, groceries, and medicine. Prescription drugs, for instance, are currently exempt from state sales tax in 44 of the 45 states levying such taxes (Illinois is the only exception, charging a […]
Press Herald: Think Tank Says Maine Has Reached ‘Tax Fairness’ Milestone
September 4, 2019
The center cited a 2018 report by the Washington, D.C.-based Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy that said only five states and the District of Columbia had tax codes in which the bottom 20 percent paid a lower average effective tax rate than the top 1 percent. It said legislative changes this year in Maine […]
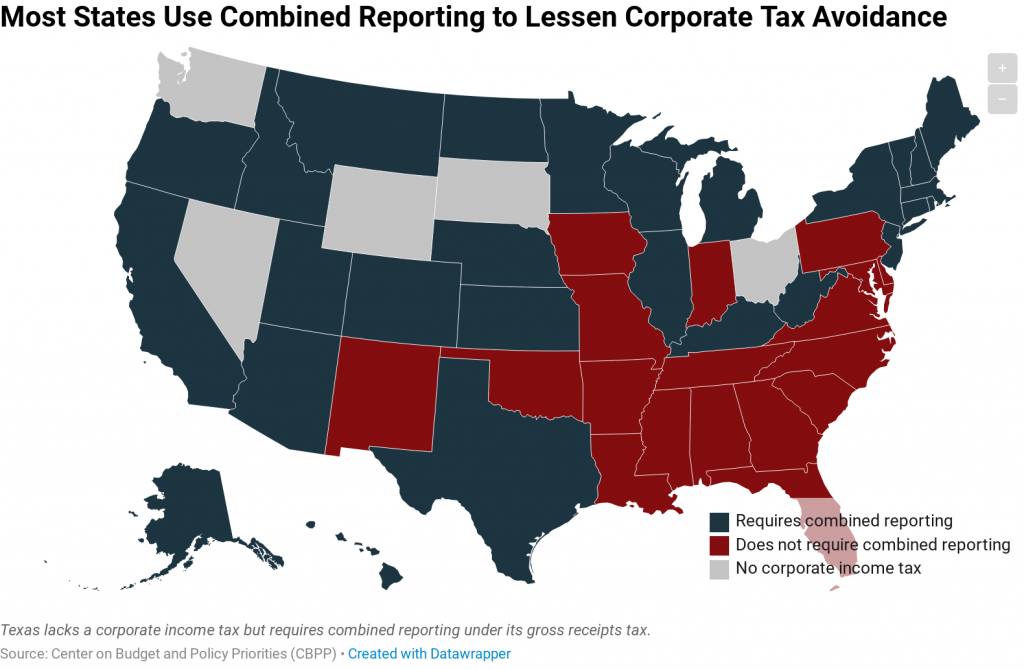
"Combined reporting" lessens the effectiveness of a tax avoidance scheme known as income shifting, in which large multi-state corporations dubiously claim that their income was earned in states with little or no corporate income tax.
Sales Tax Holidays: An Ineffective Alternative to Real Sales Tax Reform
July 17, 2019 • By Dylan Grundman O'Neill
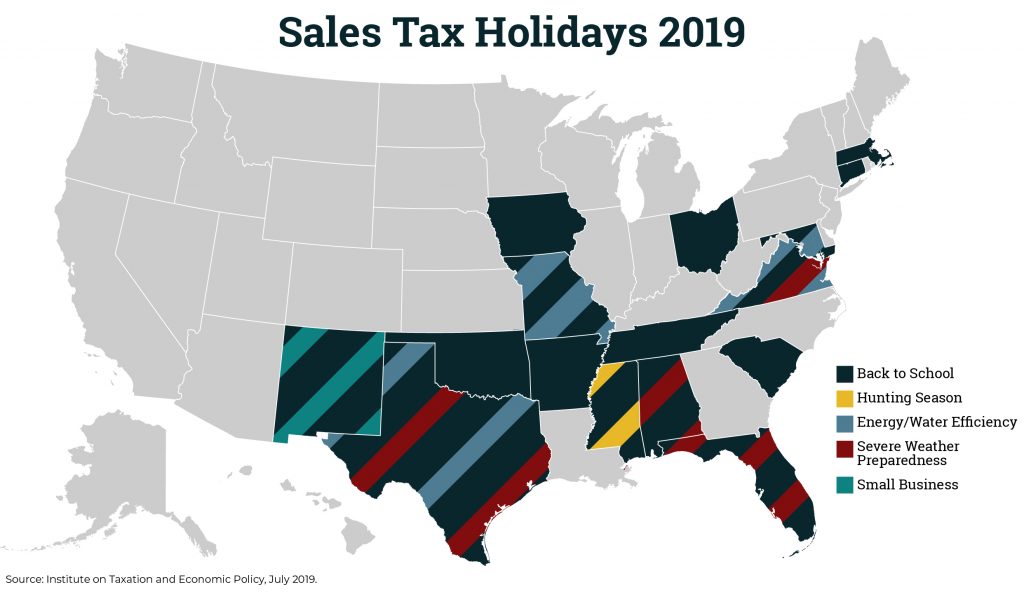
Lawmakers in many states have enacted “sales tax holidays” (16 states will hold them in 2019), to provide a temporary break on paying the tax on purchases of clothing, school supplies, and other items. While these holidays may seem to lessen the regressive impacts of the sales tax, their benefits are minimal. This policy brief looks at sales tax holidays as a tax reduction device.
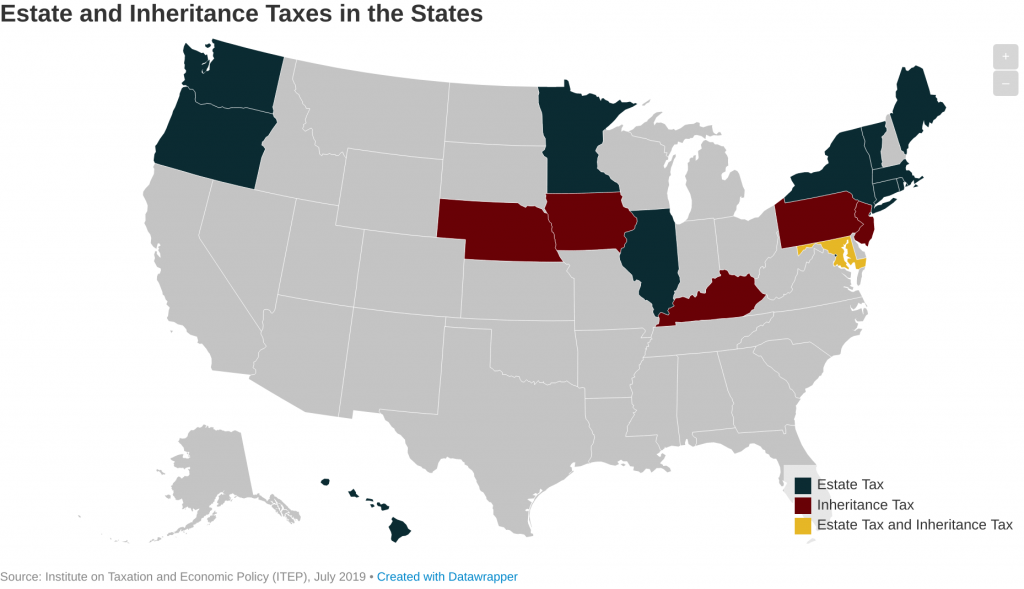
States have been repealing estate taxes since the early 2000s. Now, just 17 states and the District of Columbia (D.C.) levy estate and/or inheritance taxes. Twelve states and D.C. levy estate taxes while six states levy inheritance taxes (Maryland levies both). These taxes have long been used not just to raise revenue for vital public services, but to promote equality of opportunity and reduce the transfer of concentrated wealth from one generation to the next.
Vox: Buttigieg and Biden Acknowledged an Important Truth about Undocumented Workers
June 28, 2019
That’s not true. Contrary to this persistent myth, undocumented immigrants do in fact pay taxes. Millions of undocumented immigrants file tax returns each year, and they are paying taxes for many benefits they can’t even use. The best estimates come from research by the Institute of Taxation and Economic Policy, a left-leaning Washington, DC, think […]
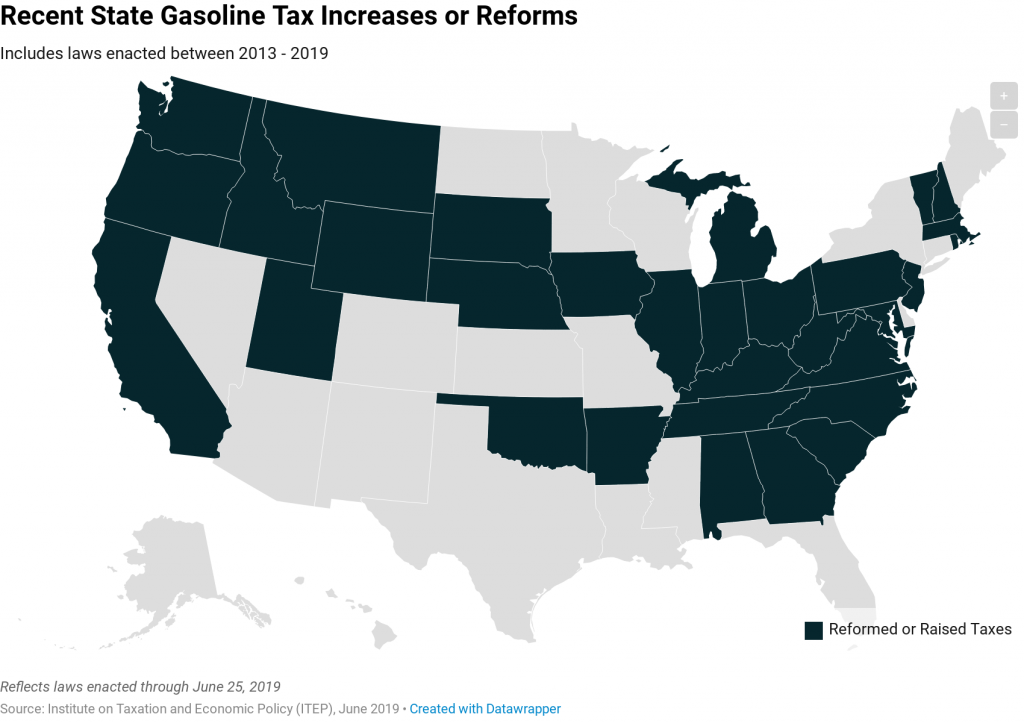
Gas taxes are the most important revenue source that states have available to pay for transportation infrastructure. In recent years, state lawmakers across the country have increasingly agreed that gas taxes must be increased to fund the maintenance and improvement of their infrastructure networks.
Ohio now enjoys the distinction of being the 30th state to raise or reform its gas tax this decade, and the third state to do so this year, under a bill signed into law by Gov. Mike DeWine. While state tax policy can be a contentious topic, there has been a remarkable level of agreement on the gasoline tax. Increasingly, state lawmakers are deciding that outdated gas taxes need to be raised and reformed to fund infrastructure projects that are vital to their economies. These actions are helping reverse losses in gas tax purchasing power caused by rising construction costs…
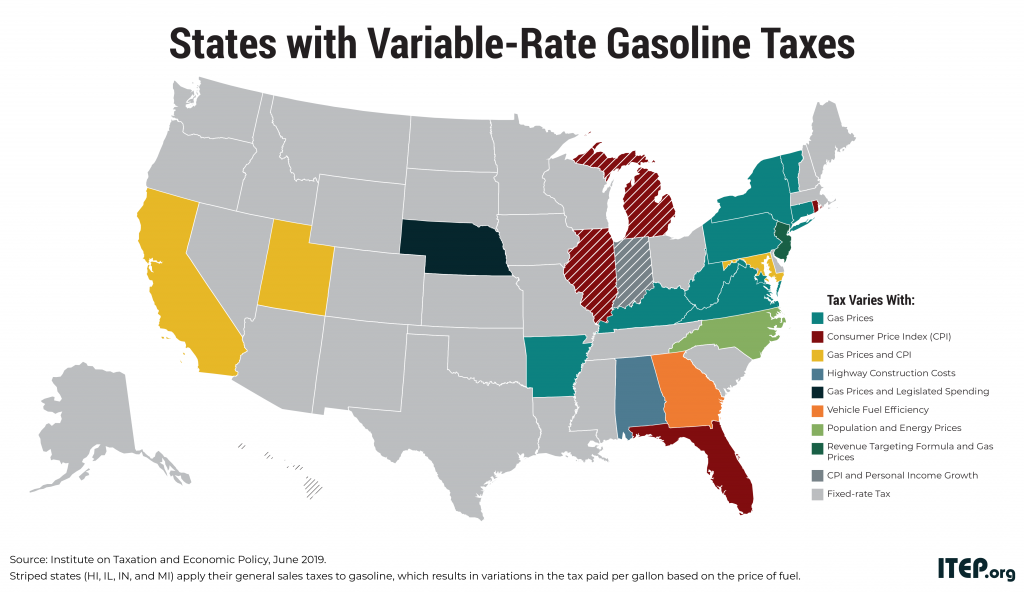
The flawed design of federal and state gasoline taxes has made it exceedingly difficult to raise adequate funds to maintain the nation’s transportation infrastructure. Twenty-eight states and the federal government levy fixed-rate gas taxes where the tax rate does not change even when the cost of infrastructure materials rises or when drivers purchase more fuel-efficient vehicles and pay less in gas tax. The federal government’s 18.4-cent gas tax, for example, has not increased in over 25 years. Many states have waited a decade or more since last raising their own gas tax rates.

States are putting evidence into practice with multiple efforts to improve services and tax codes through more progressive taxes on the wealthy. Clear evidence has spread widely this year, informing a national conversation about progressive taxation and leading lawmakers in multiple states to eschew supply-side superstition and act on real evidence instead. Taxing the rich works, and in this Just Taxes blog we review state-level efforts to put these proven findings into effect.

Like certain recent controversially concluded television shows, tax and budget debates can end in many ways and often receive mixed reviews. Illinois leaders, for example, ended on a cliffhanger by approving a historic constitutional amendment to create a graduated income tax in the state, whose ultimate conclusion will be crowdsourced by voters next November. Arizona’s fiscal finale fell flat with many observers due to corner-cutting on needed investments and a heavy focus on tax cuts. Texas legislators went for crowd-pleasing property tax cuts and school funding increases but left a gigantic “but how will we pay for this” plot hole…
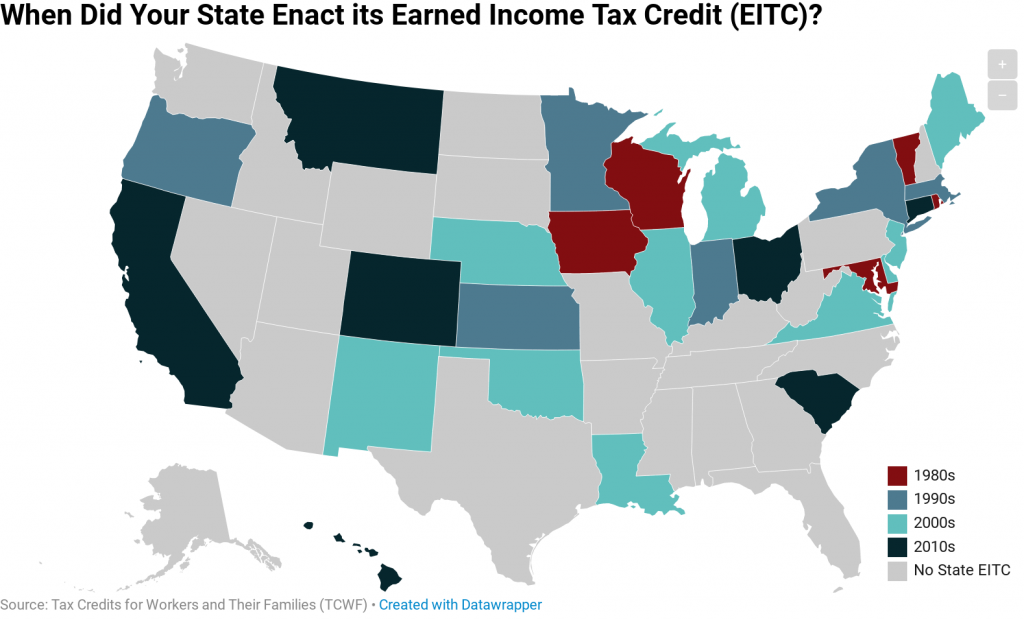
In 1986, Rhode Island became the first state to enact a tax credit patterned after the federal Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC). Since then, EITCs have become increasingly widespread at the state level with 28 states and the District of Columbia now offering them. These credits are designed to improve family economic security by bolstering […]
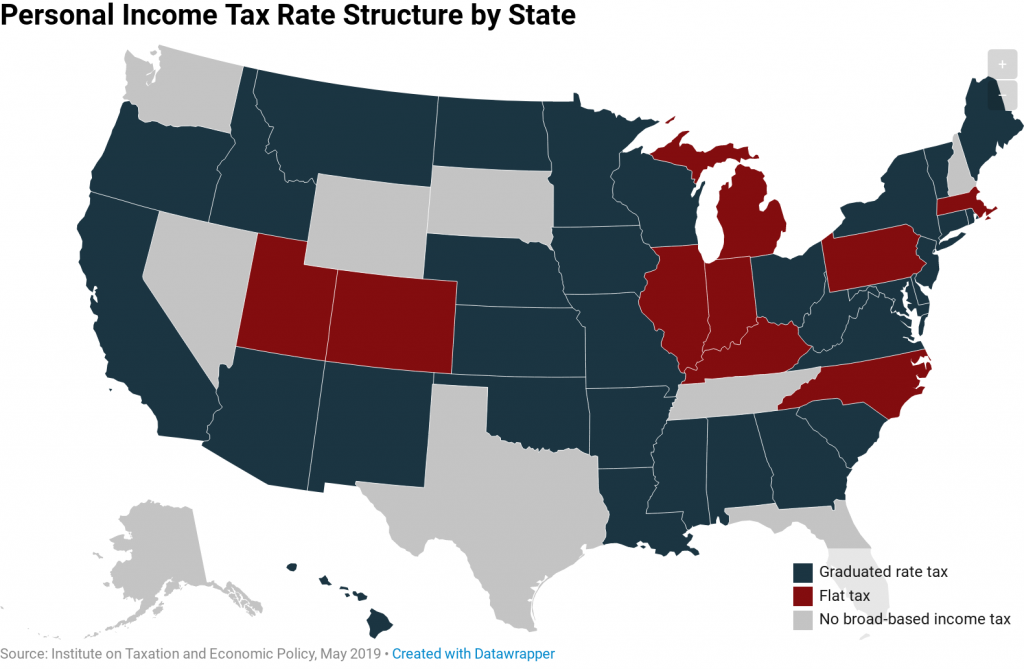
One of the most important decisions that must be made when designing a state personal income tax is whether to charge taxpayers a single flat rate on all their taxable income, or whether to levy a series of graduated rates that ask more of high-income taxpayers
State Rundown 5/22: (Some) State Lawmakers Can (Partly) Relax This Weekend
May 22, 2019 • By ITEP Staff

Lawmakers and advocates can enjoy their barbeques with only one eye on their work email this weekend in states that have essentially finished their budget debates such as Alaska, Minnesota, Nebraska, and Oklahoma, though both Alaska and Minnesota require special sessions to wrap things up. Getting to those barbeques may be a bumpy ride in Louisiana, Michigan, and other states still working to modernize outdated and inadequate gas taxes.
