
EITC
Boosting Incomes and Improving Tax Equity with State Earned Income Tax Credits in 2022
September 15, 2022 • By Aidan Davis
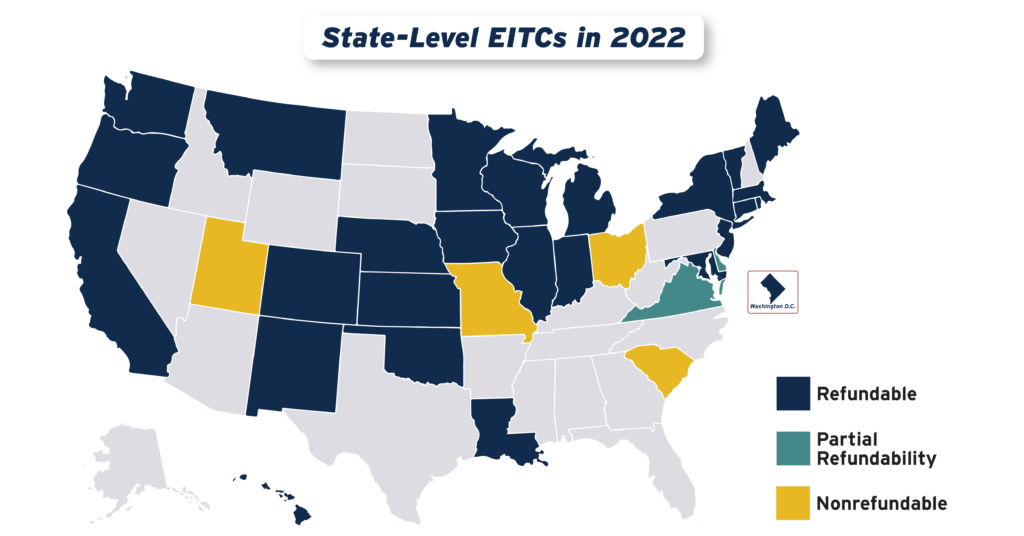
States continued their recent trend of advancing EITCs in 2022, with nine states plus the District of Columbia either creating or improving their credits. Utah enacted a 15 percent nonrefundable EITC, while the District of Columbia, Hawaii, Illinois, Maine, Vermont and Virginia expanded existing credits. Meanwhile, Connecticut, New York and Oregon provided one-time boosts to their EITC-eligible populations.
Legislative Momentum in 2022: New and Expanded Child Tax Credits and EITCs
July 22, 2022 • By Neva Butkus
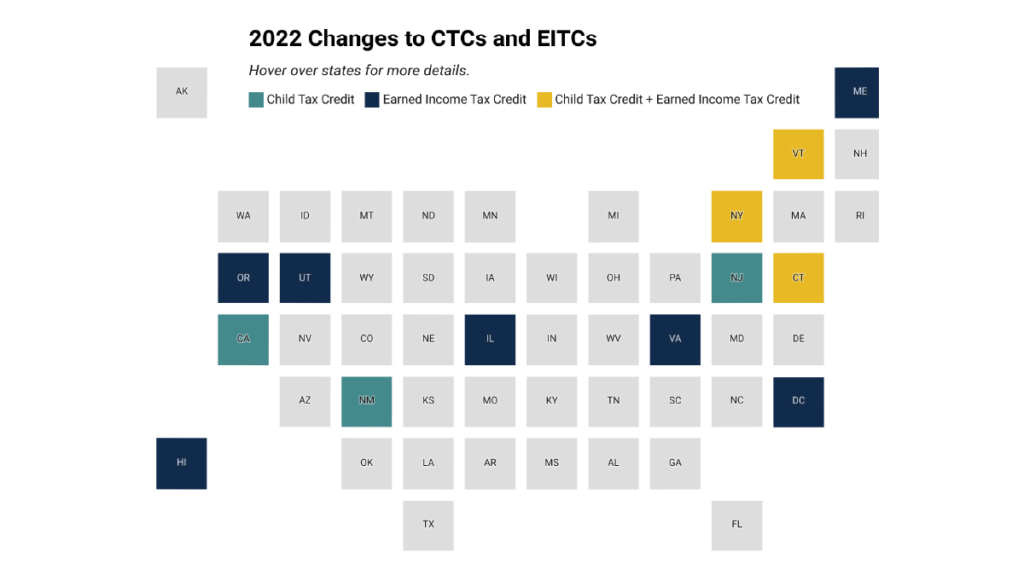
State legislatures across the country made investments in their future, centering children, families, and workers by enacting and expanding state Earned Income Tax Credits (EITCs), Child Tax Credits (CTCs), and other refundable credits this session. In total, seven states either expanded or created CTCs this session. Connecticut, New Mexico, New Jersey, Rhode Island and Vermont […]
Abortion-Restricting States Do Least for Children
July 13, 2022 • By Amy Hanauer

Lawmakers have passed laws in 22 states that either immediately or soon will greatly restrict women’s rights to decide whether and when to have children. These states have some of the worst tax, spending and labor market policies for families in the U.S.
Women’s History Month is a Reminder that Sensible Tax Policy is Central to Women’s Economic Security
March 24, 2022 • By Brakeyshia Samms

Women’s History Month is a chance to remember what happens for women when tax policy becomes more progressive, boosts income, and helps make raising a family more affordable.
What We Can Learn Today from the American Rescue Plan – and Sen. Rick Scott’s Proposed Tax Increases
March 11, 2022 • By Steve Wamhoff

The success of the American Rescue Plan Act is worth revisiting today. Instead of pursuing Sen. Rick Scott’s agenda of making life more difficult for those already working the hardest, Congress should extend or make permanent some of the beneficial policies in ARPA.
More Than One in Three Young Workers Would Benefit from EITC Reforms in Build Back Better Plan
February 8, 2022 • By Aidan Davis

Although the EITC expansion did not receive as much attention as the expanded Child Tax Credit, a new ITEP report shows the positive impact of allowing young workers without children in the home to maintain access to one of the nation’s most significant and effective anti-poverty programs.
Federal EITC Enhancements Help More Than One in Three Young Workers
February 8, 2022 • By Aidan Davis

More than one in three young adults would benefit from workers without children being eligible to receive the federal EITC. This policy change would bolster young adults’ economic security.
Pandemic Policies Demonstrate Government Can Address Widening Economic Inequality If Policymakers So Choose
December 17, 2021 • By ITEP Staff, Jenice Robinson, Joe Hughes

We are surrounded by evidence that economic inequality is spinning out of control, yet we also see straightforward examples of how government can stop the downward spiral should it choose to do so. The Build Back Better Act, which invests in communities and ensures the wealthy and corporations pay their fair share, is one such example. Congress should pass it.
ITEP Data on Child Tax Credit and Earned Income Tax Credit Provisions Before Congress
December 14, 2021 • By Steve Wamhoff

Congress expanded the Child Tax Credit (CTC) and Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) for 2021 as part of the American Rescue Plan Act (ARP). The additional benefits that millions of families and workers received under that law will end this month if Congress does not act soon. The CTC expansion boosted the annual tax credit […]
Tax Credit Reforms in Build Back Better Would Benefit a Diverse Group of Families
November 18, 2021 • By Aidan Davis

The CTC and EITC provisions would have a particularly profound effect on the poorest 20 percent of Americans, who all will have incomes of less than $22,000 in 2022. Taken together, the EITC and CTC changes would lift the average income of these households by more than 10 percent.
Boosting Incomes and Improving Tax Equity with State Earned Income Tax Credits in 2021
October 21, 2021 • By Aidan Davis

The EITC benefits low-income people of all races and ethnicities. But it is particularly impactful in historically excluded Black and Hispanic communities where discrimination in the labor market, inequitable educational systems, and countless other inequities have relegated a disproportionate share of people to low-wage jobs.
New Census Data Highlight Need for Permanent Child Tax Credit Expansion
September 14, 2021 • By Neva Butkus

The status quo was a choice, but the Census data released today shows that different policy choices can create drastically different outcomes for children and families. It is time for our state and federal legislators to put people first when it comes to recovery.
Extending Federal EITC Enhancements Would Bolster the Effects of State-Level Credits
September 13, 2021 • By Aidan Davis

The EITC expansion targets workers without children in the home. In 2022 it would provide a $12.4 billion boost, benefiting 19.5 million workers who on average would receive an income boost of $730 dollars.

A growing group of state lawmakers are recognizing the extent to which low- and middle-income Americans are struggling and the ways in which their state and local tax systems can do more to ensure the economic security of their residents over the long run. To that end, lawmakers across the country have made strides in enacting, increasing, or expanding tax credits that benefit low- and middle-income families. Here is a summary of those changes and a celebration of those successes.
Nearly 20 Million Will Benefit if Congress Makes the EITC Enhancement Permanent
May 13, 2021 • By Aidan Davis

Overall, the EITC enhancement would provide a $12.4 billion boost in 2022 if made permanent, benefiting 19.5 million workers. It would have a particularly meaningful impact on the bottom 20 percent of eligible households who would receive more than three-fourths of the total benefit. Forty-one percent of households in the bottom 20 percent of earners would benefit, receiving an average income boost of 6.3 percent, or $740 dollars.

Young workers are confronting a harsh economic reality filled with student loan debt and far too few good-paying jobs. The pandemic reinforced this group’s long history of not receiving proper benefits, such as health insurance, from their employers. They also are often overlooked when it comes to policies that promote economic wellbeing. The federal Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC), for example, is a glowing success story. It lifted 5.8 million people out of poverty in 2018, including 3 million children. But a key shortcoming of the federal EITC: working adults without children in the home receive little to no benefit.

While the federal EITC provides a great deal of support for families with children, its impact is limited for those without children or who are not raising children in their homes. Childless workers under 25 and over 64 have for far too long received no benefit from the federal credit. And workers aged 25 to 64 have received very little value from the existing credit (the maximum credit is much smaller and the income limits more restrictive). The federal EITC’s meager benefits for just some childless adults lead to an inequitable outcome: the federal income tax system—which is ostensibly based…
These EITC Reforms Would Help Struggling Families Now and Address Systemic Challenges
December 4, 2020 • By Aidan Davis

The tepid economic recovery is leaving millions behind. The nation still has nearly 10 million jobs less than it did in February, according to the latest jobs report. The number of people living in or near poverty is rising. Twelve million workers are about to lose their unemployment insurance, roughly four in 10 people report experiencing food insecurity for the first time, and conditions are likely to deteriorate further in the weeks ahead as we brace for another deadly surge in COVID cases and new or tightened restrictions on business and personal activity.
