
Texas
How the Revised Senate Tax Bill Would Affect Texas Residents’ Federal Taxes
November 14, 2017 • By ITEP Staff
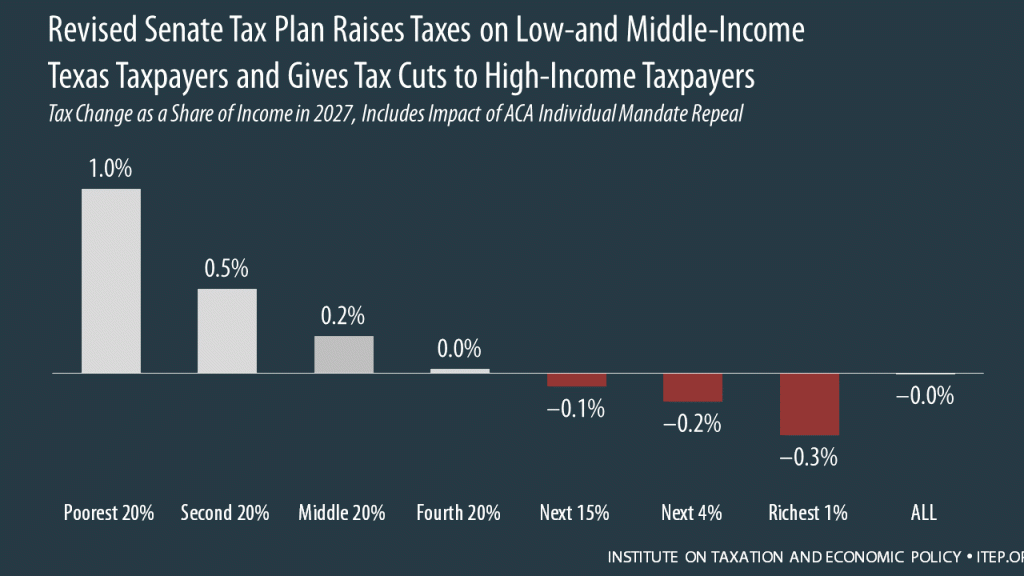
The Senate tax bill released last week would raise taxes on some families while bestowing immense benefits on wealthy Americans and foreign investors. In Texas, 54 percent of the federal tax cuts would go to the richest 5 percent of residents, and 8 percent of households would face a tax increase, once the bill is fully implemented.
Analysis of the House Tax Cuts and Jobs Act
November 6, 2017 • By Matthew Gardner, Meg Wiehe, Steve Wamhoff
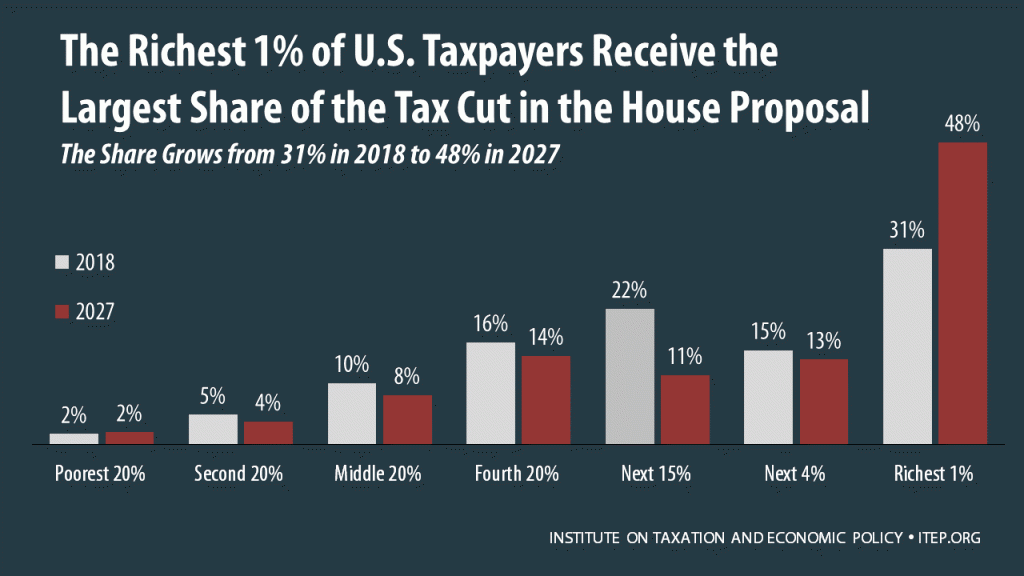
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, which was introduced on Nov. 2 in the House of Representatives, would raise taxes on some Americans and cut taxes on others while also providing significant savings to foreign investors.
How the House Tax Proposal Would Affect Texas Residents’ Federal Taxes
November 6, 2017 • By ITEP Staff
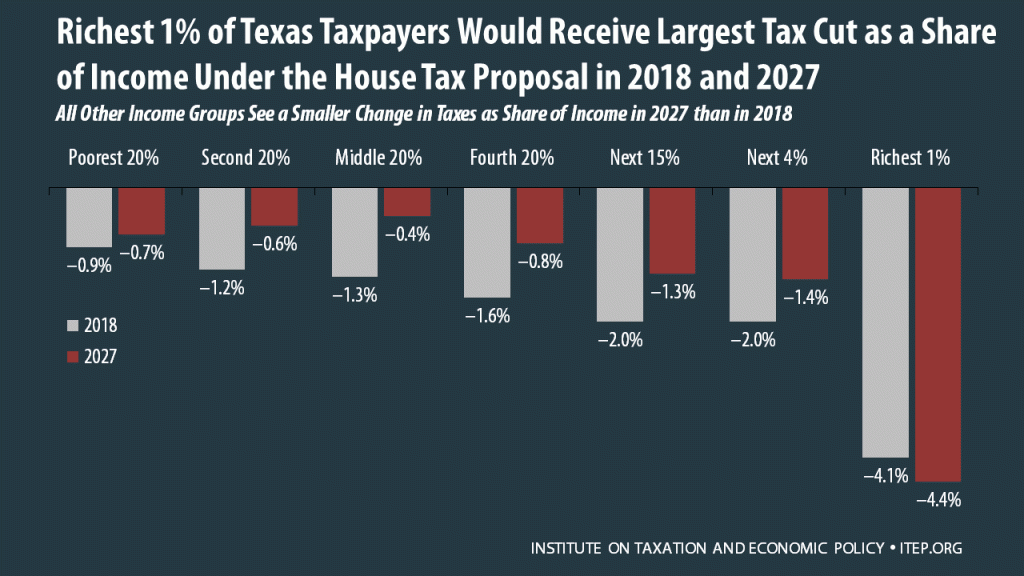
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, which was introduced on November 2 in the House of Representatives, includes some provisions that raise taxes and some that cut taxes, so the net effect for any particular family’s federal tax bill depends on their situation. Some of the provisions that benefit the middle class — like lower tax rates, an increased standard deduction, and a $300 tax credit for each adult in a household — are designed to expire or become less generous over time. Some of the provisions that benefit the wealthy, such as the reduction and eventual repeal of the estate…
International Business Times: Do Lower Taxes Spur Economic Growth? What Happened In No-Tax States
October 26, 2017
Researchers at the non-partisan and non-profit Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy compared the nine states without personal income taxes, which include Florida, Texas and Washington, to the nine states with the highest top marginal tax rates over the last decade, which include California, New York and Oregon. They found the states with the highest […]
Trickle-Down Dries Up: States without personal income taxes lag behind states with the highest top tax rates
October 26, 2017 • By Carl Davis, Nick Buffie

Lawmakers who support reducing or eliminating state personal income taxes typically claim that doing so will spur economic growth. Often, this claim is accompanied by the assertion that states without income taxes are booming, and that their success could be replicated by any state that abandons its income tax. To help evaluate these arguments, this study compares the economic performance of the nine states without broad-based personal income taxes to their mirror opposites—the nine states levying the highest top marginal personal income tax rates throughout the last decade.
The Jig Is Up: Republican Budget Resolution Finally Admits That Deficit Will Soar Under GOP Tax Plan
October 20, 2017 • By Alan Essig

For some lawmakers, annual deficits matter a lot—unless the nation is paying for tax cuts for the wealthy via deficit spending. Last night, Republican lawmakers demonstrated that previous grandstanding about the nation’s debt is much ado about nothing. The Senate approved a budget resolution on a party-line vote that would 1. fast-track legislation adding $1.5 trillion to the deficit over 10 years by cutting taxes, and 2. make it easy to enact this measure without a single Democratic vote.
State Rundown 10/4: Wildfires in Montana and Tax Cuts in Kansas Wreak Budget Havoc
October 4, 2017 • By ITEP Staff

This week, Kansas's school funding was again ruled unconstitutionally low and unfair, while Montana lawmakers indicated they'd rather let historic wildfires burn a hole through their budget than raise revenues to meet their funding needs. Meanwhile, a struggling agricultural sector continues to cause problems for Iowa and Nebraska, but legalized recreational marijuana is bringing good economic news to both California and Nevada.
Benefits of GOP-Trump Framework Tilted Toward the Richest Taxpayers in Each State
October 4, 2017 • By Steve Wamhoff
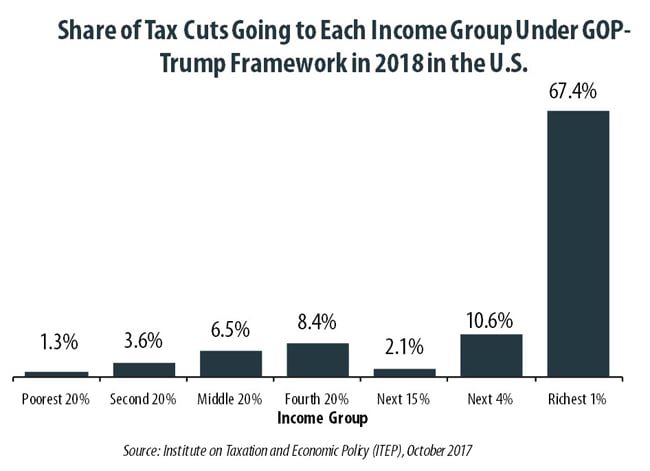
The “tax reform framework” released by the Trump administration and Congressional Republican leaders on September 27 would affect states differently, but every state would see its richest residents grow richer if it is enacted. In all but a handful of states, at least half of the tax cuts would flow to the richest one percent of residents if the framework took effect.
GOP-Trump Tax Framework Would Provide Richest One Percent in Texas with 64.4 Percent of the State’s Tax Cuts
October 4, 2017 • By ITEP Staff
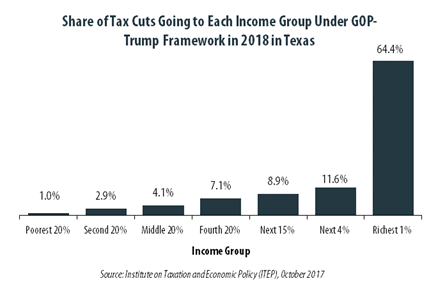
The “tax reform framework” released by the Trump administration and congressional Republican leaders on September 27 would not benefit everyone in Texas equally. The richest one percent of Texas residents would receive 64.4 percent of the tax cuts within the state under the framework in 2018. These households are projected to have an income of at least $696,400 next year. The framework would provide them an average tax cut of $119,040 in 2018, which would increase their income by an average of 5.9 percent.
Dallas Fed: Texas Taxes: Who Bears the Burden?
September 26, 2017
...Overall, the state’s tax system is less equal across income quintiles than the national average. A key reason is the state’s reliance on the sales tax, which as a share of income is 8.6 percent for those in the bottom quintile but only 2.2 percent in the top quintile...
Astonishingly, tax policies in virtually every state make it harder for those living in poverty to make ends meet. When all the taxes imposed by state and local governments are taken into account, every state imposes higher effective tax rates on poor families than on the richest taxpayers.
State Rundown 9/13: The Year of Unprecedented State Budget Impasses Continues
September 13, 2017 • By ITEP Staff

This week, Pennsylvania lawmakers risk defaulting on payments due to their extremely overdue budget and Illinois legislators will borrow billions to start paying their backlog of unpaid bills. Governing delves into why there were more such budget impasses this year than in any year in recent memory. And Oklahoma got closure from its Supreme Court on whether closing special tax exemptions counts as "raising taxes" (it doesn't).
Houston Chronicle: Should Low-Tax Texas Have to Shoulder More of Harvey’s Load?
September 8, 2017
Right now, although Texas is a low-tax state overall, that tax burden falls disproportionately on poor people. High property and sales taxes and the absence of an income tax means that folks in the lowest 20 percent of the income spectrum pay 12.5 percent of their earnings in state and local taxes, the seventh highest […]
San Antonio Express News: News of DACA’s End Hits South Texas Immigrants
September 6, 2017
Immigration activists noted that DACA recipients pay $2 billion a year in state and local taxes, including $300 million in Texas, according to a report by the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy. Read more
State Rundown 8/23: Few Lingering Budget Debates Cannot Linger Much Longer
August 23, 2017 • By ITEP Staff

This week, Oklahoma lawmakers learned they'll need to enter a special session to balance their budget and that they'll likely face a lawsuit over their low funding of public education. Pennsylvania's budget stalemate is also coming to a head as the state literally runs out of funds to pay its bills. And Amazon's tax practices are in the news again as the company has been sued in South Carolina.
In Texas 51.6 Percent of Trump’s Proposed Tax Cuts Go to People Making More than $1 Million
August 17, 2017 • By ITEP Staff
A tiny fraction of the Texas population (0.3 percent) earns more than $1 million annually. But this elite group would receive 51.6 percent of the tax cuts that go to Texas residents under the tax proposals from the Trump administration. A much larger group, 46.2 percent of the state, earns less than $45,000, but would receive just 3.7 percent of the tax cuts.
Nearly Half of Trump’s Proposed Tax Cuts Go to People Making More than $1 Million Annually
August 17, 2017 • By ITEP Staff
A tiny fraction of the U.S. population (one-half of one percent) earns more than $1 million annually. But in 2018 this elite group would receive 48.8 percent of the tax cuts proposed by the Trump administration. A much larger group, 44.6 percent of Americans, earn less than $45,000, but would receive just 4.4 percent of the tax cuts.

This week, Rhode Island lawmakers agreed on a budget, leaving only three states – Connecticut, Pennsylvania, and Wisconsin – without complete budgets. Texas, however, remains in special session and West Virginia could go back into another special session over tax issues. And in New York City, the mayor proposes a tax on the wealthy to […]
Houston Chronicle: Sanctuary Cities Law Could Cost Texas Billions
August 1, 2017
An analysis of data from the U.S. Census, the Bureau of Economic Analysis and the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy found that if 10 percent of undocumented immigrants leave Texas, the state would forfeit about $190.7 million in federal tax revenue and $223.5 million more in state and local taxes. The disappearance of those […]
State Rundown 7/27: State Legislative Debates Winding Down but Tax Talk Continues
July 27, 2017 • By ITEP Staff

While only a few states still remain mired in overtime budget debates, there is plenty of budget and tax news from around the country this week. Efforts are underway to repeal gas tax increases in California and challenge a local income tax in Seattle, Washington. And New Jersey legislators' law to modernize its tax code to tax Airbnb rentals has been vetoed for now.

2017 marked a sea change in state tax policy and a stark departure from the current federal tax debate as dubious supply-side economic theories began to lose their grip on statehouses. Compared to the predominant trend in recent years of emphasizing top-heavy income tax cuts and shifting to more regressive consumption taxes in the hopes […]
50-State Analysis of Trump’s Tax Outline: Poorer Taxpayers and Poorer States are Disadvantaged
July 20, 2017 • By Alan Essig
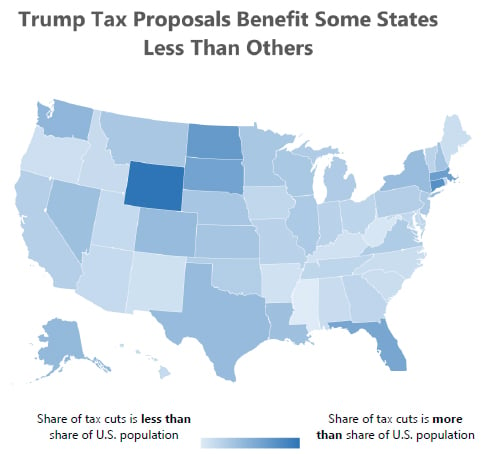
Not only would President Trump’s proposed tax plan fail to deliver on its promise of largely helping middle-class taxpayers, it also would shower a disproportionate share of the total tax cut on taxpayers in some of the richest states while southern and a few other states would receive a smaller share of the tax cut […]
Trump Tax Proposals Would Provide Richest One Percent in Texas with 59.3 Percent of the State’s Tax Cuts
July 20, 2017 • By ITEP Staff
Earlier this year, the Trump administration released some broadly outlined proposals to overhaul the federal tax code. Households in Texas would not benefit equally from these proposals. The richest one percent of the state’s taxpayers are projected to make an average income of $2,019,900 in 2018.
Trump’s $4.8 Trillion Tax Proposals Would Not Benefit All States or Taxpayers Equally
July 20, 2017 • By Matthew Gardner, Steve Wamhoff
The broadly outlined tax proposals released by the Trump administration would not benefit all taxpayers equally and they would not benefit all states equally either. Several states would receive a share of the total resulting tax cuts that is less than their share of the U.S. population. Of the dozen states receiving the least by this measure, seven are in the South. The others are New Mexico, Oregon, Maine, Idaho and Hawaii.
State Rundown 7/19: Handful of States Still Have Their Hands Full with Tax and Budget Debates
July 19, 2017 • By ITEP Staff

Tax and budget debates drag on in several states this week, as lawmakers continue to work in Alaska, Connecticut, Rhode Island, Pennsylvania, Texas, and Wisconsin. And a showdown is brewing in Kentucky between a regressive tax shift effort and a progressive tax reform plan. Be sure to also check out our "What We're Reading" section for a historical perspective on federal tax reform, a podcast on lessons learned from Kansas and California, and more!
