
Utah
House Tax Bill Would Put Property Tax Deduction Out of Reach for Most Households
November 13, 2017 • By ITEP Staff

The House of Representatives is expected to vote this week on a bill that would reduce federal revenues by roughly $1.5 trillion over the next decade. Despite the bill’s high price tag, many households would pay more in federal tax if the bill is enacted, in large part because it slashes the deduction for state […]
Analysis of the House Tax Cuts and Jobs Act
November 6, 2017 • By Matthew Gardner, Meg Wiehe, Steve Wamhoff
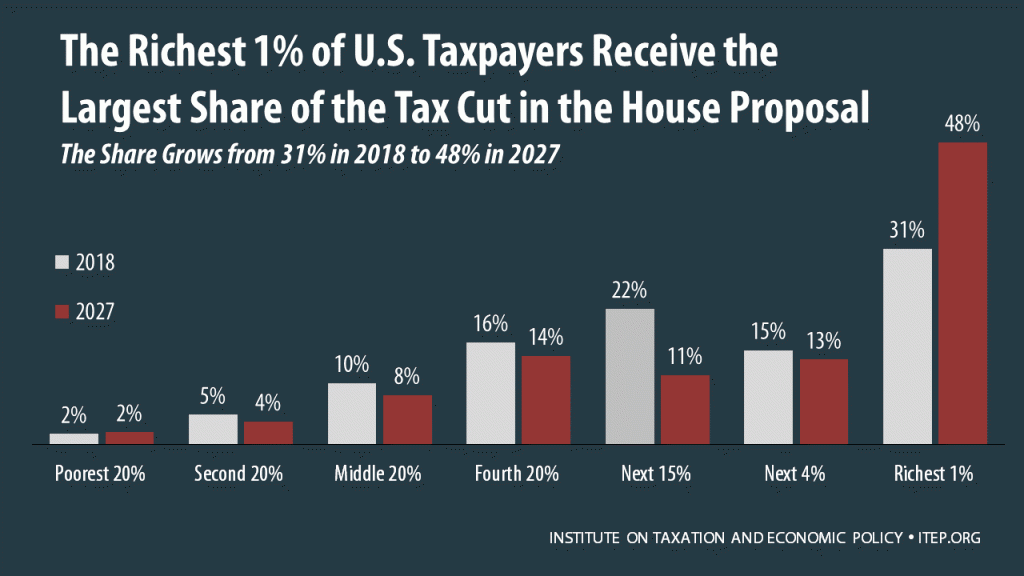
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, which was introduced on Nov. 2 in the House of Representatives, would raise taxes on some Americans and cut taxes on others while also providing significant savings to foreign investors.
How the House Tax Proposal Would Affect Utah Residents’ Federal Taxes
November 6, 2017 • By ITEP Staff
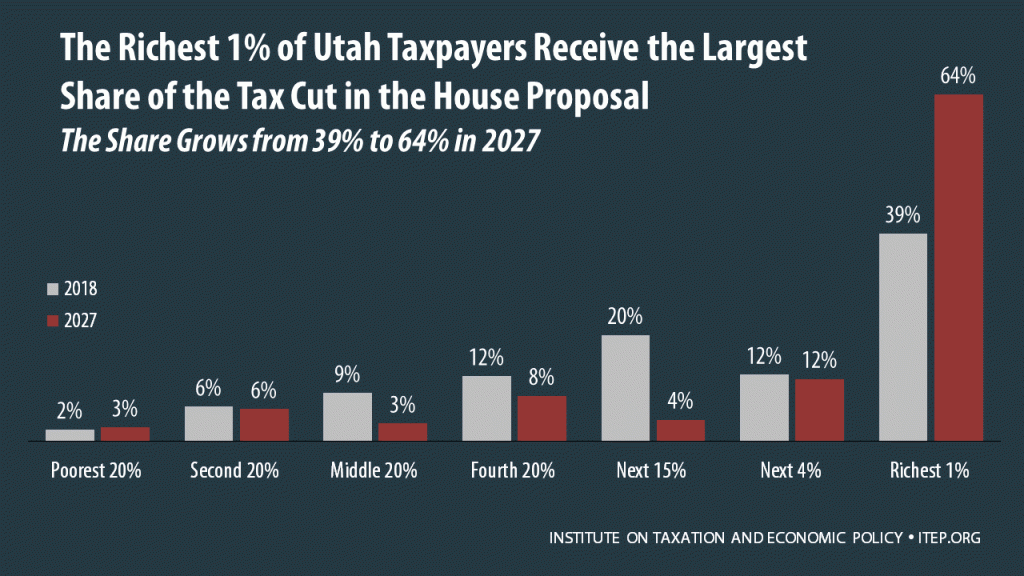
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, which was introduced on November 2 in the House of Representatives, includes some provisions that raise taxes and some that cut taxes, so the net effect for any particular family’s federal tax bill depends on their situation. Some of the provisions that benefit the middle class — like lower tax rates, an increased standard deduction, and a $300 tax credit for each adult in a household — are designed to expire or become less generous over time. Some of the provisions that benefit the wealthy, such as the reduction and eventual repeal of the estate…
Trickle-Down Dries Up: States without personal income taxes lag behind states with the highest top tax rates
October 26, 2017 • By Carl Davis, Nick Buffie

Lawmakers who support reducing or eliminating state personal income taxes typically claim that doing so will spur economic growth. Often, this claim is accompanied by the assertion that states without income taxes are booming, and that their success could be replicated by any state that abandons its income tax. To help evaluate these arguments, this study compares the economic performance of the nine states without broad-based personal income taxes to their mirror opposites—the nine states levying the highest top marginal personal income tax rates throughout the last decade.
State Rundown 10/25: Marijuana Taxes a Bright Spot amid Underperforming State Revenues
October 25, 2017 • By ITEP Staff

This week in state tax news saw Alaska begin yet another special session, Louisiana lawmakers holding meetings to begin preparing for the state’s looming (self-imposed) fiscal cliff, and Alabama policymakers beginning a study of school finance (in)adequacy and (in)equity. Meanwhile, state revenue performance is poor well into 2017 in many states, though Montana, Nevada, and Oregon are all enjoying modest but welcome revenue bumps from legalized marijuana.
The Jig Is Up: Republican Budget Resolution Finally Admits That Deficit Will Soar Under GOP Tax Plan
October 20, 2017 • By Alan Essig

For some lawmakers, annual deficits matter a lot—unless the nation is paying for tax cuts for the wealthy via deficit spending. Last night, Republican lawmakers demonstrated that previous grandstanding about the nation’s debt is much ado about nothing. The Senate approved a budget resolution on a party-line vote that would 1. fast-track legislation adding $1.5 trillion to the deficit over 10 years by cutting taxes, and 2. make it easy to enact this measure without a single Democratic vote.
State Rundown 10/18: Ballot Initiative Efforts Being Finalized
October 18, 2017 • By ITEP Staff

Ballot initiatives relating to taxes made news around the country this week, with Oregon voters to consider reversing new health care taxes, Washingtonians to vote on improving education funding, and Nebraskans to potentially vote on a state tax credit for school property taxes. Meanwhile, multiple states are finalizing their proposals to lure Amazon to build a new headquarters in their state, often through the use of massive tax subsidies. And in our "What We're Reading" section we have sobering news from Moody's Investors Service on states' struggles to fund their infrastructure and save for the next recession.
Bloomberg: GOP Tax Plan Seen Hurting Middle Class in N.Y., 8 Other States
October 5, 2017 • By ITEP Staff
The ITEP report concludes that many of the most affected people would be middle-income and upper-middle income taxpayers. For example, in Maryland, about one-third of those making from $48,700 to $73,700 would face a tax hike, while 41 percent of those between $73,700 and $126,500, would face an increase, the study says. And almost 65 […]
50-State Analysis: GOP-Trump Tax Proposal Would Give the Store Away to the Wealthy, Exacerbate the Income Divide
October 4, 2017 • By Alan Essig
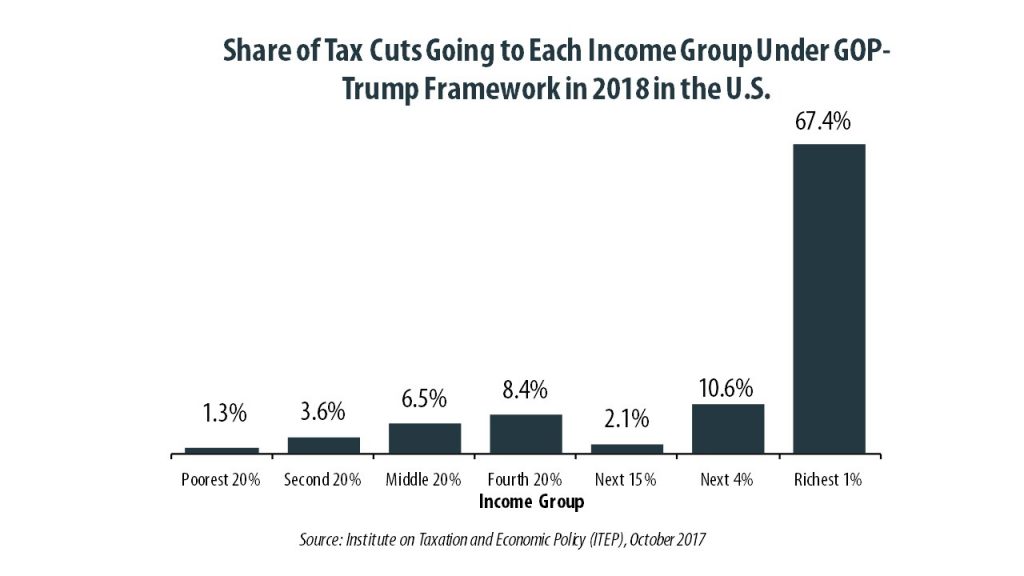
A 50-state analysis of the GOP tax framework reveals the top 1 percent of taxpayers would receive a substantial tax cut while middle- and upper-middle-income taxpayers in many states would pay more, the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy said today. The GOP continues to tout its tax plan as “beneficial to the middle class.” […]
Benefits of GOP-Trump Framework Tilted Toward the Richest Taxpayers in Each State
October 4, 2017 • By Steve Wamhoff
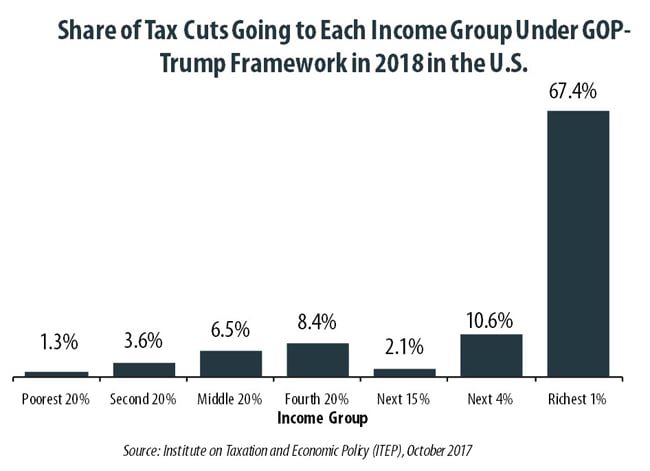
The “tax reform framework” released by the Trump administration and Congressional Republican leaders on September 27 would affect states differently, but every state would see its richest residents grow richer if it is enacted. In all but a handful of states, at least half of the tax cuts would flow to the richest one percent of residents if the framework took effect.
GOP-Trump Tax Framework Would Provide Richest One Percent in Utah with 78.9 Percent of the State’s Tax Cuts
October 4, 2017 • By ITEP Staff
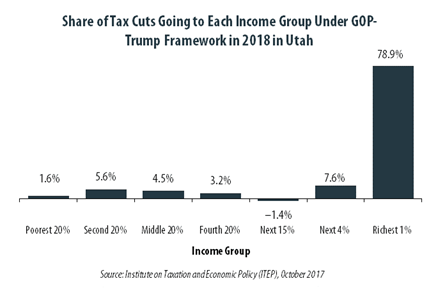
The “tax reform framework” released by the Trump administration and congressional Republican leaders on September 27 would not benefit everyone in Utah equally. The richest one percent of Utah residents would receive 78.9 percent of the tax cuts within the state under the framework in 2018. These households are projected to have an income of at least $545,500 next year. The framework would provide them an average tax cut of $82,990 in 2018, which would increase their income by an average of 5.3 percent.
State Rundown 9/13: The Year of Unprecedented State Budget Impasses Continues
September 13, 2017 • By ITEP Staff

This week, Pennsylvania lawmakers risk defaulting on payments due to their extremely overdue budget and Illinois legislators will borrow billions to start paying their backlog of unpaid bills. Governing delves into why there were more such budget impasses this year than in any year in recent memory. And Oklahoma got closure from its Supreme Court on whether closing special tax exemptions counts as "raising taxes" (it doesn't).
In Utah 41.9 Percent of Trump’s Proposed Tax Cuts Go to People Making More than $1 Million
August 17, 2017 • By ITEP Staff
A tiny fraction of the Utah population (0.3 percent) earns more than $1 million annually. But this elite group would receive 41.9 percent of the tax cuts that go to Utah residents under the tax proposals from the Trump administration. A much larger group, 41.0 percent of the state, earns less than $45,000, but would receive just 5.3 percent of the tax cuts.
Nearly Half of Trump’s Proposed Tax Cuts Go to People Making More than $1 Million Annually
August 17, 2017 • By ITEP Staff
A tiny fraction of the U.S. population (one-half of one percent) earns more than $1 million annually. But in 2018 this elite group would receive 48.8 percent of the tax cuts proposed by the Trump administration. A much larger group, 44.6 percent of Americans, earn less than $45,000, but would receive just 4.4 percent of the tax cuts.
State Rundown 8/2: Legislative Tax Debates Wind Down as Ballot Initiative Efforts Ramp Up
August 2, 2017 • By ITEP Staff

Budget deliberations continue in earnest this week in Alaska, Connecticut, Pennsylvania, and Rhode Island. In South Dakota and Utah, the focus is on gearing up for ballot initiative efforts to raise needed revenue, though be sure to read about legislators nullifying voter-approved initiatives in Maine and elsewhere in our "what we're reading" section.
Utah Public News Service: Trump’s Economic Policies to Increase Economic Inequality
July 31, 2017
The Trump administration’s tax proposals would not benefit all taxpayers or states equally, according to new analysis from the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy. Matt Gardner, a senior fellow with the institute, says the richest 1 percent of taxpayers would receive more than 60 percent of the tax benefits. He adds that poorer states, largely […]

2017 marked a sea change in state tax policy and a stark departure from the current federal tax debate as dubious supply-side economic theories began to lose their grip on statehouses. Compared to the predominant trend in recent years of emphasizing top-heavy income tax cuts and shifting to more regressive consumption taxes in the hopes […]
Trump Tax Proposals Would Provide Richest One Percent in Utah with 65.5 Percent of the State’s Tax Cuts
July 20, 2017 • By ITEP Staff
Earlier this year, the Trump administration released some broadly outlined proposals to overhaul the federal tax code. Households in Utah would not benefit equally from these proposals. The richest one percent of the state’s taxpayers are projected to make an average income of $1,573,600 in 2018.
Trump’s $4.8 Trillion Tax Proposals Would Not Benefit All States or Taxpayers Equally
July 20, 2017 • By Matthew Gardner, Steve Wamhoff
The broadly outlined tax proposals released by the Trump administration would not benefit all taxpayers equally and they would not benefit all states equally either. Several states would receive a share of the total resulting tax cuts that is less than their share of the U.S. population. Of the dozen states receiving the least by this measure, seven are in the South. The others are New Mexico, Oregon, Maine, Idaho and Hawaii.
State Rundown 7/19: Handful of States Still Have Their Hands Full with Tax and Budget Debates
July 19, 2017 • By ITEP Staff

Tax and budget debates drag on in several states this week, as lawmakers continue to work in Alaska, Connecticut, Rhode Island, Pennsylvania, Texas, and Wisconsin. And a showdown is brewing in Kentucky between a regressive tax shift effort and a progressive tax reform plan. Be sure to also check out our "What We're Reading" section for a historical perspective on federal tax reform, a podcast on lessons learned from Kansas and California, and more!

The flawed design of federal and state gasoline taxes has made it exceedingly difficult to raise adequate funds to maintain the nation’s transportation infrastructure. Thirty states and the federal government levy fixed-rate gas taxes where the tax rate does not change even when the cost of infrastructure materials rises or when drivers transition toward more fuel-efficient vehicles and pay less in gas tax. The federal government’s 18.4 cent gas tax, for example, has not increased in over twenty-three years. Likewise, nineteen states have waited a decade or more since last raising their own gas tax rates.

This week, we celebrate a victory in Kansas where lawmakers rolled back Brownback's tax cuts for the richest taxpayers. Governors in West Virginia and Alaska promote compromise tax plans. Texas heads into special session and Vermont faces another budget veto, while Louisiana and New Mexico are on the verge of wrapping up. Voters in Massachusetts may soon be able to weigh in on a millionaire's tax, the California Senate passed single-payer health care, and more!
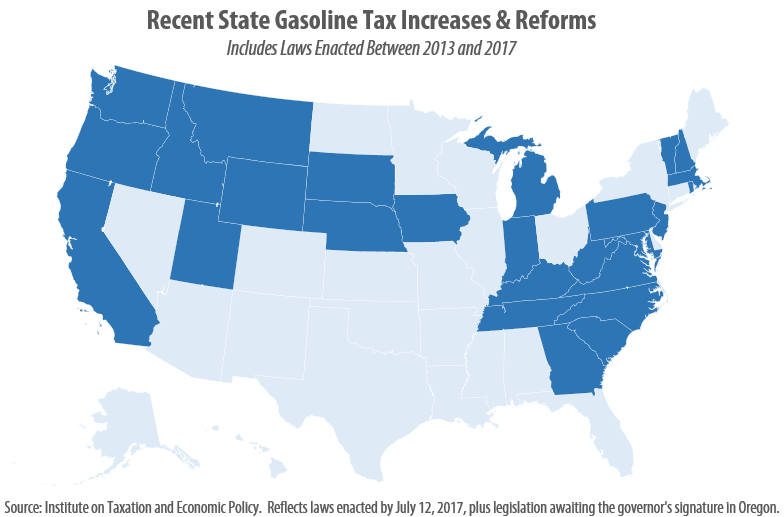
This post was updated July 12, 2017 to reflect recent gas tax increases in Oregon and West Virginia. As expected, 2017 has brought a flurry of action relating to state gasoline taxes. As of this writing, eight states (California, Indiana, Montana, Oregon, South Carolina, Tennessee, Utah, and West Virginia) have enacted gas tax increases this year, bringing the total number of states that have raised or reformed their gas taxes to 26 since 2013.
3 Percent and Dropping: State Corporate Tax Avoidance in the Fortune 500, 2008 to 2015
April 27, 2017 • By Aidan Davis, Matthew Gardner, Richard Phillips
The trend is clear: states are experiencing a rapid decline in state corporate income tax revenue. Despite rebounding and even booming bottom lines for many corporations, this downward trend has become increasingly apparent in recent years. Since our last analysis of these data, in 2014, the state effective corporate tax rate paid by profitable Fortune 500 corporations has declined, dropping from 3.1 percent to 2.9 percent of their U.S. profits. A number of factors are driving this decline, including: a race to the bottom by states providing significant “incentives” for specific companies to relocate or stay put; blatant manipulation of…
In the Tax Justice Digest we recap the latest reports, blog posts, and analyses from Citizens for Tax Justice and the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy. Here’s a rundown of what we’ve been working on lately. Corporations Offshore Cash Hoard Grows to $2.6 Trillion U.S. corporations now hold a record $2.6 trillion offshore, a […]
