
Blog
1308 posts
One Tax System for Most Americans, and a Second System for the Wealthiest
August 16, 2019 • By Matthew Gardner

Last year, the Walton family's fortune grew by $100 million a day. This level of wealth is particularly obscene in the context of the Walmart Corporation’s dark store strategy. The company works nationwide to reduce its property tax assessments, which, when successful, deprives local communities of revenue necessary to fund education, libraries, parks, public health and other services.
State Rundown 8/15: A Tax-Subsidy Cease-Fire in Kansas and Missouri
August 15, 2019 • By ITEP Staff

Over the last couple of weeks, leaders in Kansas and Missouri reached a historic agreement to stop giving away tax subsidies just to entice companies a couple of miles across their shared state line. Meanwhile, policymakers in Alaska resolved a stand-off over education funding...by cutting education funding slightly less. And California voters may be voting in 2020 on a stronger reform to the notoriously inequitable property tax effects of “Proposition 13.”
IRS’s SALT Workaround Regulations Should be Strengthened, Not Rejected
August 13, 2019 • By Carl Davis

Lawmakers are seeking to achieve a backdoor repeal of the $10,000 cap on deductions for state and local taxes paid (SALT) by invalidating recent IRS regulations that cracked down on schemes that let taxpayers dodge the cap. If successful, their efforts would drain tens of billions of dollars from federal coffers each year, with the vast majority of the benefits going to the nation’s wealthiest families.

Given how much more exclusively this deduction now benefits the highest-income households, its continued existence is hard to justify. Even when the credit was available to a larger swath of families, it was ineffective at promoting homeownership.
Taxing Offshore Profits and Domestic Profits Equally Could Curb Corporate Tax Dodging
August 9, 2019 • By Steve Wamhoff

In recent days, presidential candidates Sen. Kamala Harris and New York Mayor Bill DeBlasio have called for taxing corporate profits the same whether they are earned in the United States or abroad. These calls echo the position of Sen. Bernie Sanders, who has long had a proposal along these lines. As ITEP has explained, correcting […]
State and Local Cannabis Tax Revenue on Pace for $1.6 Billion in 2019
August 7, 2019 • By Carl Davis
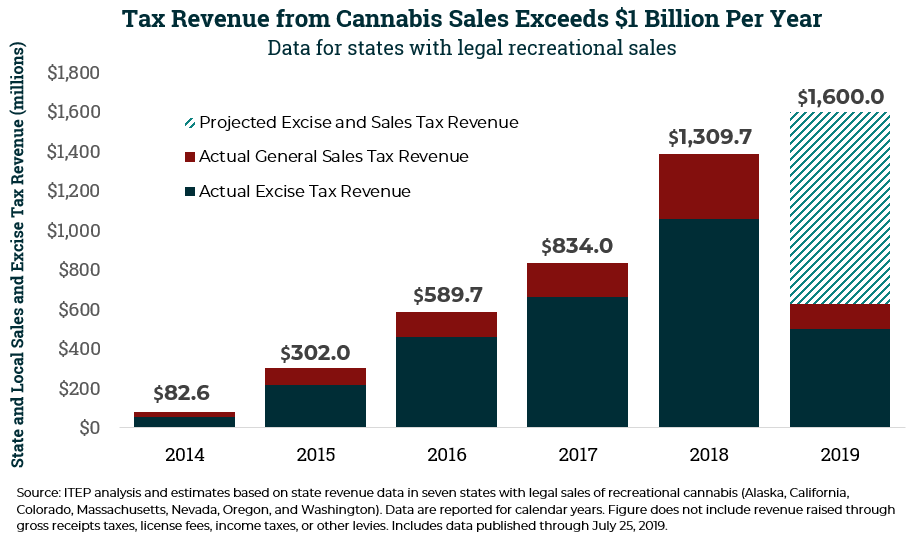
Cannabis tax revenue is becoming more significant as legal sales grow. The tax is far from a budgetary panacea, but an ITEP analysis of revenue data reported by the seven states with legal cannabis sales underway suggests that excise and sales tax revenues from the sale of the drug could reach $1.6 billion this year.
Opportunity Zones Have Nothing to Do with Reparations, Except …
August 2, 2019 • By Jenice Robinson

Among other things, this blog highlights how federal, state and local policies systematically work to reinforce the racial wealth gap by, for example, using the tax code to redistribute the nation’s wealth to billionaire developers and keeping low-income people of color in a perpetual cycle of debt through fines and fees to fund local governments. Opportunity zones and the top-heavy 2017 tax law are emblematic of a long history of policymaking that advantages wealthy white families.

A direct federal tax on wealth, as described in a January report from ITEP and proposed by Sen. Elizabeth Warren, could raise substantial revenue to make public investments, curb rising inequality, and is supported by a large majority of Americans. But would it work? Recent research highlighted in a new academic paper outlines approaches that would make it easier than you might think.

OHIO legislators passed a budget with unfortunate income tax cuts for high-income households. Other states turned their attention to unconventional ideas during their legislative off-seasons, for better and for worse. And there are many gems to be found in our “What We’re Reading” section below, including new research on the racial inequities that continue to pervade our communities and schools.

If a future Congress and president enact a real tax reform, one that requires corporations to pay their fair share and ends TCJA’s various corporate breaks for offshore profits, then companies will use inversions and other tactics to dodge taxes once again—if lawmakers let them. That’s why any real tax reform will include something like the Stop Corporate Inversions Act, introduced last week by Sens. Dick Durbin and Jack Reed to block inversions.
Many States Move Toward Higher Taxes on the Rich; Lower Taxes on Poor People
July 18, 2019 • By Meg Wiehe

Several states this year proposed or enacted tax policies that would require high-income households and/or businesses to pay more in taxes. After years of policymaking that slashed taxes for wealthy households and deprived states of revenue to adequately fund public services, this is a necessary and welcome reversal.
Follow the Money to See How Sales Tax Holidays Are Poor Policy
July 17, 2019 • By Dylan Grundman O'Neill

Sales tax holidays are wasteful, misguided policies that will drain more than $300 million of funding away from shared priorities like schools, roads, and health care this year in 16 states, while delivering little benefit to the families that could most use the help. Our newly updated brief reviews recent developments in sales tax holiday policy—including how online sales taxes are changing the picture—and explains why they are a misguided policy option for states. And the story below “follows the money” to show how sales tax holidays are a bad deal for families and communities alike.

We've said it before, and we'll say it again: states don't have to wait for federal lawmakers to make moves toward progressive tax policy. And so far, 2019 has been a good year for equitable and sustainable tax policy in the states. With July 1 marking the start of a new fiscal year for most states, this special edition of the Rundown looks at how discussions in 2019 have been dominated by plans to raise revenue for vital investments, tax the rich and corporations fairly, use the tax code to help workers and families and advance racial equity, and shore…
Missouri’s Creative Approach to Ending the “Race to the Bottom” in State Business Taxes
July 10, 2019 • By Matthew Gardner
Each year, state and local governments spend billions of dollars on targeted tax incentives—special tax breaks ostensibly designed to encourage businesses to relocate, expand or simply stay where they are. A law enacted by the Missouri legislature creates a template for states to work bilaterally to put the brakes on the “race to the bottom” in state business taxes.

Mercury is rising, presidential primary debates are underway and most state legislative sessions have adjourned for summer. Whether you’re curling up with a good book (or your favorite e-Reader) or looking for a new television show to binge-watch, check out these recommendations on ITEP’s Summer Reading (and Watching) List.
Gaps in Sales Tax Collection Linger at Amazon.com and Among Other E-Retailers
July 1, 2019 • By Carl Davis
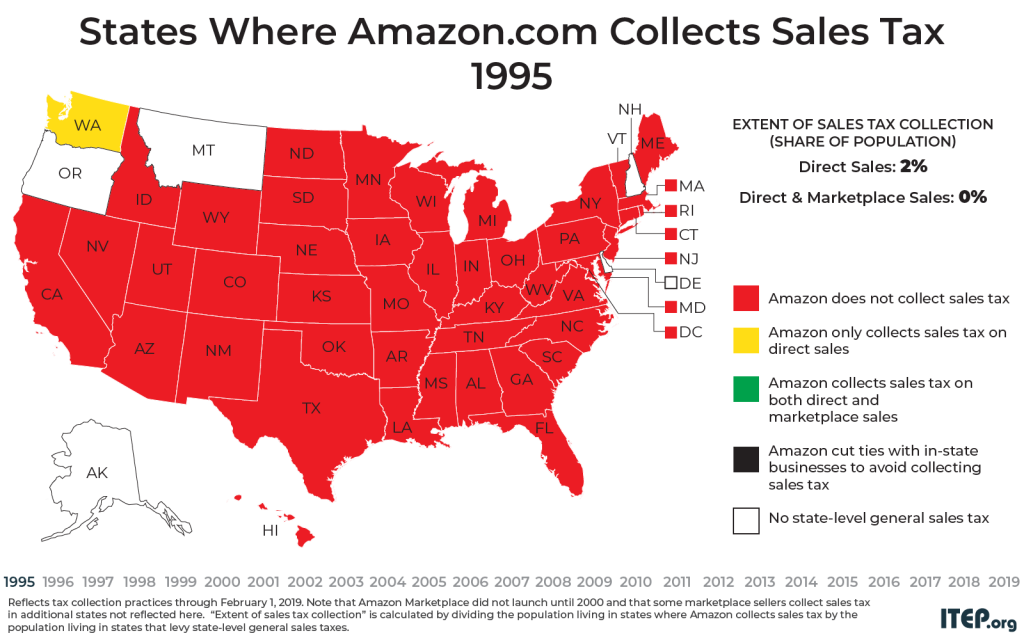
The last few years have brought big changes to sales tax collection for purchases made at Amazon.com and other e-retail websites. As recently as 2011, Amazon was only collecting sales tax on its direct sales in five states – a fact that gave the company a competitive edge over brick and mortar stores during a critical time in its growth. Today, Amazon is collecting state-level sales taxes on all its direct sales, but it still usually fails to collect sales tax on the large volume of sales it makes through the “Amazon Marketplace.” This points to a broader problem in…
Why Trump Administration’s Plan to Index Capital Gains to Inflation Is Just Another Giveaway to the Wealthy
June 28, 2019 • By Steve Wamhoff

The White House is reported to be planning to unilaterally adjust the way capital gains are assessed to benefit the wealthiest Americans. The proposal would adjust capital gains for inflation, reducing taxes disproportionately for the wealthiest households who own most assets by limiting their taxable gains to those above and beyond the inflation rate.
State Rundown 6/27: States Look at Raising Incomes at the Bottom, Taxes at the Top
June 27, 2019 • By ITEP Staff

Low-income working families got good news and bad news this week, as Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) enhancements passed in California and advanced in Oregon, while minimum wage increases failed in Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, and Wisconsin. Meanwhile, the momentum for taxing wealth and the very rich continued to grow, as more one-percenters called for enacting progressive taxes, and Inequality.org held a star-studded conference on why and how to do so.

A summary of ITEP reports, analyses and blogs this month.
Wealth Tax Is Supported by Basically Everyone Who Is Not a Politician
June 27, 2019 • By Steve Wamhoff

A February survey found that 61 percent of registered voters supported a wealth tax proposal, including 51 percent of Republican voters. And it’s not just the non-rich wanting to tax the very rich. A June survey found that 60 percent of millionaires support the idea.
Gas Taxes Rise in a Dozen States, Including an Historic Increase in Illinois
June 27, 2019 • By Carl Davis
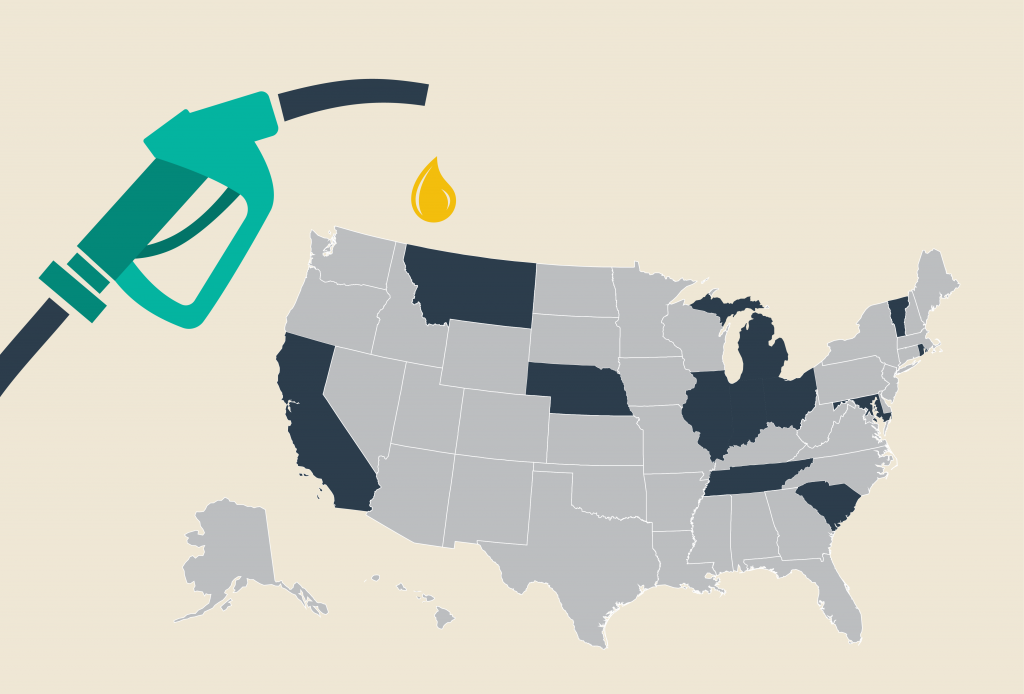
On July 1, 12 states will boost their gasoline taxes and 11 will boost their diesel taxes. The reasons for these increases vary, but they’re generally intended to fund maintenance and improvement of our nation’s transportation infrastructure–a job at which Congress has not excelled in recent years.
Ohio now enjoys the distinction of being the 30th state to raise or reform its gas tax this decade, and the third state to do so this year, under a bill signed into law by Gov. Mike DeWine. While state tax policy can be a contentious topic, there has been a remarkable level of agreement on the gasoline tax. Increasingly, state lawmakers are deciding that outdated gas taxes need to be raised and reformed to fund infrastructure projects that are vital to their economies. These actions are helping reverse losses in gas tax purchasing power caused by rising construction costs…
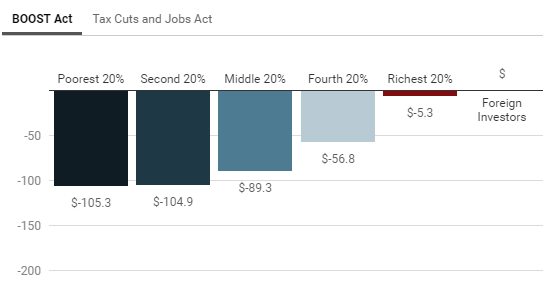
A refundable tax credit proposed by Rep. Rashida Tlaib (D-MI) would be more expansive than other recent tax credit proposals, new estimates from ITEP show. Rep. Tlaib’s proposal, unlike others, does not require households to work to receive the benefit.
What to Watch for on Tax Policy During the Presidential Primary
June 25, 2019 • By Steve Wamhoff

America needs a new tax code. The Democratic presidential debates beginning this week present an opportunity for candidates to make clear how they would address inequality or to raise enough revenue to make public investments that make the economy work for everyone. Here are some of the big tax issues that we hope they will touch on.
The SALT Cap Isn’t Harming State and Local Revenues. Myths About It May Be.
June 24, 2019 • By Carl Davis

A House Ways and Means subcommittee hearing on Tuesday will explore a highly controversial provision of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) that prevents individuals and families from writing off more than $10,000 in state and local tax (SALT) payments on their federal tax forms each year. The focus of the hearing will be whether the cap negatively affects state and local revenue streams that fund schools, firefighters, and other services. There are at least three ways this could happen though only one of those is plausible, and it’s not the one that the organizers of this hearing likely…
