
Recent Work by ITEP
Cities Fail to Disclose Tax Incentives in Bids for Amazon’s HQ2
April 3, 2018 • By Guest Blogger

The Amazon HQ2 project would be the biggest in U.S. history as measured in projected jobs, yet little is known about the incentives cities have offered Amazon to lure its second headquarters. This lack of disclosure prevents public participation in the deal, including raising important questions about whether tax incentives that cities are offering are in the best short- and long-term interest of their residents. This is the main finding of Public Auction, Private Dealings: Will Amazon’s HQ2 Veer to Secrecy Create A Missed Opportunity for Inclusive, Accountable Development?, a Good Jobs First study released today.
Teachers’ Strikes Are Emblematic of Larger Tax Challenges for States
March 30, 2018 • By Meg Wiehe

As other researchers as well as journalists have noted, teachers striking or threatening to strike over low wages and overall lack of investment isn’t simply a narrative about schools and public workers’ pay. It is illustrative of a broader conflict over tax laws and how states and local jurisdictions fund critical public services that range from K-12 education, public safety, roads and bridges, health care, parks, to higher education.

President Trump’s latest Twitter target, the Amazon Corporation, is now under the microscope for its state and local tax avoidance. In a Thursday tweet, the President claimed that “[u]nlike others, they pay little or no taxes to state & local governments.” Such a statement is a startling reversal for a president who previously said his own ability to avoid paying income taxes “makes me smart.”
State Rundown 3/30: Several Major Tax Debates Will March on into April
March 30, 2018 • By ITEP Staff

This week, after the recent teacher strike in West Virginia, teacher pay crises brought on by years of irresponsible tax cuts also made headlines in Arizona and Oklahoma. Maine and New York lawmakers continue to hash out how they will respond to the federal tax bill. And their counterparts in Missouri and Nebraska attempt to push forward their tax cutting agendas.
Trends We’re Watching in 2018, Part 3: Improvements to Tax Credits for Workers and Families
March 26, 2018 • By Aidan Davis

This has been a big year for state action on tax credits that support low-and moderate-income workers and families. And this makes sense given the bad hand low- and middle-income families were dealt under the recent Trump-GOP tax law, which provides most of its benefits to high-income households and wealthy investors. Many proposed changes are part of states’ broader reaction to the impact of the new federal law on state tax systems. Unfortunately, some of those proposals left much to be desired.
Amazon and Other E-Retailers Get a Free Pass from Some Local-Level Sales Taxes
March 26, 2018 • By Carl Davis

A new ITEP analysis reveals that in seven states (Alabama, Alaska, Idaho, Iowa, Mississippi, New Mexico, and Pennsylvania), the nation’s largest e-retailer, Amazon.com, is either not collecting local-level sales taxes or is charging a lower tax rate than local retailers. In other states, such as Colorado and Illinois, Amazon is collecting local tax because it has an in-state presence, but localities cannot collect taxes from other e-retailers based outside the state.
Many Localities Are Unprepared to Collect Taxes on Online Purchases: Amazon.com and other E-Retailers Receive Tax Advantage Over Local Businesses
March 26, 2018 • By Carl Davis
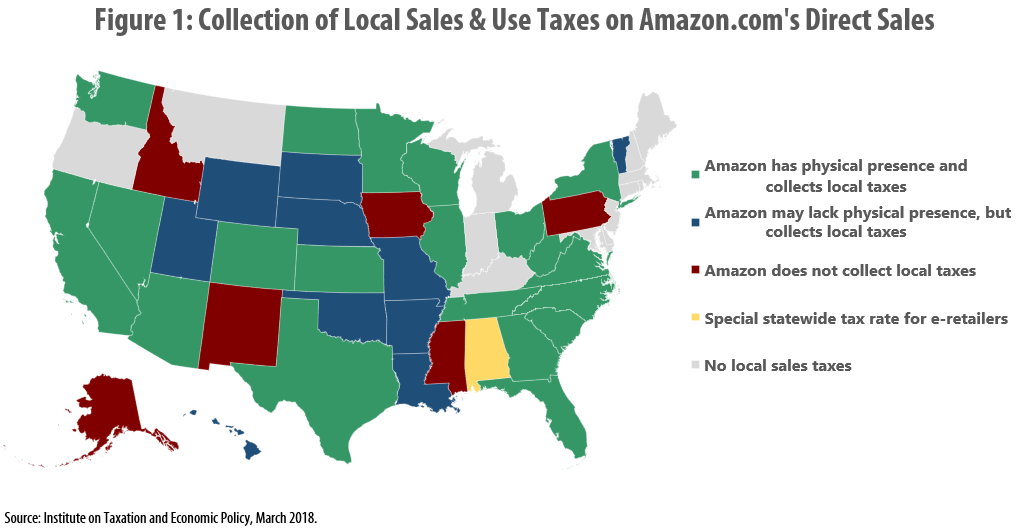
Online retailer Amazon.com made headlines last year when it began collecting every state-level sales tax on its direct sales. Savvy observers quickly noted that this change did not affect the company’s large and growing “marketplace” business, where it conducts sales in partnership with third-parties and rarely collects tax. But far fewer have noticed that even on its direct sales, Amazon is still not collecting some local-level taxes.
Unintended Consequences of the New Tax Bill Keep Cropping Up
March 23, 2018 • By Dacey Anechiarico

Due to its rushed passage in a matter of weeks, without public hearings or enough time even for basic proofreading, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) contains numerous unintended consequences that Congress is now scrambling to fix. The authors of the new law have openly admitted that the law includes major mistakes. One of the most prominent drafting errors is what is now known as the “grain glitch,” which temporarily created a huge incentive for farmers to sell their products to cooperatives over businesses taking other forms.
State Rundown 3/22: Some Spring State Tax Debates in Full Bloom, Others Just Now Surfacing
March 22, 2018 • By ITEP Staff

The onset of spring this week proved to be fertile ground for state fiscal policy debates. A teacher strike came to an end in West Virginia as another seems ready to begin in Oklahoma. Budgets were finalized in Florida, West Virginia, and Wyoming, are set to awaken from hibernation in Missouri and Virginia, and are being hotly debated in several other states. Meanwhile Idaho, Iowa, Maryland, and Minnesota continued to grapple with implications of the federal tax-cut bill. And our What We're Reading section includes coverage of how states are attempting to further public priorities by taxing carbon, online gambling,…
The Heritage Foundation, the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy (ITEP), and the Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget (CRFB) routinely disagree on a wide range of policy issues, but a recent Ways and Means Tax Policy Subcommittee hearing revealed they all agree that the continual and unpaid-for extension of temporary tax breaks needs to end.
