
Vermont
Trends We’re Watching in 2018, Part 5: 21st Century Consumption Taxes
April 20, 2018 • By Misha Hill

We're highlighting the progress of a few newer trends in consumption taxation. This includes using the tax code to discourage consumption of everything from plastic bags to carbon and collecting revenue from emerging industries like ride sharing services and legalized cannabis sales.
Trends We’re Watching in 2018, Part 3: Improvements to Tax Credits for Workers and Families
March 26, 2018 • By Aidan Davis

This has been a big year for state action on tax credits that support low-and moderate-income workers and families. And this makes sense given the bad hand low- and middle-income families were dealt under the recent Trump-GOP tax law, which provides most of its benefits to high-income households and wealthy investors. Many proposed changes are part of states’ broader reaction to the impact of the new federal law on state tax systems. Unfortunately, some of those proposals left much to be desired.
State Rundown 3/22: Some Spring State Tax Debates in Full Bloom, Others Just Now Surfacing
March 22, 2018 • By ITEP Staff

The onset of spring this week proved to be fertile ground for state fiscal policy debates. A teacher strike came to an end in West Virginia as another seems ready to begin in Oklahoma. Budgets were finalized in Florida, West Virginia, and Wyoming, are set to awaken from hibernation in Missouri and Virginia, and are being hotly debated in several other states. Meanwhile Idaho, Iowa, Maryland, and Minnesota continued to grapple with implications of the federal tax-cut bill. And our What We're Reading section includes coverage of how states are attempting to further public priorities by taxing carbon, online gambling,…

With many state legislative sessions about halfway through, the ripple effects of the federal tax-cut bill took a back seat this week as states focused their energies on their own tax and budget issues. Major proposals were released in Nebraska and New Jersey, one advanced in Missouri, and debates wrapped up in Florida, Utah, and Washington. Oklahoma and Vermont are considering ways to improve education funding, while California, New York, and Vermont look to require more of their most fortunate residents. And check in on "what we're reading" for resources on the online sales tax debate, the role of property…
Trends We’re Watching in 2018, Part 1: State Responses to Federal Tax Cut Bill
March 5, 2018 • By Dylan Grundman O'Neill
Over the next few weeks we will be blogging about what we’re watching in state tax policy during 2018 legislative sessions. And there is no trend more pervasive in states this year than the need to sort through and react to the state-level impact of federal tax changes enacted late last year.
Preventing State Tax Subsidies for Private K-12 Education in the Wake of the New Federal 529 Law
February 23, 2018 • By Ronald Mak

This policy brief explains the federal and various state-level breaks for 529 plans and explores the potential impact that the change in federal treatment of 529 plans will have on state revenues.

This week, major tax packages relating to the federal tax-cut bill made news in Georgia, Iowa, and Louisiana, as Minnesota and Oregon lawmakers also continue to work out how their states will be affected. New Mexico's legislative session has finished without significant tax changes, while Idaho and Illinois's sessions are beginning to heat up, and Vermont's school funding system is under the microscope.
State Rundown 2/8: State Responses to Federal Bill Gaining Steam
February 8, 2018 • By ITEP Staff

Several states this week are looking at ways to revamp their tax codes in response to the federal tax cut bill, with Georgia, Idaho, Maryland, Nebraska, and Vermont all actively considering proposals. Meanwhile, Connecticut, Louisiana, and Pennsylvania are working on resolving their budget shortfalls. And transportation funding is getting needed attention in Mississippi, Utah, and Wisconsin.
What the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act Means for States – A Guide to Impacts and Options
January 26, 2018 • By ITEP Staff
The recently enacted Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) has major implications for budgets and taxes in every state, ranging from immediate to long-term, from automatic to optional, from straightforward to indirect, from certain to unknown, and from revenue positive to negative. And every state can expect reduced federal investments in shared public priorities like health care, education, public safety, and basic infrastructure, as well as a reduced federal commitment to reducing economic inequality and slowing the concentration of wealth. This report provides detail that state residents and lawmakers can use to better understand the implications of the TCJA for…
State Rundown 1/25: States Begin Tax Debates while Still Racing to Understand Federal Bill
January 25, 2018 • By ITEP Staff

State legislative sessions are in full swing this week as states grapple with revenue shortfalls and the ramifications of the federal tax cut bill. Lawmakers in Alaska and Louisiana, for example, are debating how to handle their revenue shortfalls, and a tax cut proposal in Idaho has been received tepidly. And be sure to peruse our "What We're Reading" section for helpful perspectives on how states are affected by the federal tax cut bill.
State Rundown 1/12: Tax Cut Tunnel Vision Threatens to Bore State Budget Holes Even Deeper
January 12, 2018 • By ITEP Staff

As states continue to sift through wreckage of the federal tax cut bill to try to determine how they will be affected, two things should be clear to everyone: the richest people in every state just got a massive federal tax cut, and federal funding for shared priorities like education and health care is certain to continue to decline. State leaders who care about those priorities should consider asking those wealthy beneficiaries of the federal cuts to pay more to the state in order to minimize the damage of the looming federal funding cuts, but so far policymakers in Idaho,…
Select state coverage of ITEP’s analyses of Republican tax Plans
January 1, 2018
Burlington County Times: Will Phil Murphy raise NJ’s taxes (and 4 other political questions for .. Kaplan Herald: This chart exhibits how the GOP tax plan will hit your pockets Wiscnews: Tax cuts increase inequity Patch.com: MacArthur Touts Tax Reform; Will It Help NJ As Much As He Says? NJ.com: Long lines spring up as […]
How the Final GOP-Trump Tax Bill Would Affect Vermont Residents’ Federal Taxes
December 16, 2017 • By ITEP Staff
The final tax bill that Republicans in Congress are poised to approve would provide most of its benefits to high-income households and foreign investors while raising taxes on many low- and middle-income Americans. The bill would go into effect in 2018 but the provisions directly affecting families and individuals would all expire after 2025, with […]
The Final Trump-GOP Tax Plan: National and 50-State Estimates for 2019 & 2027
December 16, 2017 • By ITEP Staff
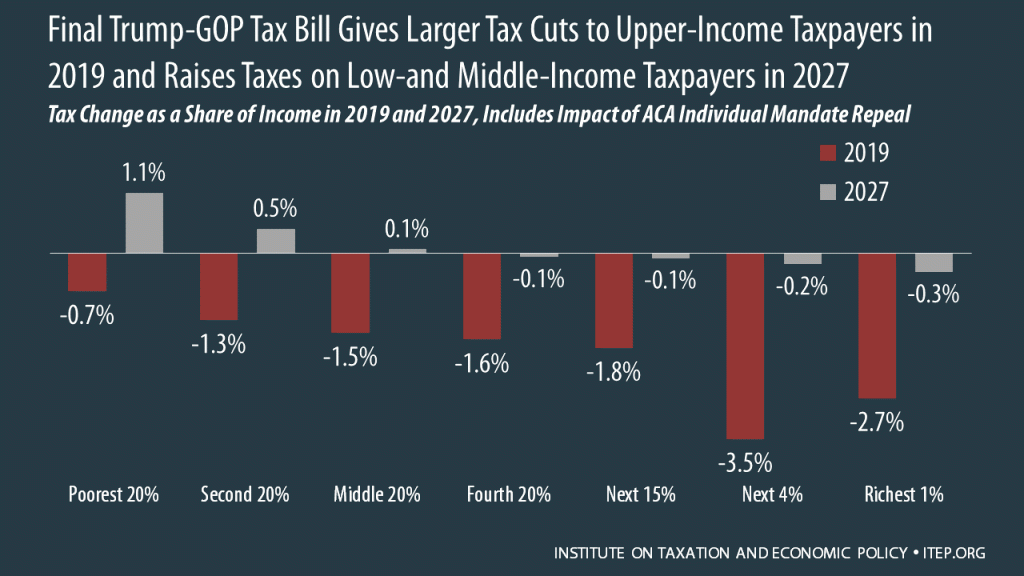
The final Trump-GOP tax law provides most of its benefits to high-income households and foreign investors while raising taxes on many low- and middle-income Americans. The bill goes into effect in 2018 but the provisions directly affecting families and individuals all expire after 2025, with the exception of one provision that would raise their taxes. To get an idea of how the bill will affect Americans at different income levels in different years, this analysis focuses on the bill’s impacts in 2019 and 2027.

As 2017 draws to close, Congress has yet to take legislative action to protect Dreamers. The young undocumented immigrants who were brought to the United States as children, and are largely working or in school, were protected by President Obama’s 2012 executive action, Deferred Action for Childhood Arrivals (DACA). But in September, President Trump announced that he would end DACA in March 2018. Instead of honoring the work authorizations and protection from deportation that currently shields more than 685,000 young people, President Trump punted their lives and livelihood to a woefully divided Congress which is expected to take up legislation…
State Rundown 12/7: States Try to Plan While Awaiting Federal Tax Decisions
December 7, 2017 • By ITEP Staff

Though most eyes were on Congress rather than states this week, several states have been taking stock of their fiscal situations. Wyoming lawmakers considered ways to resolve budget shortfalls, Kansas and New Mexico legislators got some minor good news about their states' revenues, their counterparts in Minnesota and Vermont grappled with less encouraging revenue news, and those in West Virginia were just happy to hear their revenues had at least met expectations for once.
How the House and Senate Tax Bills Would Affect Vermont Residents’ Federal Taxes
December 6, 2017 • By ITEP Staff
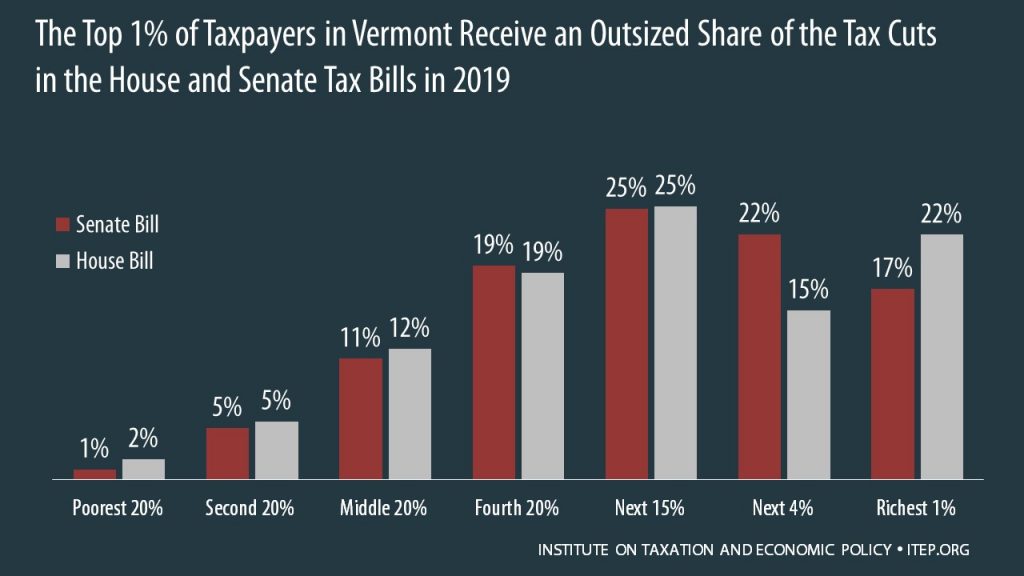
The House passed its “Tax Cuts and Jobs Act” November 16th and the Senate passed its version December 2nd. Both bills would raise taxes on many low- and middle-income families in every state and provide the wealthiest Americans and foreign investors substantial tax cuts, while adding more than $1.4 trillion to the deficit over ten years. The graph below shows that both bills are skewed to the richest 1 percent of Vermont residents.
National and 50-State Impacts of House and Senate Tax Bills in 2019 and 2027
December 6, 2017 • By ITEP Staff
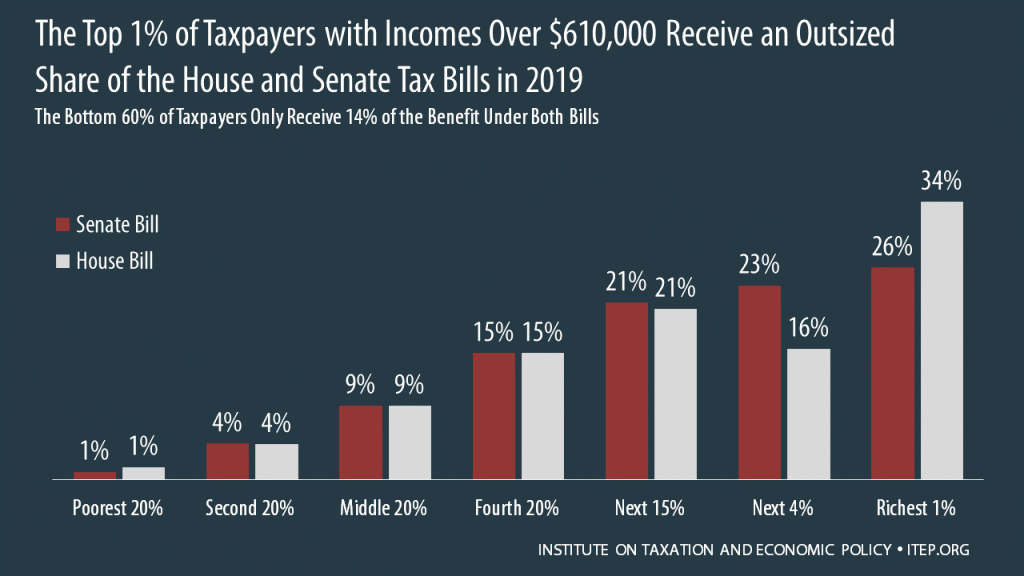
The House passed its “Tax Cuts and Jobs Act” November 16th and the Senate passed its version December 2nd. Both bills would raise taxes on many low- and middle-income families in every state and provide the wealthiest Americans and foreign investors substantial tax cuts, while adding more than $1.4 trillion to the deficit over ten years. National and 50-State data available to download.
Revised Senate Plan Would Raise Taxes on at Least 29% of Americans and Cause 19 States to Pay More Overall
November 18, 2017 • By ITEP Staff
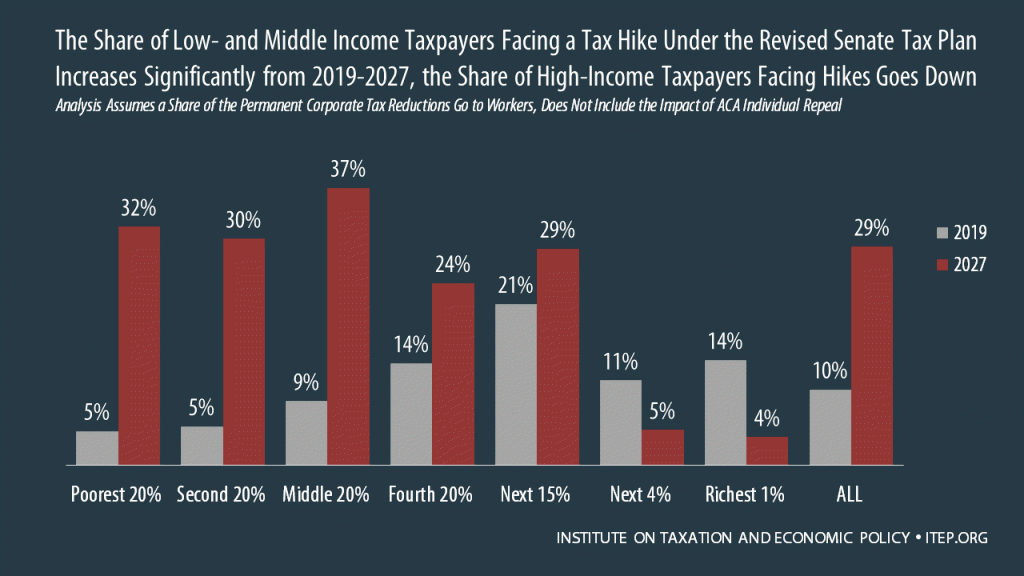
The tax bill reported out of the Senate Finance Committee on Nov. 16 would raise taxes on at least 29 percent of Americans and cause the populations of 19 states to pay more in federal taxes in 2027 than they do today.
How the Revised Senate Tax Bill Would Affect Vermont Residents’ Federal Taxes
November 14, 2017 • By ITEP Staff
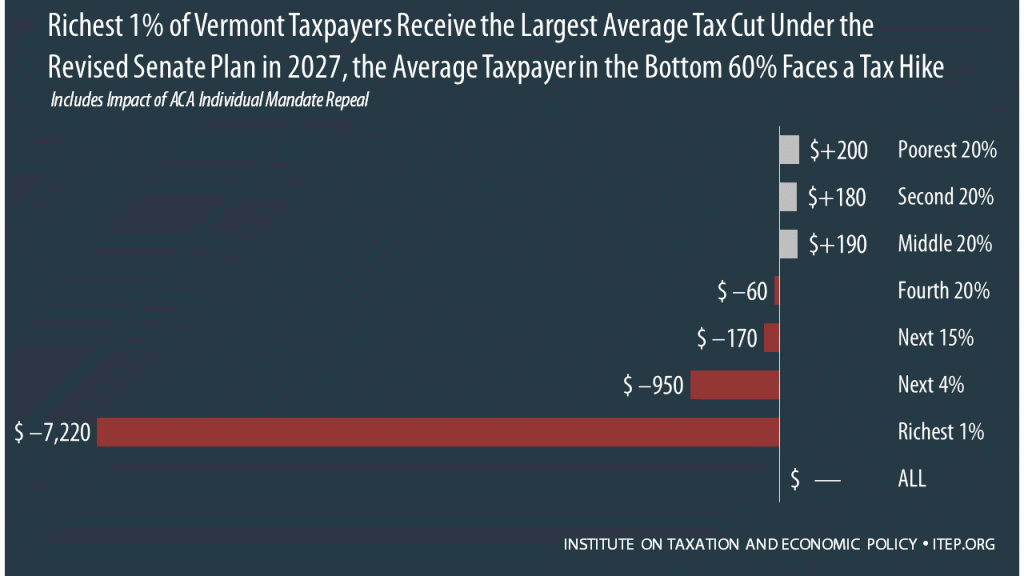
The Senate tax bill released last week would raise taxes on some families while bestowing immense benefits on wealthy Americans and foreign investors. In Vermont, 40 percent of the federal tax cuts would go to the richest 5 percent of residents, and 11 percent of households would face a tax increase, once the bill is fully implemented.
Analysis of the House Tax Cuts and Jobs Act
November 6, 2017 • By Matthew Gardner, Meg Wiehe, Steve Wamhoff
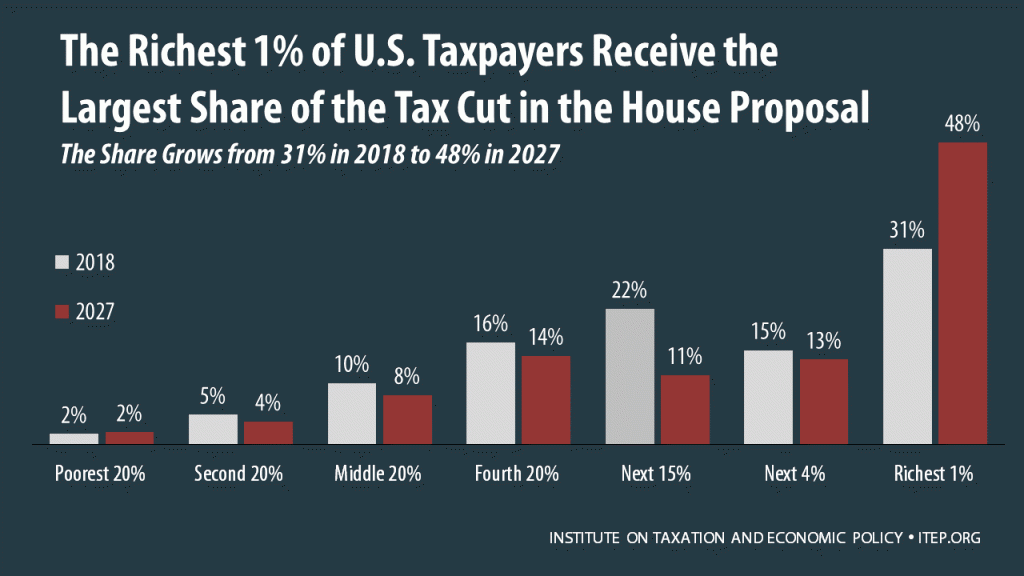
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, which was introduced on Nov. 2 in the House of Representatives, would raise taxes on some Americans and cut taxes on others while also providing significant savings to foreign investors.
How the House Tax Proposal Would Affect Vermont Residents’ Federal Taxes
November 6, 2017 • By ITEP Staff
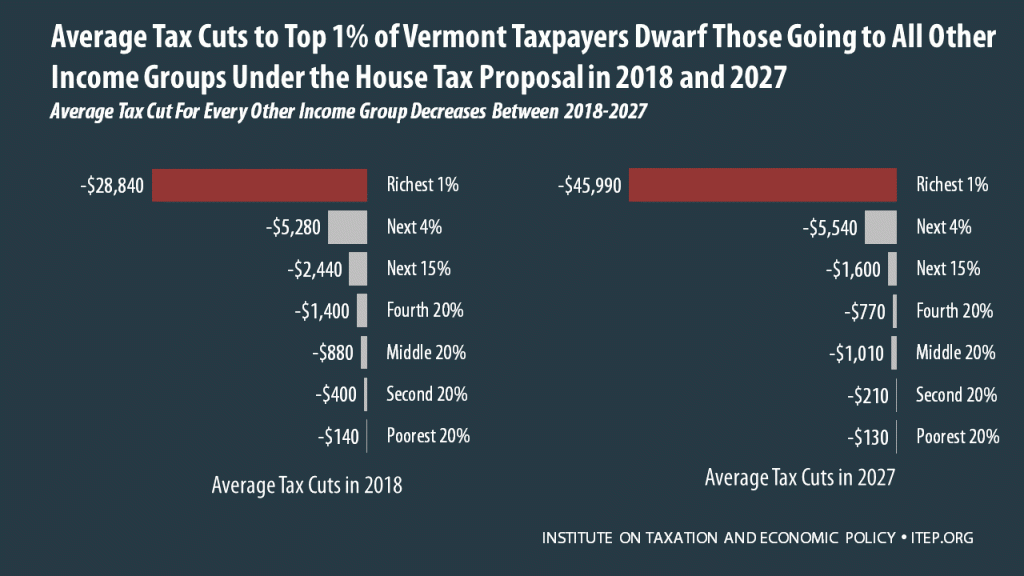
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, which was introduced on November 2 in the House of Representatives, includes some provisions that raise taxes and some that cut taxes, so the net effect for any particular family’s federal tax bill depends on their situation. Some of the provisions that benefit the middle class — like lower tax rates, an increased standard deduction, and a $300 tax credit for each adult in a household — are designed to expire or become less generous over time. Some of the provisions that benefit the wealthy, such as the reduction and eventual repeal of the estate…
Trickle-Down Dries Up: States without personal income taxes lag behind states with the highest top tax rates
October 26, 2017 • By Carl Davis, Nick Buffie

Lawmakers who support reducing or eliminating state personal income taxes typically claim that doing so will spur economic growth. Often, this claim is accompanied by the assertion that states without income taxes are booming, and that their success could be replicated by any state that abandons its income tax. To help evaluate these arguments, this study compares the economic performance of the nine states without broad-based personal income taxes to their mirror opposites—the nine states levying the highest top marginal personal income tax rates throughout the last decade.
Benefits of GOP-Trump Framework Tilted Toward the Richest Taxpayers in Each State
October 4, 2017 • By Steve Wamhoff
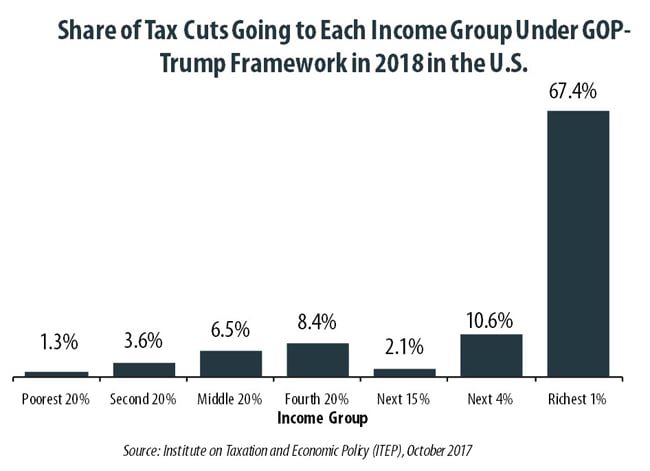
The “tax reform framework” released by the Trump administration and Congressional Republican leaders on September 27 would affect states differently, but every state would see its richest residents grow richer if it is enacted. In all but a handful of states, at least half of the tax cuts would flow to the richest one percent of residents if the framework took effect.
GOP-Trump Tax Framework Would Provide Richest One Percent in Vermont with 45.1 Percent of the State’s Tax Cuts
October 4, 2017 • By ITEP Staff
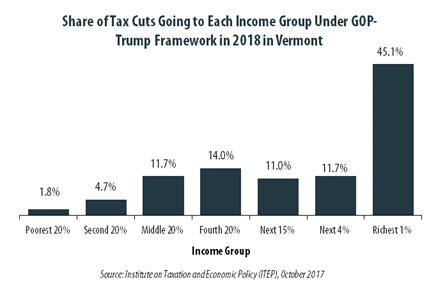
The “tax reform framework” released by the Trump administration and congressional Republican leaders on September 27 would not benefit everyone in Vermont equally. The richest one percent of Vermont residents would receive 45.1 percent of the tax cuts within the state under the framework in 2018. These households are projected to have an income of at least $505,400 next year. The framework would provide them an average tax cut of $45,250 in 2018, which would increase their income by an average of 3.8 percent.
