
Blog
1308 posts
State Rundown 8/22: Wayfair Fallout Could Hit the Pavement Soon
August 22, 2018 • By ITEP Staff

Arizona voters learned this week that they will have an opportunity this fall to restore school funding through a progressive tax measure. The effects of the Supreme Court’s Wayfair decision could soon be seen on Michigan and Mississippi roads, as leaders in both states have proposed devoting new online sales tax revenues to infrastructure needs. And new research highlighted in our “What We’re Reading” section discredits one-size-fits-all prescriptions for state economic growth such as supply-side tax-cut orthodoxy, advocating instead for more nuanced and state-specific policymaking.
State Rundown 8/16: November Ballots and 2019 Debates Coming into Focus
August 16, 2018 • By ITEP Staff

Even as the haze from western wildfires reduced visibility across the nation this week, voters got more clarity on what to expect to see on their ballots this fall, particularly in California (commercial property taxes and corporate surcharges), Colorado (income taxes for education), Missouri (gas tax update), and North Dakota (recreational cannabis). Meanwhile, although Virginia lawmakers won’t return until 2019, they got a preview of a clear-headed federal conformity plan they should strongly consider. And look to our “What We’re Reading“ section for further enlightenment from researchers on the [in]effectiveness of charitable contribution credits, the [lack of] wage growth for…
1964: Unconditional War on Poverty; 2018: Unconditional War on the Poor
August 15, 2018 • By Misha Hill

During his first State of the Union address in January 1964, Lyndon Baines Johnson declared a War on Poverty in response to a national poverty rate of more than 19 percent. The legislative result of this war was an early education program, expanded funding for secondary education, job training and work opportunity programs and the […]
How Opportunity Zones Benefit Investors and Promote Displacement
August 10, 2018 • By ITEP Staff
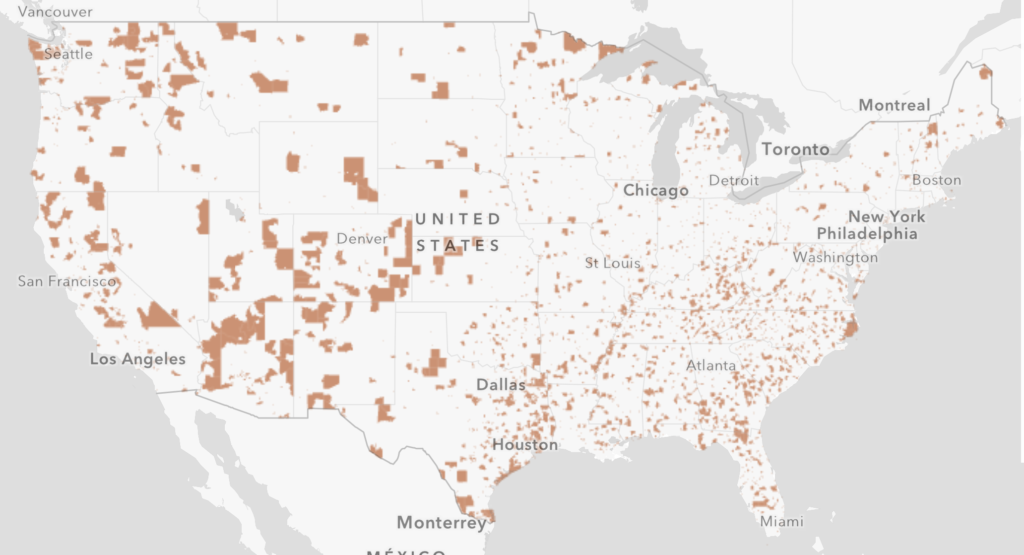
The idea behind the new tax break is to provide an incentive for wealthy individuals to invest in the economies of struggling communities. Despite alleged intentions, it appears opportunity zones are turning into yet another windfall for wealthy investors and may encourage displacement of people in low-income areas, working against the provision’s intended goal.
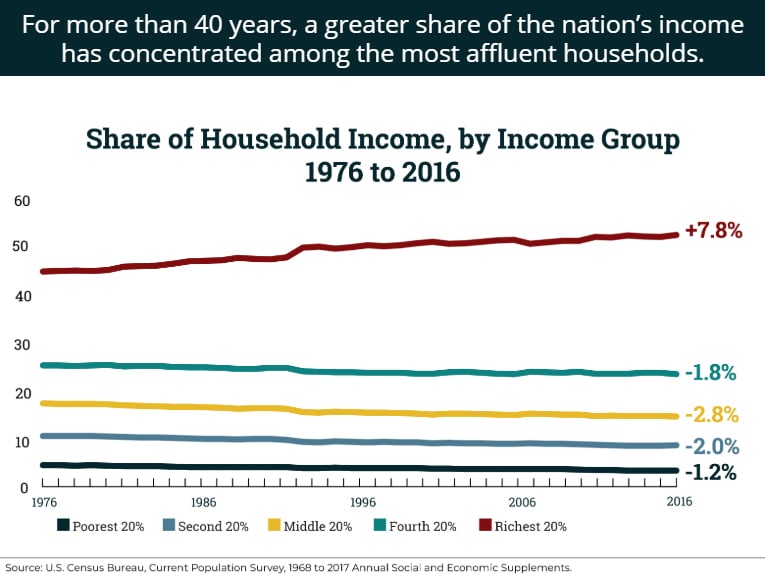
In this illustrated breakdown of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) and Tax Cuts 2.0, ITEP staff examine TCJA's role in growing income inequality, broken promises from corporations pledging to invest tax savings into workers and wages, and the embarrassment of riches flowing to the wealthiest Americans as a result of these “middle-class tax cuts.”
State Rundown 8/8: States Setting Rules for Upcoming Tax Decisions
August 8, 2018 • By ITEP Staff

August is often a season for states to define the parameters of tax debates to come, and that is true this week in several states: a tax task force in Arkansas is nearing its final recommendations; residents of Missouri, Montana, and North Carolina await results of court challenges that will decide whether tax measures will show up on their ballots this fall; and Michigan and South Dakota are taking different approaches to making sure they’re ready to collect online sales taxes next year.

Consumers’ growing interest in online shopping and “gig economy” services like Uber and Airbnb has forced states and localities to revisit their sales taxes, for instance. Meanwhile new evidence on the dangers and causes of obesity has led to rising interest in soda taxes, but the soda industry is fighting back. Carbon taxes are being discussed as a tool for combatting climate change. And changing attitudes toward cannabis use have spurred some states to move away from outright prohibition in favor of legalization, regulation and taxation.

Although most state legislatures are out of session during the summer, the pursuit of better fiscal policy has no "off-season." Here at ITEP, we've been revamping the State Rundown to bring you your favorite summary of state budget and tax news in the new-and-improved format you see here. Meanwhile, leaders in Massachusetts and New Jersey have been hard at work in recent weeks and are already looking ahead their next round of budget and tax debates. Lawmakers in many states are using their summer break to prepare for next year's discussions over how to implement online sales tax legislation. And…
The Preferential Tax Treatment of Capital Gains Income Should Be Curbed, Not Substantially Expanded
August 1, 2018 • By Richard Phillips
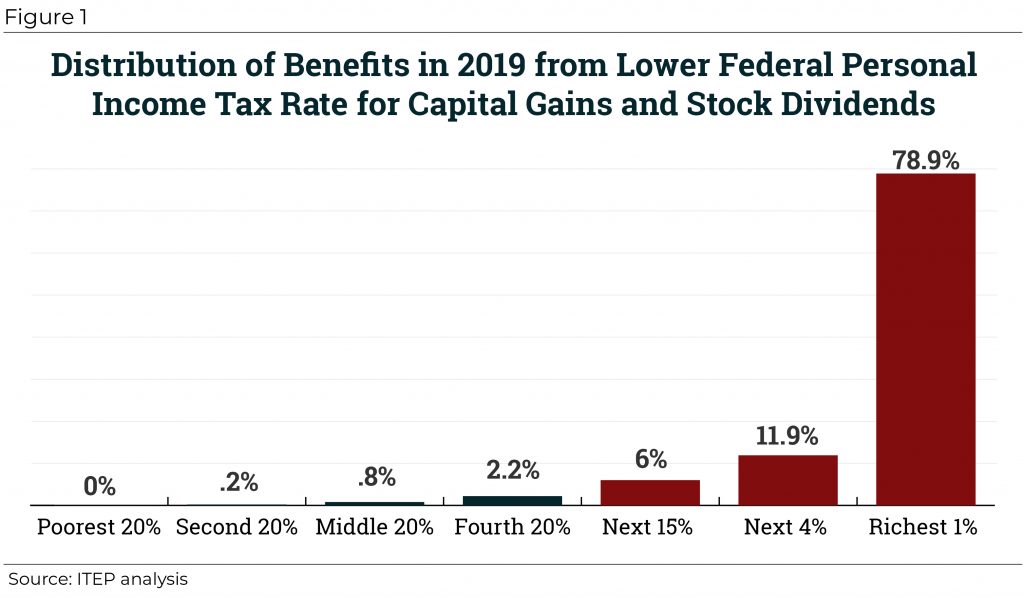
For true believers in supply-side economics, however, one major flaw of the TCJA is that it did not further cut taxes for the wealthy by reducing capital gains tax rates. But now the Trump Administration is considering using executive action to remedy this by indexing capital gains to inflation for tax purposes.
The Fight for Education Funding: State Revenue Needs and Responses in 2018
July 24, 2018 • By Aidan Davis

States’ need for revenue and increased investment in key public services is not unique to this legislative session. But the extent of disinvestment—particularly in education—has been a driving force behind policy discussion and state legislative action this year. In many cases ill-advised tax cuts coupled with persistent school funding cuts led states to this common fate, initiating a powerful and growing trend. Here’s how lawmakers in a handful of state responded:
State Rundown 7/19: Wayfair Fallout and Ballot Preparation Dominate State Tax Talk
July 19, 2018 • By ITEP Staff

In the wake of the U.S. Supreme Court's recent Wayfair decision authorizing states to collect taxes owed on online sales, Utah lawmakers held a one-day special session that included (among other tax topics) legislation to ensure the state will be ready to collect those taxes, and a Nebraska lawmaker began pushing for a special session for the same reason. Voters in Colorado and Montana got more clarity on tax-related items they'll see on the ballot in November. And Massachusetts moves closer toward becoming the final state to enact a budget for the new fiscal year that started July 1 in…

How should lawmakers fix the system? A new ITEP report breaks down how the international corporate tax code under the TCJA works, and how lawmakers can fix it. The report lays out three key principles for reform: equalize the rates, eliminate inversions, and create transparency.
18 States Will Take Holidays from Sound Tax Policy This Year
July 12, 2018 • By Dylan Grundman O'Neill
State sales tax holidays, our newly updated policy brief shows, are the equivalent of the bad kind of holiday vacation: tax policy that sounds nice at first but ultimately cuts corners, wastes money, precludes better options, and leaves states worse off than they would be without them. Unfortunately, while several states have wised up about sales tax holidays in recent years, 18 states will fall for the superficial attraction of these tax policy gimmicks in 2018.
The Immediate Economic Impact of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act Could be Even Less Than Expected
July 11, 2018 • By Richard Phillips
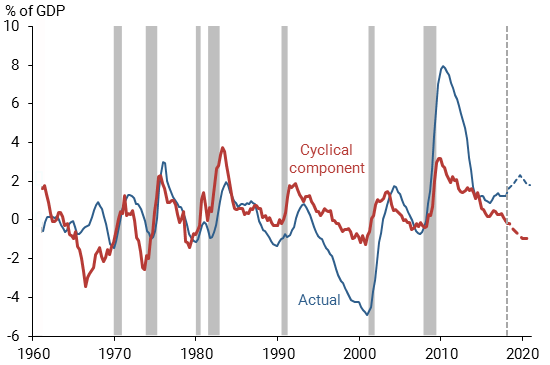
Now, new research from the Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco finds that the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act may not be so much of a stimulus after all. In other words, lawmakers have left themselves with few options should the country face an economic recession, and the country may not receive a substantive economic benefit in the short term.
Building on Momentum from Recent Years, 2018 Delivers Strengthened Tax Credits for Workers and Families
July 10, 2018 • By Aidan Davis

Despite some challenging tax policy debates, a number of which hinged on states’ responses to federal conformity, 2018 brought some positive developments for workers and their families. This post updates a mid-session trends piece on this very subject. Here’s what we have been following:

New Jersey avoided a second consecutive shutdown and proved that even against staunch opposition, progressive solutions to states' fiscal issues are attainable, and Arizona voters will likely have a chance to solve their education funding crisis in a similar way. Budget and tax debates remain to be resolved, however, in Maine and Massachusetts. Meanwhile, voters are gaining a clearer picture of what questions they will be asked on ballots this fall as signature drives conclude in several states.
With many state fiscal years beginning July 1, most states that will make decisions this year about federal tax conformity have now done so, so it is now time for an update on how well state policymakers have kept to, or veered from, the path we charted out earlier this year. Most states that have enacted laws in response to the federal changes have adhered to some but not all of the principles we laid out, with a few responding rather prudently and a handful charting a much more treacherous course of unfair, unsustainable policy based on unfounded promises of…

Ah, summertime – a season synonymous with sunshine, backyard barbecues and mercury rising. Outside of our day jobs analyzing tax policy, we occasionally take a break from our screens to reconnect with the written and spoken word. However you enjoy your summer downtime – visiting your childhood home, lounging at the lake, planning the ultimate […]

This week, lawmakers in Louisiana, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont, and the District of Columbia wrapped up their budgets in time for the new fiscal year that starts July first in most states, with some of these resolutions coming after contentious debates and repeated special sessions. New Jersey's debate is not yet finished as leaders clash over spending priorities and the taxes on millionaires and corporations needed to fund them. Meanwhile, signature drives to put tax-related questions on fall ballots are heating up in several other states. And our "What We're Reading" section includes helpful resources on implications of the Supreme…
Rigging the System and Poor Shaming (Rightly) Are Incompatible Political Strategies
June 27, 2018 • By Jenice Robinson

The absurdity of blaming poor and moderate-income people for their circumstances is close to running its course as an effective political tool, particularly as some elected officials more boldly assert their intent to cater to the whims of the wealthy. Take last year’s GOP-led drive to eliminate the Affordable Care Act (ACA), for example. House […]
Gas Taxes Rise in Seven States, Including an Historic Increase in Oklahoma
June 26, 2018 • By Carl Davis
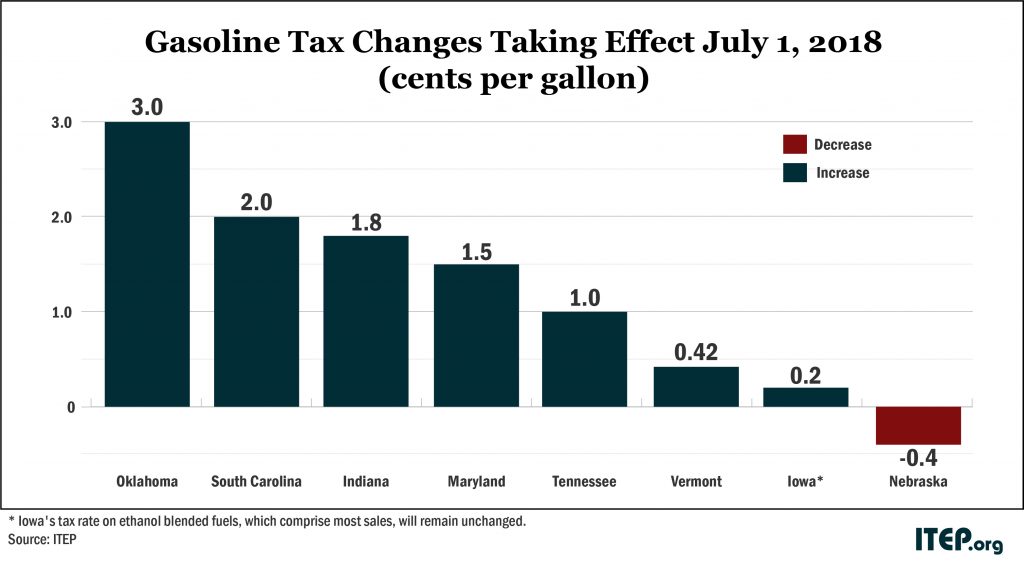
A rare sight is coming to Oklahoma. The last time the Sooner State raised its gas tax rate, the Berlin Wall was still standing, and Congress was debating whether to ban smoking on flights shorter than two hours. Fast forward 31 years, and Oklahoma is finally at it again. On Sunday, the state’s gas tax rate will rise by 3 cents and its diesel tax rate by 6 cents. Both taxes will now stand at 19 cents per gallon—still among the lowest in the country. But Oklahoma isn’t the only state where gas taxes will soon rise.
What’s at Stake in South Carolina’s Upcoming Tax Conformity Debate
June 22, 2018 • By Dylan Grundman O'Neill
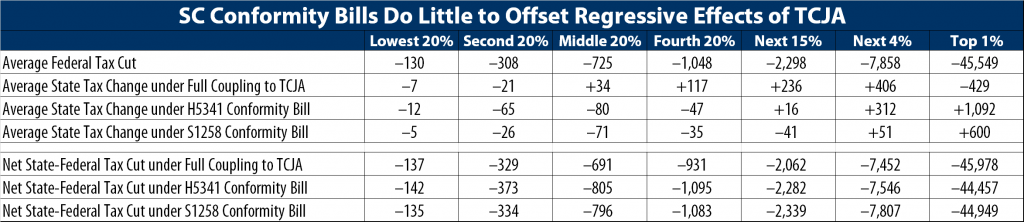
South Carolina legislators will return next week to try to finalize a few issues before the end of their session and fiscal year on June 30th, including the question of how to respond to the federal Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA). That's a short timeframe with some important questions at stake, and some misinformation has been spread, so here's a quick guide to the facts, issues, and options.

The U.S. Supreme Court made big news this morning by allowing states to collect taxes due on internet purchases, which will help put main-street and online retailers on an even playing field while also improving state and local revenues and the long-term viability of the sales tax as a revenue source. Many states remain focused on more local issues, however, as Louisiana's third special session of the year kicked off, Massachusetts won a living wage battle while losing an opportunity to put a popular millionaires tax proposal before voters, and major fiscal debates continue in Maine, New Jersey, and Vermont.
Supreme Court Decision in Wayfair Is a Leap Forward for Sales Tax Modernization
June 21, 2018 • By Carl Davis

For years, state and local governments have been dealing with a tax enforcement nightmare as out-of-state Internet retailers have refused to collect sales tax. That non-collection was facilitated by a Supreme Court precedent that tax collection can only be required when a retailer has a “physical presence” inside of a state. In today’s ruling in […]
State Rundown 6/13: Budget Crunch Time Sets in as State Fiscal Years Come to Close
June 13, 2018 • By ITEP Staff

With many state fiscal years ending June 30th, budget negotiations were completed recently in California, Illinois, Michigan, and North Carolina. New Jersey remains a state to watch as a government shutdown looms but leaders continue to disagree about a proposed millionaires tax, corporate taxes, and school funding. In other states looking to wealthy individuals and large corporations for needed revenues, Arizona's teacher pay crisis could be solved with a tax on its highest-income residents and a similar proposal in Massachusetts is polling well, but Seattle's new "head tax" could be on the chopping block.
