
Blog
1308 posts
All Bets are Off: State-Sponsored Sports Betting Isn’t Worth the Risk
June 13, 2018 • By Misha Hill

Many state legislators and regulators are considering expanding state-sponsored gambling by allowing betting on major league sports games. But the revenue states could bring in isn’t worth the risk.
New Legislation Would Close Significant Offshore Loopholes in the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act
June 6, 2018 • By Richard Phillips

One simple rule should drive the nation’s international tax policies: tax the offshore profits of American companies the same way their domestic profits are taxed. The latest legislation to approach that ideal is the Per-Country Minimum Act (H.R. 6015), from Rep. Peter DeFazio (D-OR). The DeFazio bill closes the loophole that allows corporations to use foreign tax credits to shelter profits in tax havens from U.S. taxes. No other bill addresses this.
State Rundown 6/1: Time Is Ripe for Closer Look at Intergovernmental Relations
June 1, 2018 • By ITEP Staff

This week, Virginia lawmakers overcame their budget impasse and approved an expansion of Medicaid, North Carolina's behind closed doors budget debate appears to be wrapping up, and Vermont's special session continues in the wake of the governor's vetoes of the state budget and accompanying tax bills. New research highlighted in our What We're Reading section shows that both corporate income tax cuts and business tax subsidies contribute to wider economic inequality. And the possible reconstitution of a federal commission on intergovernmental relations could not come soon enough, as other headlines this week include a state-to-local shift in school funding, governments…
Facebook Facing Shareholder Scrutiny for Its Offshore Tax Avoidance
May 30, 2018 • By Richard Phillips

In advance of its annual shareholders meeting on May 31, Facebook was confronted with a shareholder resolution asking it to endorse a set of principles to guide its tax policy and to ensure that such principles consider the impact of its tax strategies on local economies and public services. The resolution is a signal from a group of concerned shareholders that Facebook’s tax avoidance hurts its reputation, the communities in which it operates, and creates financial risks to the company’s shareholders.
As IRS Prepares to Act, Red-State Taxpayers Profit from Use of SALT “Workaround Credits”
May 24, 2018 • By Carl Davis

A new ITEP report explains the close parallels between the new workaround credits and existing state tax credits, including those benefiting private schools. The report comes the same day that the IRS and Treasury Department announced they would seek new regulations related to these tax credits. It notes that the SALT workarounds are emblematic of a broader weakness with the federal charitable deduction. And it cautions regulators to avoid a “narrow fix” that will only address the newest SALT workarounds (which, so far, have only been enacted in blue states) without also addressing other abuses of the deduction, which have…
New Legislation Would End Tax Incentives to Move Jobs and Profits Offshore
May 24, 2018 • By Richard Phillips

New legislation introduced today, the No Tax Breaks for Outsourcing Act, by Rep. Lloyd Doggett (D-TX) and Sen. Sheldon Whitehouse (D-RI) would help repair the damage to the international tax code wrought by the new Trump-GOP tax law and move toward a system where U.S. corporations can’t reap tax benefits from shifting jobs and profits offshore.
State Rundown 5/23: Special Sessions Abound Amid Budget Vetoes, Stalemates, Federal Tax Bill
May 23, 2018 • By ITEP Staff

This week the governors of Louisiana and Minnesota both vetoed budget bills, leading to another special session in Louisiana and unanswered questions in Minnesota, and Missouri legislators managed to push through a tax shift bill just before adjourning their regular session and heading right into a special session to impeach their governor. Wisconsin and Wyoming localities are both looking at ways to raise revenues as state funding drops. And our What We're Reading section contains helpful pieces on changing demographics, the effects of wealth inequality on families with children, and the impacts of the Supreme Court sports gambling and online…
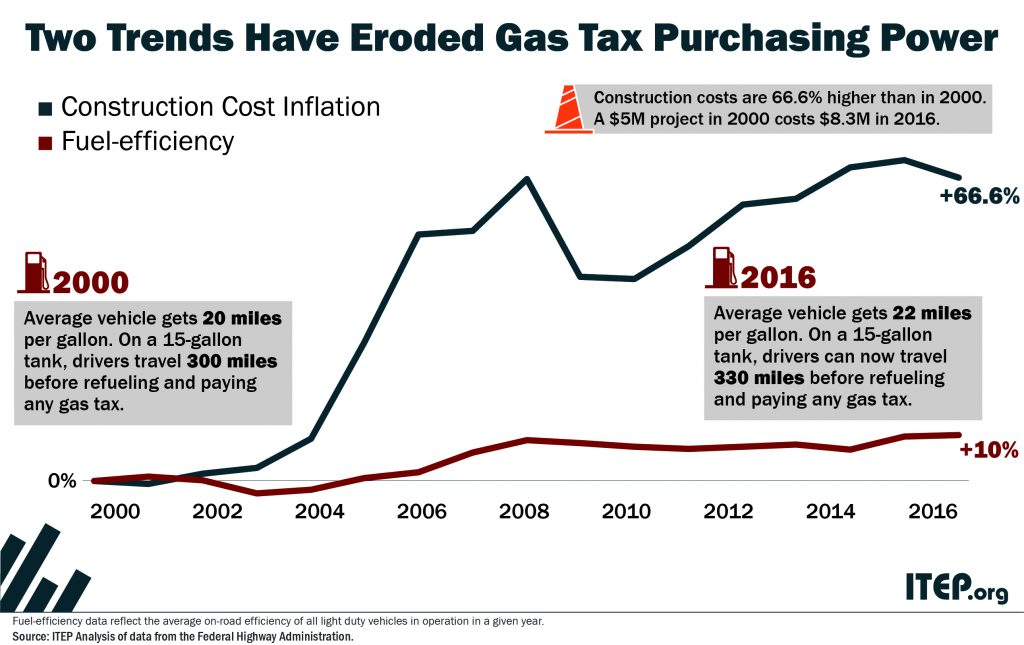
An updated version of this blog was published in April 2019. State tax policy can be a contentious topic, but in recent years there has been a remarkable level of agreement on one tax in particular: the gasoline tax. Increasingly, state lawmakers are deciding that outdated gas taxes need to be raised and reformed to fund infrastructure projects that are vital to their economies.

New Jersey’s new governor, Phil Murphy campaigned on a promise to raise state income taxes on millionaires, a proposal that is supported by 70 percent of the state and was, until recently, backed by New Jersey’s Senate President, Steve Sweeney. In recent months, Sweeney changed his position on the proposed millionaires tax and called for an increase in New Jersey’s corporate tax instead. The idea of hiking taxes on corporations is not a bad one, particularly since corporations received a windfall from the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act. But Sweeney’s new opposition to an income tax hike for the state’s…
State Rundown 5/17: Don’t Bet on Legal Sports Betting Solving State Budget Woes
May 17, 2018 • By ITEP Staff

This week the U.S. Supreme Court opened the door to legal sports gambling in the states (see our What We're Reading section), which will surely be a hot topic in state legislative chambers, but most states currently have more pressing matters before them. The teacher pay crisis made news in North Carolina, Alabama, and nationally. Louisiana, Oregon, and Vermont lawmakers are headed for special sessions over tax and budget issues. And several other states have recently reached or are very near the end of their legislative sessions.
Why Proponents of the Trump-GOP Tax Law Can’t Get their Story Straight
May 16, 2018 • By Steve Wamhoff

If you listened closely to today’s House Ways and Means Committee hearing on the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), you could sense that the witnesses speaking in favor of the new tax law were not 100 percent on the same page. This has been apparent ever since the law was enacted at the end of last year. The economists who speak in favor of the law (including Douglas Holtz-Eakin at today’s hearing) tend to focus on other indicators of its success. They know that the talk of bonuses and raises is nothing more than a desperate corporate PR campaign…
There Is No Evidence That the New Tax Law Is Growing Our Economy or Creating Jobs
May 15, 2018 • By Steve Wamhoff

The House Ways and Means Committee will hold a hearing on the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) Wednesday. Proponents of the law likely will use the occasion to tout its alleged economic benefits and argue that its temporary provisions should be made permanent. The title of the hearing is “Growing Our Economy and Creating Jobs,” but there is little evidence that the law does either of these things.
NC Teachers’ March on Raleigh and the Tax Cuts that Led Them There
May 15, 2018 • By Aidan Davis
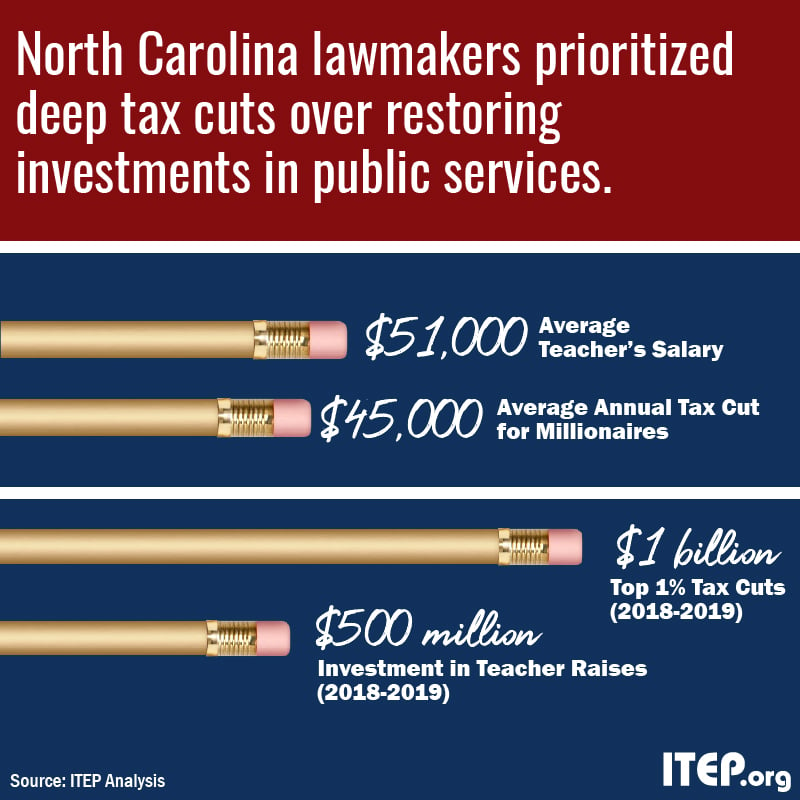
Once again, public school teachers are taking a stand for education and against irresponsible, top-heavy tax cuts that deprive states of the revenue they need to sufficiently fund public services, including education.
No Work Requirements for the Richest 1 Percent — Most of Their Tax Cuts Are for Unearned Income
May 10, 2018 • By Steve Wamhoff

The Trump Administration is pushing to add or strengthen work requirements for programs that benefit low- and middle-income people but holds a different view when it comes to the wealthy. Most tax cuts enjoyed by the richest 1 percent of households under the recently enacted Tax Cuts and Job Act (TCJA) are tax cuts for unearned income.
State Rundown 5/9: Iowa Digs a New Hole as Other States Try to Avoid or Climb Out of Theirs
May 9, 2018 • By ITEP Staff

This week we have news of a destructive tax cut plan finally approved in Iowa just as one was narrowly avoided in Kansas. Tax debates in Minnesota and Missouri will go down to the wire. And residents of Arizona and Colorado are considering progressive revenue solutions to their states' education funding crises.
New Tax Subsidy for Private K-12 Tuition in Massachusetts Creates a Host of Problems
May 9, 2018 • By Carl Davis

Last year’s federal tax cut bill changed 529 college savings accounts in a major way, expanding them so that they can be used as tax shelters by higher-income families who choose to send their children to private K-12 schools. This controversial change was added in the Senate by the slimmest of margins—requiring a tie-breaking vote […]
In the Face of the Trump Administration’s Anti-Immigrant Agenda, We Must Rely on Evidence to Highlight the Contributions of and Dispel Myths About Dreamers
May 4, 2018 • By Misha Hill

Immigrants face tremendous uncertainty and little hope under the Trump Administration. The administration’s actions—banning travel from residents of primarily Muslim countries, the deportation of Christian Iraqi asylum seekers, and the rescission of DACA, the program that provides temporary reprieve to young immigrants; public statements on the value of immigrants from countries like Norway; and leaked […]
Tax Wars: 3 Lessons about Tax Policy from the Star Wars Universe
May 4, 2018 • By Richard Phillips

Even in the universe of Jedi, Death Stars and Ewoks, tax policy plays a surprisingly important role in driving the events of the day. In celebration of Star Wars Day, we just wanted to share some of the little-known tax policy lessons from the Star Wars universe.
Under Pressure, Trump Organization Abandons Risky Sales Tax Avoidance Strategy in New York. Will It Face Penalties for Taxes it Did Not Collect?
May 3, 2018 • By Carl Davis
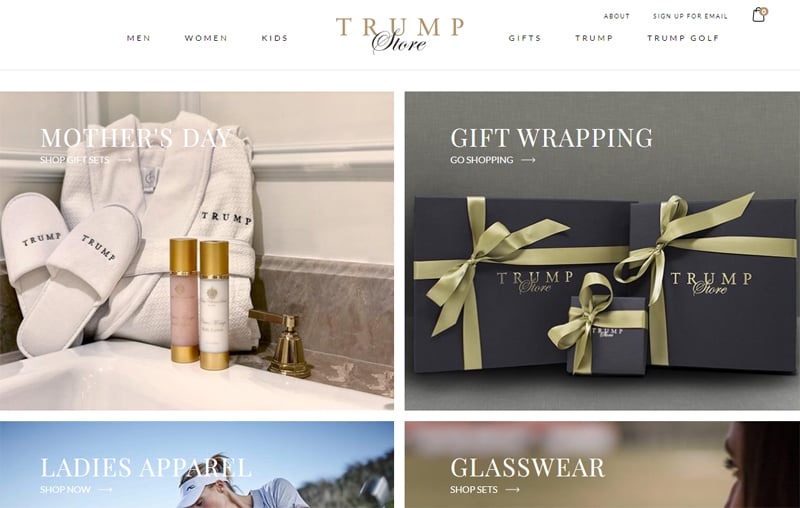
While President Trump was busy publicly shaming Amazon for failing to collect some state and local sales taxes, his own business’s online store was not only failing to collect the same taxes, but was arguably more aggressive than Amazon in refusing to do so. As of last month, TrumpStore.com was not even collecting sales tax in New York State despite having a “flagship retail store” inside Trump Tower, in Manhattan. As ITEP pointed out at that time: “It seems likely that the presence of a New York location should be enough to put TrumpStore.com within reach of New York’s sales…
State Rundown 5/3: Progressive Revenue Solutions to Fiscal Woes Gaining Traction
May 3, 2018 • By ITEP Staff

This week, Arizona teachers continued to strike over pay issues and advocates unveiled a progressive revenue solution they hope to put before voters, while a progressive income tax also gained support as part of a resolution to Illinois's budget troubles. Iowa and Missouri legislators continued to try to push through unsustainable tax cuts before their sessions end. And Minnesota and South Carolina focused on responding to the federal tax-cut bill.
New UK Law May Shut Down the Biggest Tax Havens — Aside from the U.S.
May 2, 2018 • By Steve Wamhoff

The United Kingdom’s parliament has enacted a new law requiring its overseas territories — which include notorious tax havens like Bermuda, the Cayman Islands, and the British Virgin Islands — to start disclosing by 2020 the owners of corporations they register. This could shut down a huge amount of offshore tax evasion and other financial crimes because individuals from anywhere in the world, including the United States. have long been able to set up secret corporations in these tax havens to stash their money.
Apple’s Three-Month Tax Savings under President Trump’s New Tax Law: $1.68 Billion
May 2, 2018 • By Matthew Gardner

By now, it should come as no shock that profitable Fortune 500 corporations are reaping huge benefits from the corporate tax cuts enacted last December. But as first quarter earnings reports are released, we’re learning just how big.
Newly Unveiled Ballot Initiative Aims to Tax Arizona’s Top 1 Percent to Fund Education
May 1, 2018 • By Aidan Davis
Today marks Day 4 of the Arizona teachers’ walkout. After decades of tax cuts and underfunding of public education, education advocates are now driving the debate and urging lawmakers to act. Their newest proposal would raise taxes on incomes above half a million dollars for married couples, or above $250,000 for single taxpayers—that is, the same wealthy taxpayers that just received a generous tax cuts under last year’s federal tax overhaul.
No Need for the MythBusters, the Millionaire Tax Flight Myth is Busted Again
May 1, 2018 • By Dacey Anechiarico

One of the most repeated myths in state tax policy is called “millionaire tax flight,” where millionaires are allegedly fleeing states with high income tax rates for states with lower rates. This myth has been used as an argument in state tax debates for years but Cristobal Young argues in his book, “The Myth of the Millionaire Tax Flight,” that both Democrats and Republicans are “searching for a crisis that does not really exist,” and that there is no evidence to support this myth.
State Rundown 4/27: Arbor Day Brings Some Fruitful Tax Developments, Some Shady Proposals
April 27, 2018 • By ITEP Staff

This Arbor Day week, the seeds of discontent with underfunded school systems and underpaid teachers continued to spread, with walkouts occurring in both Arizona and Colorado. And recognizing the need to see the forest as well as the trees, the Arizona teachers have presented revenue solutions to get to the true root of the problem. In the plains states, tax cut proposals continue to pop up like weeds in Kansas and threaten to spread to Iowa and Missouri, where lawmakers are running out of time but are still hoping their efforts to pass destructive tax cuts will bear fruit.
