
Sales, Gas and Excise Taxes
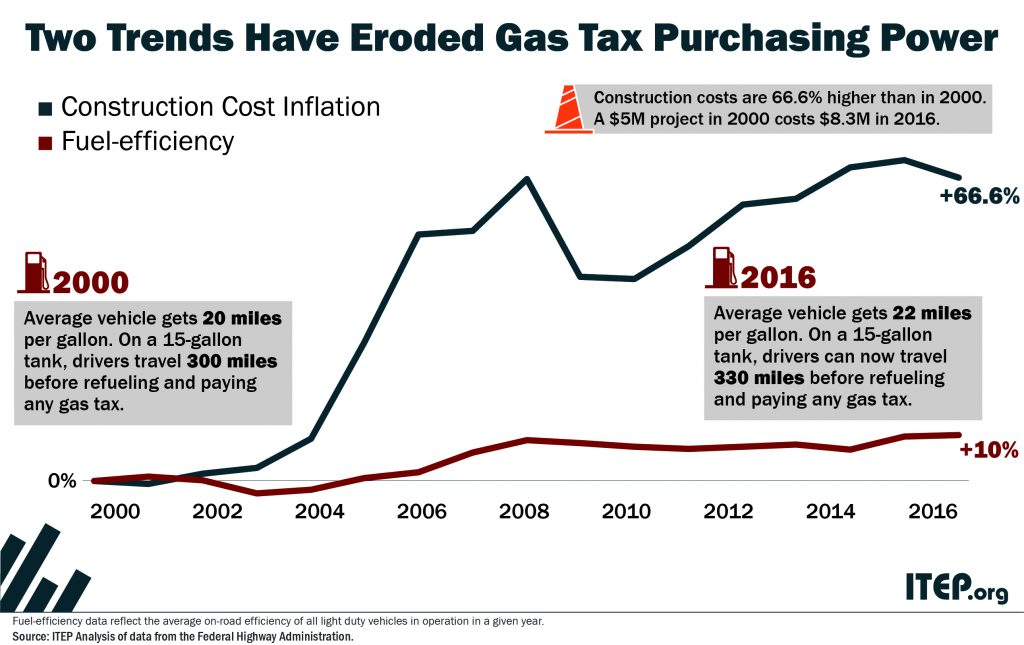
An updated version of this blog was published in April 2019. State tax policy can be a contentious topic, but in recent years there has been a remarkable level of agreement on one tax in particular: the gasoline tax. Increasingly, state lawmakers are deciding that outdated gas taxes need to be raised and reformed to fund infrastructure projects that are vital to their economies.
Many state governments are struggling to repair and expand their transportation infrastructure because they are attempting to cover the rising cost of asphalt, machinery, and other construction materials with fixed-rate gasoline taxes that are rarely increased.
Under Pressure, Trump Organization Abandons Risky Sales Tax Avoidance Strategy in New York. Will It Face Penalties for Taxes it Did Not Collect?
May 3, 2018 • By Carl Davis
While President Trump was busy publicly shaming Amazon for failing to collect some state and local sales taxes, his own business’s online store was not only failing to collect the same taxes, but was arguably more aggressive than Amazon in refusing to do so. As of last month, TrumpStore.com was not even collecting sales tax in New York State despite having a “flagship retail store” inside Trump Tower, in Manhattan. As ITEP pointed out at that time: “It seems likely that the presence of a New York location should be enough to put TrumpStore.com within reach of New York’s sales…
Trends We’re Watching in 2018, Part 5: 21st Century Consumption Taxes
April 20, 2018 • By Misha Hill

We're highlighting the progress of a few newer trends in consumption taxation. This includes using the tax code to discourage consumption of everything from plastic bags to carbon and collecting revenue from emerging industries like ride sharing services and legalized cannabis sales.

The U.S. Supreme Court is scheduled to consider a case next week (South Dakota v. Wayfair, Inc.) that has the potential to significantly improve states and localities’ ability to enforce their sales tax laws on Internet purchases.
What to Expect if the Supreme Court Allows for Online Sales Tax Collection
April 11, 2018 • By Carl Davis

Online shopping is hardly a new phenomenon. And yet states and localities still lack the authority to require many Internet retailers to collect the sales taxes that their locally based, brick and mortar competitors have been collecting for decades.

President Trump’s latest Twitter target, the Amazon Corporation, is now under the microscope for its state and local tax avoidance. In a Thursday tweet, the President claimed that “[u]nlike others, they pay little or no taxes to state & local governments.” Such a statement is a startling reversal for a president who previously said his own ability to avoid paying income taxes “makes me smart.”
Amazon and Other E-Retailers Get a Free Pass from Some Local-Level Sales Taxes
March 26, 2018 • By Carl Davis

A new ITEP analysis reveals that in seven states (Alabama, Alaska, Idaho, Iowa, Mississippi, New Mexico, and Pennsylvania), the nation’s largest e-retailer, Amazon.com, is either not collecting local-level sales taxes or is charging a lower tax rate than local retailers. In other states, such as Colorado and Illinois, Amazon is collecting local tax because it has an in-state presence, but localities cannot collect taxes from other e-retailers based outside the state.
Astonishingly, tax policies in virtually every state make it harder for those living in poverty to make ends meet. When all the taxes imposed by state and local governments are taken into account, every state imposes higher effective tax rates on poor families than on the richest taxpayers.

Sales taxes are one of the most important revenue sources for state and local governments; however, they are also among the most unfair taxes, falling more heavily on low- and middle-income households. Therefore, it is important that policymakers nationwide find ways to make sales taxes more equitable while preserving this important source of funding for public services. This policy brief discusses two approaches to a less regressive sales tax: broad-based exemptions and targeted sales tax credits.
States May Be Finally Learning Their Lesson on Back-To-School Sales Tax Holidays
July 21, 2017 • By Dylan Grundman O'Neill
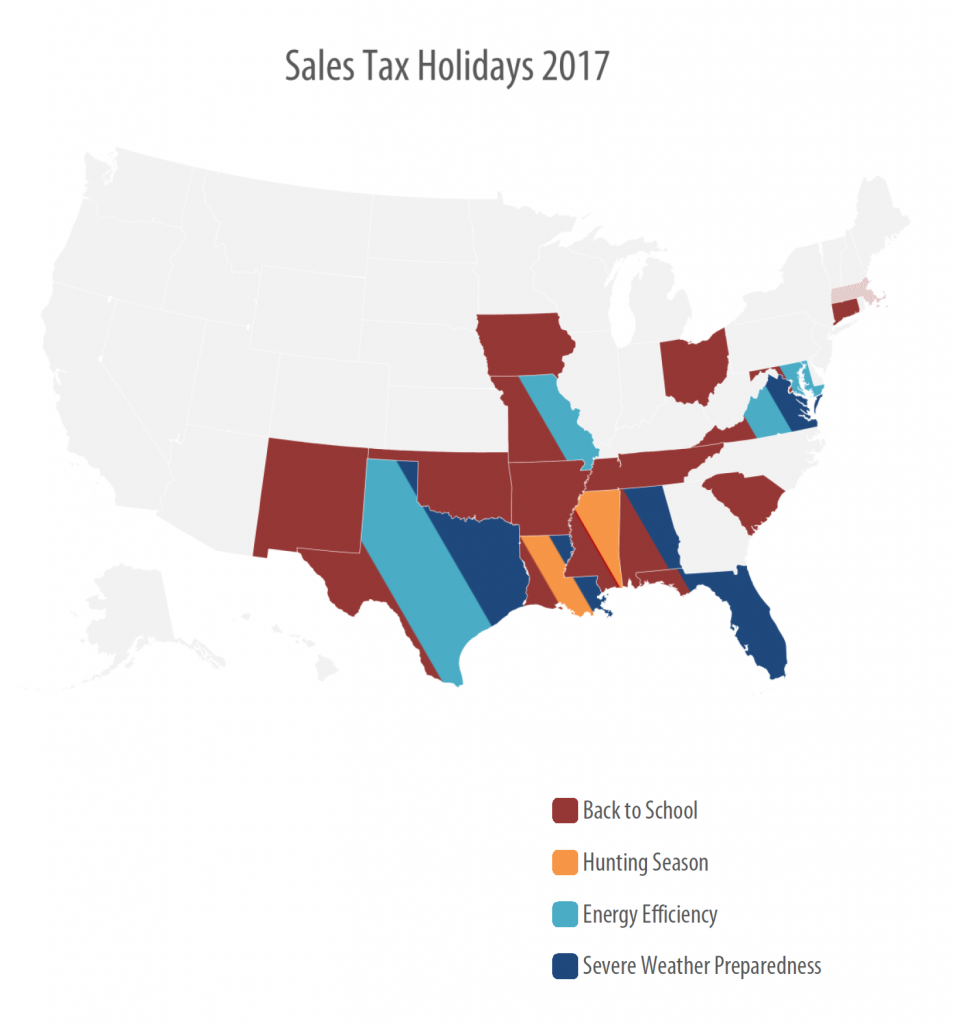
State lawmakers face a dilemma when it comes to sales tax holidays, an attractive and popular policy that nonetheless proves to be a poor choice compared to developing thoughtful, targeted tax policies or investing in well-executed public services. Luckily, word seems to be getting out that the costs associated with these holidays far outweigh their purported benefits.
Sales Tax Holidays: An Ineffective Alternative to Real Sales Tax Reform
July 12, 2017 • By ITEP Staff

Sales taxes are an important revenue source, composing close to half of all state tax revenues. But sales taxes are also inherently regressive because the lower a family’s income, the more the family must spend on goods and services subject to the tax. Lawmakers in many states have enacted “sales tax holidays” (at least 16 states will hold them in 2017), to provide a temporary break on paying the tax on purchases of clothing, school supplies, and other items. While these holidays may seem to lessen the regressive impacts of the sales tax, their benefits are minimal. This policy brief…
Gas Taxes Will Rise in 7 States to Fund Transportation Improvements
June 28, 2017 • By Carl Davis

Summer gas prices are at their lowest level in twelve years, which makes right now a sensible time to ask drivers to pay a little more toward improving the transportation infrastructure they use every day. Seven states will be doing this on Saturday, July 1 when they raise their gasoline tax rates. At the same time, two states will be implementing small gas tax rate cuts.

Many state governments are struggling to repair and expand their transportation infrastructure because they are attempting to cover the rising cost of asphalt, machinery, and other construction materials with fixed-rate gasoline taxes that are rarely increased.

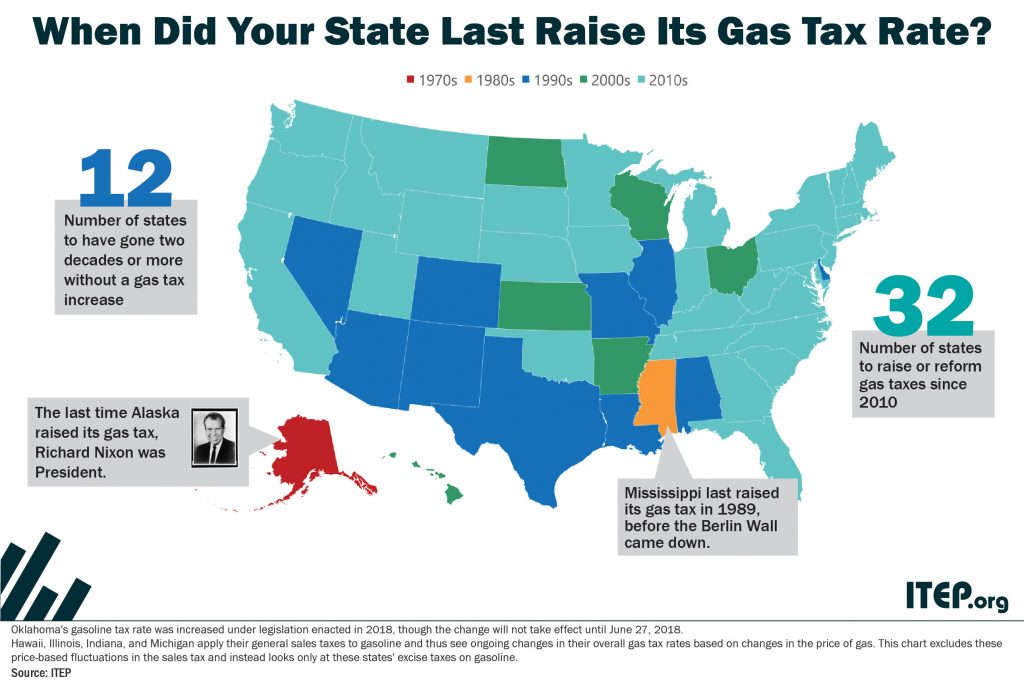
The flawed design of federal and state gasoline taxes has made it exceedingly difficult to raise adequate funds to maintain the nation’s transportation infrastructure. Thirty states and the federal government levy fixed-rate gas taxes where the tax rate does not change even when the cost of infrastructure materials rises or when drivers transition toward more fuel-efficient vehicles and pay less in gas tax. The federal government’s 18.4 cent gas tax, for example, has not increased in over twenty-three years. Likewise, nineteen states have waited a decade or more since last raising their own gas tax rates.
South Carolina’s Gas Tax Deal: Could Have Been Worse, Could Have Been Better
May 12, 2017 • By Dylan Grundman O'Neill

South Carolina lawmakers this week raised the state’s gas tax for the first time in 28 years, a time period that tied for the third-longest in the nation. While the increase was meaningful and hard-fought, the final result remains flawed in ways that could have been easily remedied or avoided. The biggest positive of the […]
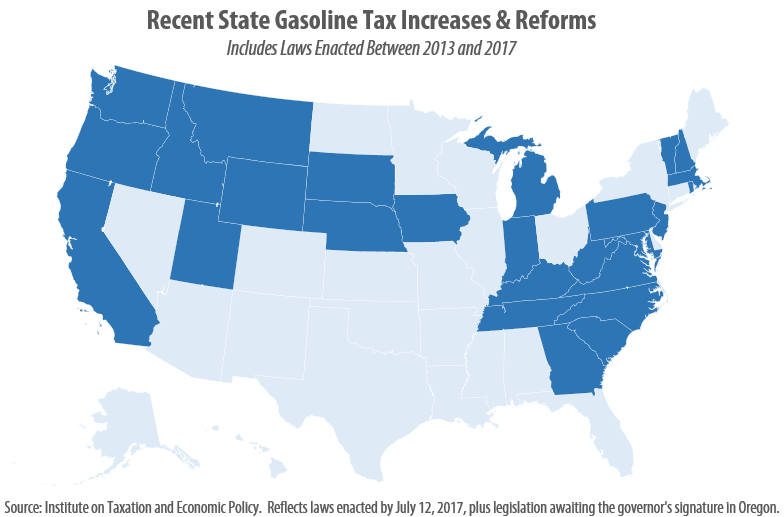
This post was updated July 12, 2017 to reflect recent gas tax increases in Oregon and West Virginia. As expected, 2017 has brought a flurry of action relating to state gasoline taxes. As of this writing, eight states (California, Indiana, Montana, Oregon, South Carolina, Tennessee, Utah, and West Virginia) have enacted gas tax increases this year, bringing the total number of states that have raised or reformed their gas taxes to 26 since 2013.
New Analysis: Average Alaskan Would Pay Less Under Income Tax Than Under Other Fiscal Options
April 23, 2017 • By ITEP Staff
Cutting the Permanent Fund Dividend (PFD) or Implementing a Sales Tax Would Be Costlier than Income Tax for Most Alaskans A new analysis by the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy (ITEP) finds that for most Alaskans, a state income tax would capture less of their income than other revenue-raising alternatives such as cutting the […]
April 1 will mark the longest-running streak that the federal gas tax has remained stagnant, a short analysis from the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy reveals. Saturday will mark the 8,584th day (23.5 years) that the nation’s federal gasoline tax rate has remained at 18.3 cents per gallon. This surpasses the previous record of […]
The April Fool’s Joke Is on Consumers: April 1 Marks Record-Breaking Procrastination on Federal Gas Tax Policy
March 29, 2017 • By Carl Davis
It’s only appropriate that April 1 will mark a new milestone in foolish federal transportation infrastructure policy. On Saturday, the nation’s federal gasoline tax rate will have been stuck at 18.3 cents per gallon for 8,584 days in a row—or more than 23.5 years. This surpasses the previous record of 8,583 days without an update […]
Our ever-changing economy demands that lawmakers update our tax laws to keep pace. Take, for example, the growth of online sales. As recently as six years ago, Amazon, the nation’s biggest online retailer, only collected sales tax on consumer purchases in five states. This meant that state treasuries were missing critical sales tax revenue, a […]
For decades, Amazon.com helped its customers dodge the sales taxes they owed to gain an advantage over its competitors. But as the company’s business strategy has changed, so has its tax collection. As recently as 2011, the nation’s largest e-retailer was collecting sales tax in just 5 states, home to 11 percent of the country’s […]
A growing number of Americans are getting rides or booking short-term accommodations through online platforms such as Uber and Airbnb. This is nothing new in concept; brokers have operated for hundreds of years as go-betweens for producers and consumers. The ease with which this can be done through the Internet, however, has led to millions of people using these services, and to some of the nation's fastest-growing, high-profile businesses. The rise of this on-demand sector, sometimes referred to as the "gig economy" or, by its promoters, the "sharing economy," has raised a host of questions. For state and local governments,…
What to Watch in the States: Modernizing Sales Taxes for a 21st Century Economy
February 15, 2017 • By Misha Hill
This is the fourth installment of our six-part series on 2017 state tax trends. The introduction to this series is available here. State lawmakers often find themselves looking for ways to raise revenue to fund vital public services, fill budget gaps, or pay for the elimination or weakening of progressive taxes. Lately, that search has […]
Every state levies taxes on gasoline and diesel fuel, usually just called "gas taxes." These taxes are an important source of state revenue--particularly for transportation--but their poor design has resulted in sluggish revenue growth that fails to keep pace with state infrastructure needs. This ITEP Policy Brief explains how state gas taxes work, their importance as a transportation revenue source, the problems confronting gas taxes, and the types of gas tax reforms that are needed to overcome these problems.
Sales, excise, and gas taxes are an important source of revenue for states. The sales tax, in fact accounts for half of all state tax revenue. Forty-five states levy broad-based sales taxes, every state levies at least some type of tax on consumption, and all states have a tax on gasoline. But these taxes aren’t without problems.
Sales taxes are inherently regressive—requiring lower- and middle-income taxpayers to spend a larger share of their household budgets in tax than their wealthier neighbors. The gas tax provides funding for infrastructure, but many states have not modernized their gas tax, meaning it no longer raises adequate revenue. ITEP resources on sales, excise and gas taxes provide general and state-specific information about the mechanics of these taxes and options for reform.
