
Michigan
National and 50-State Impacts of House and Senate Tax Bills in 2019 and 2027
December 6, 2017 • By ITEP Staff
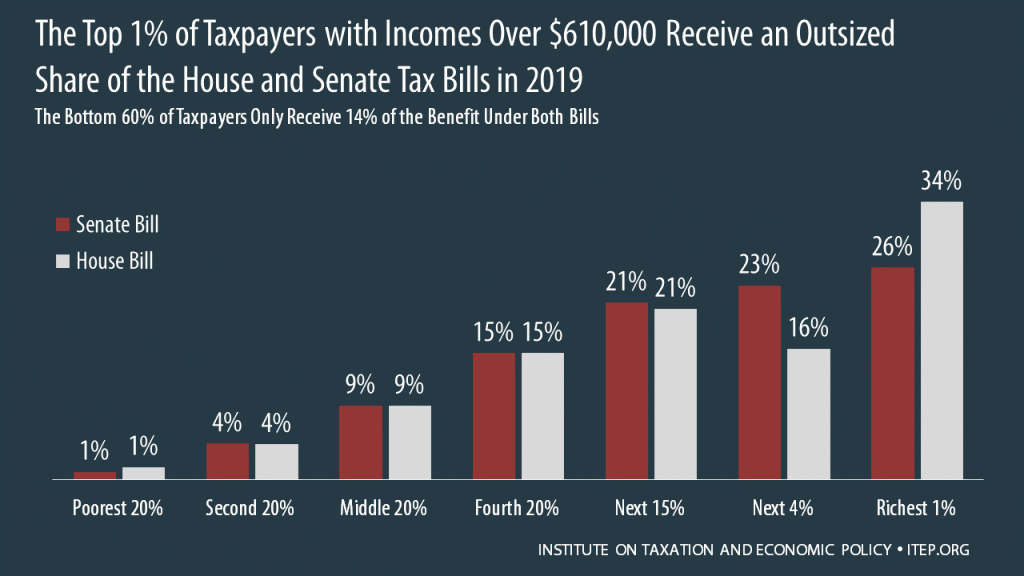
The House passed its “Tax Cuts and Jobs Act” November 16th and the Senate passed its version December 2nd. Both bills would raise taxes on many low- and middle-income families in every state and provide the wealthiest Americans and foreign investors substantial tax cuts, while adding more than $1.4 trillion to the deficit over ten years. National and 50-State data available to download.
Revised Senate Plan Would Raise Taxes on at Least 29% of Americans and Cause 19 States to Pay More Overall
November 18, 2017 • By ITEP Staff
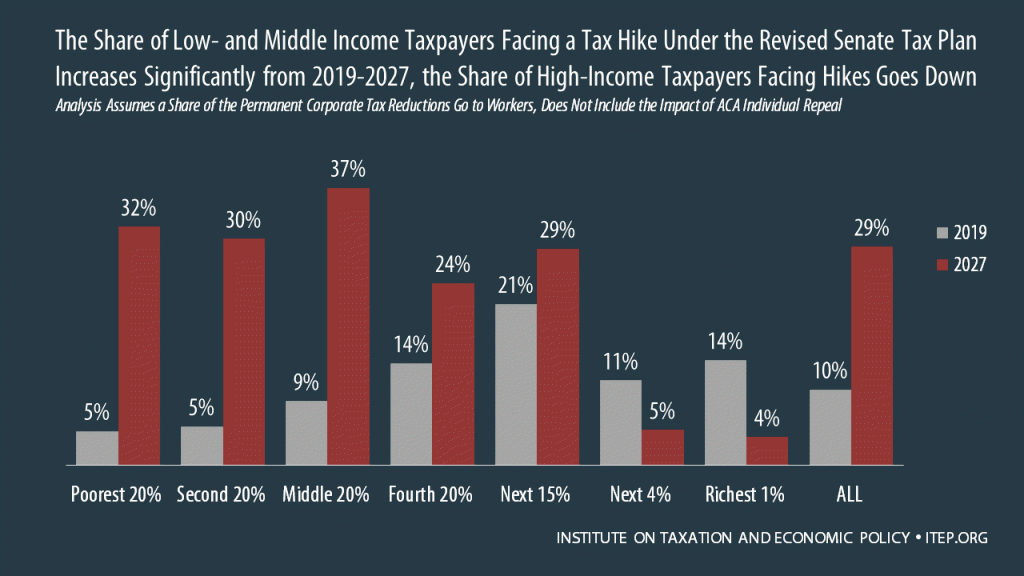
The tax bill reported out of the Senate Finance Committee on Nov. 16 would raise taxes on at least 29 percent of Americans and cause the populations of 19 states to pay more in federal taxes in 2027 than they do today.
How the Revised Senate Tax Bill Would Affect Michigan Residents’ Federal Taxes
November 13, 2017 • By ITEP Staff
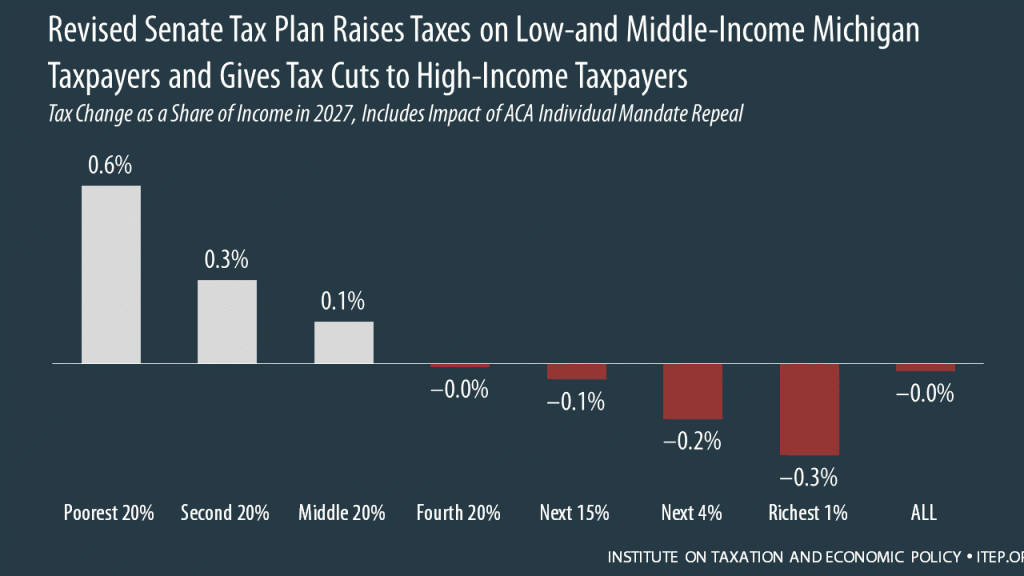
The Senate tax bill released last week would raise taxes on some families while bestowing immense benefits on wealthy Americans and foreign investors. In Michigan, 49 percent of the federal tax cuts would go to the richest 5 percent of residents, and 10 percent of households would face a tax increase, once the bill is fully implemented.
How the House Tax Proposal Would Affect Michigan Residents’ Federal Taxes
November 6, 2017 • By ITEP Staff
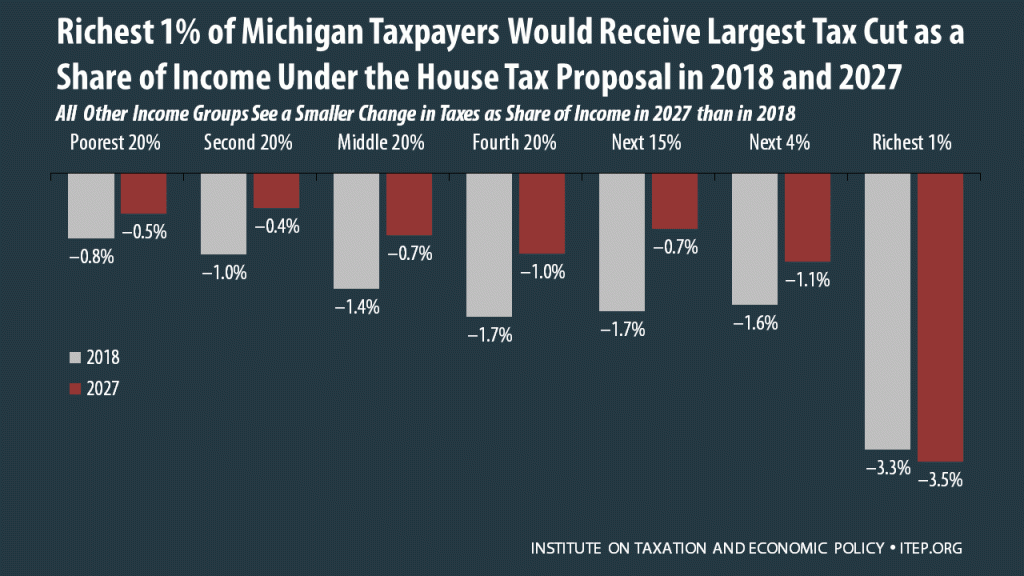
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, which was introduced on November 2 in the House of Representatives, includes some provisions that raise taxes and some that cut taxes, so the net effect for any particular family’s federal tax bill depends on their situation. Some of the provisions that benefit the middle class — like lower tax rates, an increased standard deduction, and a $300 tax credit for each adult in a household — are designed to expire or become less generous over time. Some of the provisions that benefit the wealthy, such as the reduction and eventual repeal of the estate…
Analysis of the House Tax Cuts and Jobs Act
November 6, 2017 • By Matthew Gardner, Meg Wiehe, Steve Wamhoff
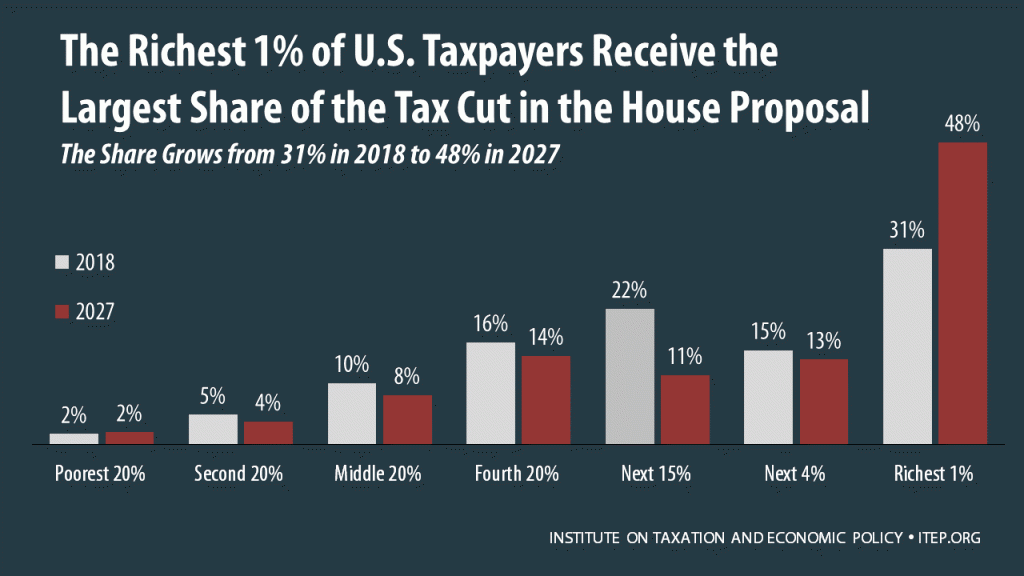
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, which was introduced on Nov. 2 in the House of Representatives, would raise taxes on some Americans and cut taxes on others while also providing significant savings to foreign investors.
State Rundown 11/1: Connecticut Balances Budget, Leaves Tax Code Out of Whack
November 1, 2017 • By ITEP Staff

This week a "historic" but highly problematic budget agreement was finally reached in Connecticut, Michigan lawmakers banned localities from taxing any food or beverages, and Nebraska and North Dakota both got unpleasant news about future revenues. Also see our "what we're reading" section for news on 11 states that have run up long-term fiscal deficits since 2002 and the impacts of flooding on local tax bases.
Trickle-Down Dries Up: States without personal income taxes lag behind states with the highest top tax rates
October 26, 2017 • By Carl Davis, Nick Buffie

Lawmakers who support reducing or eliminating state personal income taxes typically claim that doing so will spur economic growth. Often, this claim is accompanied by the assertion that states without income taxes are booming, and that their success could be replicated by any state that abandons its income tax. To help evaluate these arguments, this study compares the economic performance of the nine states without broad-based personal income taxes to their mirror opposites—the nine states levying the highest top marginal personal income tax rates throughout the last decade.
State Rundown 10/25: Marijuana Taxes a Bright Spot amid Underperforming State Revenues
October 25, 2017 • By ITEP Staff

This week in state tax news saw Alaska begin yet another special session, Louisiana lawmakers holding meetings to begin preparing for the state’s looming (self-imposed) fiscal cliff, and Alabama policymakers beginning a study of school finance (in)adequacy and (in)equity. Meanwhile, state revenue performance is poor well into 2017 in many states, though Montana, Nevada, and Oregon are all enjoying modest but welcome revenue bumps from legalized marijuana.
CNN: How Trump’s Policies Could Hurt the Rust Belt
October 25, 2017
Rust Belt states Ohio, Michigan and Indiana are not home to large populations of $1 million household income earners. Rather, they’re in the middle or bottom of the pack, according a summary from the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy. States with a higher percentage of millionaire earners voted for Hillary Clinton in the 2016 […]
Michigan League for Public Policy: Immigrant families in Michigan: A state profile
October 18, 2017
Michigan immigrants also contribute millions in tax revenue each year, and in doing so help pay for important public programs and infrastructure in the state. In 2015 for example, undocumented immigrants in Michigan paid approximately $86.6 million in state and local taxes. Young undocumented immigrants also contribute their share in taxes. In 2015, DACA-eligible immigrants […]
State Rundown 10/18: Ballot Initiative Efforts Being Finalized
October 18, 2017 • By ITEP Staff

Ballot initiatives relating to taxes made news around the country this week, with Oregon voters to consider reversing new health care taxes, Washingtonians to vote on improving education funding, and Nebraskans to potentially vote on a state tax credit for school property taxes. Meanwhile, multiple states are finalizing their proposals to lure Amazon to build a new headquarters in their state, often through the use of massive tax subsidies. And in our "What We're Reading" section we have sobering news from Moody's Investors Service on states' struggles to fund their infrastructure and save for the next recession.
State Rundown 10/13: Soda Taxes, Business Subsidies, and Gas Taxes Considered in Several States
October 13, 2017 • By ITEP Staff

A comprehensive tax study is underway in Arkansas this week as other states hone in on more specific issues. Soda taxes hit setbacks in Illinois and Michigan, business tax subsidies faced scrutiny in Iowa and Missouri, and gas tax update efforts are underway in Mississippi and North Dakota.
Benefits of GOP-Trump Framework Tilted Toward the Richest Taxpayers in Each State
October 4, 2017 • By Steve Wamhoff
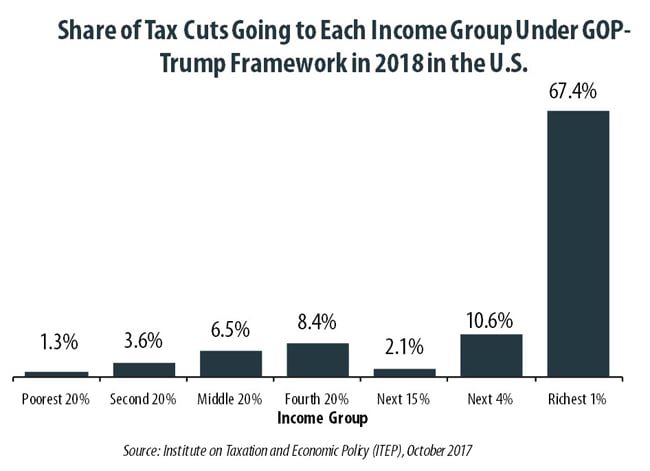
The “tax reform framework” released by the Trump administration and Congressional Republican leaders on September 27 would affect states differently, but every state would see its richest residents grow richer if it is enacted. In all but a handful of states, at least half of the tax cuts would flow to the richest one percent of residents if the framework took effect.
GOP-Trump Tax Framework Would Provide Richest One Percent in Michigan with 62.5 Percent of the State’s Tax Cuts
October 4, 2017 • By ITEP Staff
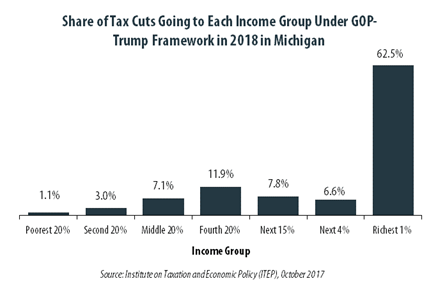
The “tax reform framework” released by the Trump administration and congressional Republican leaders on September 27 would not benefit everyone in Michigan equally. The richest one percent of Michigan residents would receive 62.5 percent of the tax cuts within the state under the framework in 2018. These households are projected to have an income of at least $502,500 next year. The framework would provide them an average tax cut of $76,560 in 2018, which would increase their income by an average of 4.7 percent.

Sales taxes are one of the most important revenue sources for state and local governments; however, they are also among the most unfair taxes, falling more heavily on low- and middle-income households. Therefore, it is important that policymakers nationwide find ways to make sales taxes more equitable while preserving this important source of funding for public services. This policy brief discusses two approaches to a less regressive sales tax: broad-based exemptions and targeted sales tax credits.
In Michigan 38.6 Percent of Trump’s Proposed Tax Cuts Go to People Making More than $1 Million
August 17, 2017 • By ITEP Staff
A tiny fraction of the Michigan population (0.2 percent) earns more than $1 million annually. But this elite group would receive 38.6 percent of the tax cuts that go to Michigan residents under the tax proposals from the Trump administration. A much larger group, 43.3 percent of the state, earns less than $45,000, but would receive just 4.2 percent of the tax cuts.
Nearly Half of Trump’s Proposed Tax Cuts Go to People Making More than $1 Million Annually
August 17, 2017 • By ITEP Staff
A tiny fraction of the U.S. population (one-half of one percent) earns more than $1 million annually. But in 2018 this elite group would receive 48.8 percent of the tax cuts proposed by the Trump administration. A much larger group, 44.6 percent of Americans, earn less than $45,000, but would receive just 4.4 percent of the tax cuts.
State Rundown 7/27: State Legislative Debates Winding Down but Tax Talk Continues
July 27, 2017 • By ITEP Staff

While only a few states still remain mired in overtime budget debates, there is plenty of budget and tax news from around the country this week. Efforts are underway to repeal gas tax increases in California and challenge a local income tax in Seattle, Washington. And New Jersey legislators' law to modernize its tax code to tax Airbnb rentals has been vetoed for now.
Trump Tax Proposals Would Provide Richest One Percent in Michigan with 53.2 Percent of the State’s Tax Cuts
July 20, 2017 • By ITEP Staff
Earlier this year, the Trump administration released some broadly outlined proposals to overhaul the federal tax code. Households in Michigan would not benefit equally from these proposals. The richest one percent of the state’s taxpayers are projected to make an average income of $1,621,600 in 2018. They would receive 53.2 percent of the tax cuts that go to Michigan’s residents and would enjoy an average cut of $120,010 in 2018 alone.
Trump’s $4.8 Trillion Tax Proposals Would Not Benefit All States or Taxpayers Equally
July 20, 2017 • By Matthew Gardner, Steve Wamhoff
The broadly outlined tax proposals released by the Trump administration would not benefit all taxpayers equally and they would not benefit all states equally either. Several states would receive a share of the total resulting tax cuts that is less than their share of the U.S. population. Of the dozen states receiving the least by this measure, seven are in the South. The others are New Mexico, Oregon, Maine, Idaho and Hawaii.
Sales Tax Holidays: An Ineffective Alternative to Real Sales Tax Reform
July 12, 2017 • By ITEP Staff
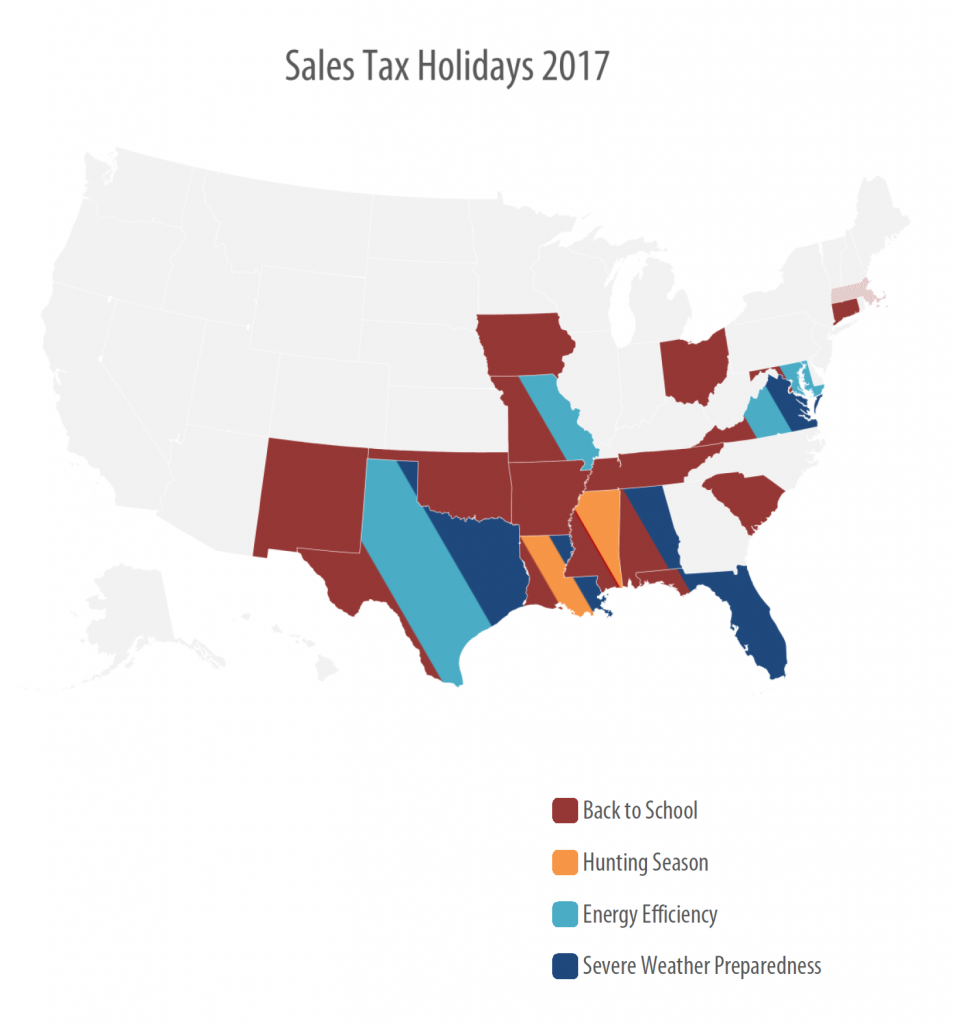
Sales taxes are an important revenue source, composing close to half of all state tax revenues. But sales taxes are also inherently regressive because the lower a family’s income, the more the family must spend on goods and services subject to the tax. Lawmakers in many states have enacted “sales tax holidays” (at least 16 states will hold them in 2017), to provide a temporary break on paying the tax on purchases of clothing, school supplies, and other items. While these holidays may seem to lessen the regressive impacts of the sales tax, their benefits are minimal. This policy brief…

The flawed design of federal and state gasoline taxes has made it exceedingly difficult to raise adequate funds to maintain the nation’s transportation infrastructure. Thirty states and the federal government levy fixed-rate gas taxes where the tax rate does not change even when the cost of infrastructure materials rises or when drivers transition toward more fuel-efficient vehicles and pay less in gas tax. The federal government’s 18.4 cent gas tax, for example, has not increased in over twenty-three years. Likewise, nineteen states have waited a decade or more since last raising their own gas tax rates.
State Rundown 6/14: Some States Wrapping Up Tax Debates, Others Looking Ahead to Next Round
June 14, 2017 • By ITEP Staff

This week lawmakers in California and Nevada resolved significant tax debates, while budget and tax wrangling continued in West Virginia, and structural revenue shortfalls were revealed in Iowa and Pennsylvania. Airbnb increased the number of states in which it collects state-level taxes to 21. We also share interesting reads on state fiscal uncertainty, the tax experiences of Alaska and Wyoming, the future of taxing robots, and more!
State Rundown 5/10: Spring Tax Debates at Different Stages in Different States
May 10, 2017 • By Meg Wiehe

This week saw a springtime mix of state tax debates in all stages of life. In West Virginia and Louisiana, debates over income tax reductions and comprehensive tax reform are full of vigor. Other debates that bloomed earlier are now settled, such as Florida‘s now-complete budget debate and the more florid debates over gas taxes […]
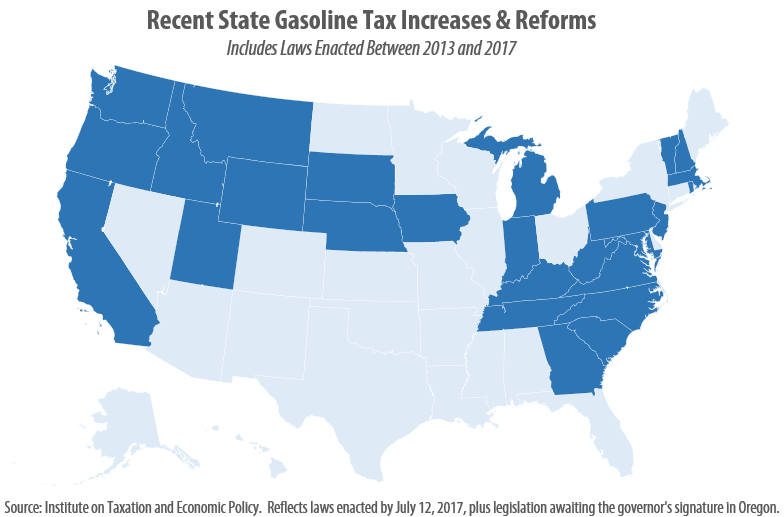
This post was updated July 12, 2017 to reflect recent gas tax increases in Oregon and West Virginia. As expected, 2017 has brought a flurry of action relating to state gasoline taxes. As of this writing, eight states (California, Indiana, Montana, Oregon, South Carolina, Tennessee, Utah, and West Virginia) have enacted gas tax increases this year, bringing the total number of states that have raised or reformed their gas taxes to 26 since 2013.
