
Property Taxes
In the face of immense uncertainty around looming federal tax and budget decisions, many of which could threaten state budgets, state lawmakers have an opportunity to show up for their constituents by raising and protecting the revenue needed to fund shared priorities. Lawmakers have a choice: advance tax policies that improve equity and help communities thrive, or push tax policies that disproportionately benefit the wealthy, drain funding for critical public services, and make it harder for most families to get ahead.
Policymakers Unwisely Propose Cutting Property Taxes in Favor of Sales Taxes
January 14, 2025 • By Rita Jefferson

Lawmakers across the country are taking aim at property taxes with a new strategy: raising sales taxes instead. Doing so would create a regressive tax shift that puts unfair burdens on renters and reduces the strength of local government revenues.
How Local Governments Raise Revenue — and What it Means for Tax Equity
December 5, 2024 • By Galen Hendricks, Rita Jefferson
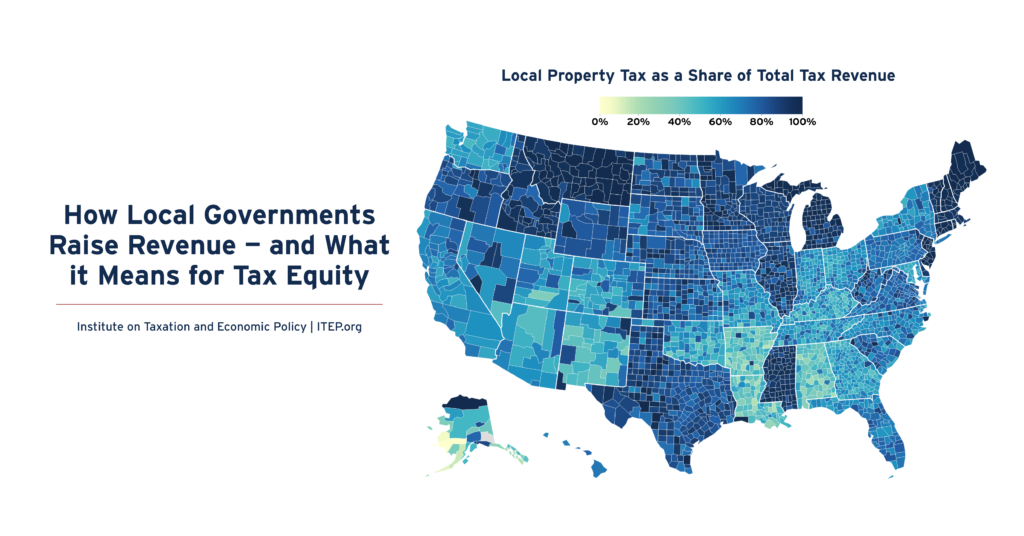
Local taxes are key to thriving communities. One in seven tax dollars in the U.S.—about $886 billion annually—is levied by local governments in support of education, infrastructure, public health, and other priorities. Three fourths of this funding comes from property taxes, 18 percent comes from sales and excise taxes, and six percent comes from income taxes.
On Election Day, Voters Across the Country Chose to Invest in Their States & Communities
November 19, 2024 • By Kamolika Das

On election day, voters across the country — in states red and blue and communities rural and urban — approved a wide range of state and local ballot measures on taxation and public investment. The success of these measures clearly shows that voters are willing to invest in public priorities that feel tangible and close to home.

Billionaires and businesses have too much power in Washington. Tax revenue is needed to pay for things we all need. If we want economic justice, racial justice and climate justice, we must have tax justice.
2024 Local Tax Ballot Measures: Voters in Dozens of Communities Will Shape Local Policy
October 17, 2024 • By Rita Jefferson

Next month, voters across the country will weigh in on many local ballot measures that will have a profound effect on the adequacy of our local tax systems and whether cities and communities can fund public needs. These are in addition to statewide ballot questions, many of which have local implications this year.

Many cities, counties, and townships across the country are in a difficult, or at least unstable, budgetary position. Localities are responding to these financial pressures in a variety of ways with some charging ahead with enacting innovative reforms like short-term rental and vacancy taxes, and others setting up local tax commissions to study the problem.

Major tax cuts were largely rejected this year, but states continue to chip away at income taxes. And while property tax cuts were a hot topic across the country, many states failed to deliver effective solutions to affordability issues.
Property Tax Circuit Breakers Can Help States Create More Equitable Tax Codes
June 24, 2024 • By Brakeyshia Samms

Well-designed property tax circuit breaker programs allow states to reduce the impact that property taxes have on the upside-down tilt of their tax codes.

Juneteenth is a reminder of the hard-fought victories that helped Black Americans secure their delayed freedom, justice, and suffrage. And in the chapters about tax policy, the tales are no less fraught. From America’s prologue to the last paragraph of the Civil War, governments raised more tax revenue from the taxation of Black bodies than […]
Tax History Matters: A Q&A with Professor Andrew Kahrl, Author of ‘The Black Tax’
April 24, 2024 • By Brakeyshia Samms

In his new book, The Black Tax: 150 Years of Theft, Exploitation, and Dispossession in America, Professor Andrew Kahrl walks readers through the history of the property tax system and its structural defects that have led to widespread discrimination against Black Americans.
Ahead of the ‘Bring Chicago Home’ Vote, Remember That Local Mansion Taxes are Tried and Tested
March 14, 2024 • By Andrew Boardman, Kamolika Das

As Chicago and other localities look for ways to shore up resources for critical public investments, it's important to remember that over a dozen cities and counties have already benefited from policies like mansion taxes.
Local Mansion Taxes: Building Stronger Communities with Progressive Taxes on High-Value Real Estate
March 14, 2024 • By Andrew Boardman

More than one dozen cities and counties levy progressive taxes on high-price real estate transactions — sometimes called mansion taxes — and over a dozen more are considering such policies. By asking buyers and sellers with greater financial means to contribute more to the common good, these policies are equipping communities with resources to make progress on critical challenges of local and national concern.
America Used to Have a Wealth Tax: The Forgotten History of the General Property Tax
November 2, 2023 • By Carl Davis, Eli Byerly-Duke

Over time, broad wealth taxes were whittled away to become the narrower property taxes we have today. These selective wealth taxes apply to the kinds of wealth that make up a large share of middle-class families’ net worth (like homes and cars), but usually exempt most of the net worth of the wealthy (like business equity, bonds, and pooled investment funds).The rationale for this pared-back approach to wealth taxation has grown weaker in recent decades as inequality has worsened, the share of wealth held outside of real estate has increased, and the tools needed to administer a broad wealth tax…
2023’s State and Local Tax Ballot Measures: Voters to Weigh in on Property Taxes, Wealth Taxes, and More
October 24, 2023 • By Jon Whiten

Even in this slow year for candidate elections, the decisions that voters in states and cities make could strengthen or weaken revenue for needs in their communities and could change how taxes are distributed across the income spectrum. In the places where tax fairness is on the ballot, much is at stake.
Circuit Breakers and Other Income-Based Property Tax Programs in 2023
May 19, 2023 • By ITEP Staff
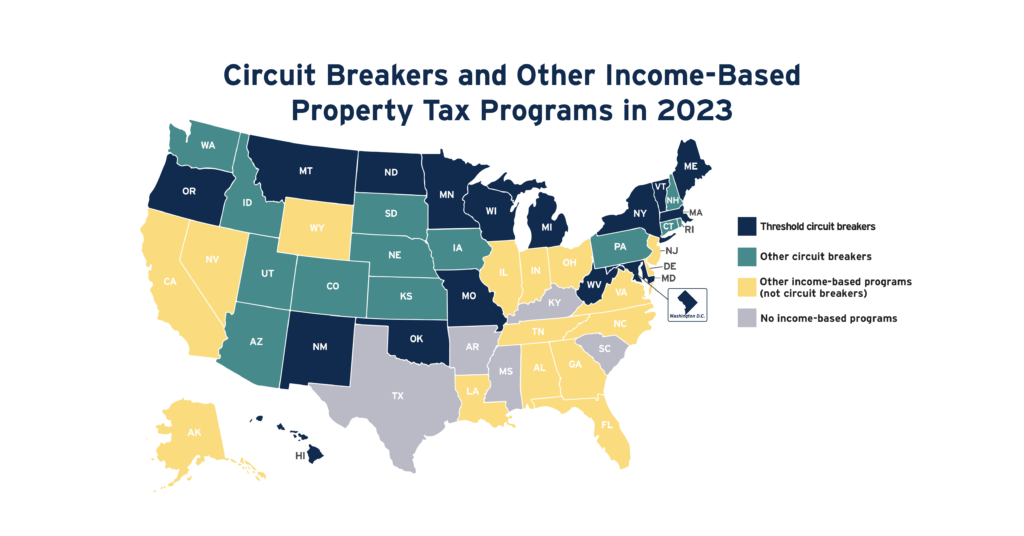
No tax cut offers a more targeted solution to property tax affordability problems than circuit breaker credits. This is because circuit breakers are the only tools for reducing property taxes that measure the affordability of property taxes relative to families’ ability to pay. Circuit breakers protect families from property tax “overload” much like how traditional […]
States are Talking About the Wrong Kind of Property Tax Cuts
May 11, 2023 • By Brakeyshia Samms, Carl Davis

Concerns over property tax affordability have been at the forefront this year as housing prices have climbed and property tax bills have often increased along with them. As lawmakers mull a range of property tax cuts, circuit breakers are the best possible approach—and these policies are receiving far too little attention in the states.
Preventing an Overload: How Property Tax Circuit Breakers Promote Housing Affordability
May 11, 2023 • By Brakeyshia Samms, Carl Davis

Circuit breaker credits are the most effective tool available to promote property tax affordability. These policies prevent a property tax “overload” by crediting back property taxes that go beyond a certain share of income. Circuit breakers intervene to ensure that property taxes do not swallow up an unreasonable portion of qualifying households’ budgets.
State Lawmakers Should Break the 2023 Tax Cut Fever Before It’s Too Late
January 18, 2023 • By Miles Trinidad

Despite mixed economic signals for 2023, including a possible recession, many state lawmakers plan to use temporary budget surpluses to forge ahead with permanent, regressive tax cuts that would disproportionately benefit the wealthy at the expense of low- and middle-income households. These cuts would put state finances in a precarious position and further erode public investments in education, transportation and health, all of which are crucial for creating inclusive, vibrant communities where everyone, not just the rich, can achieve economic security and thrive. In the event of an economic downturn, these results would be accelerated and amplified.
Tax Foundation’s ‘State Business Tax Climate Index’ Bears Little Connection to Business Reality
October 31, 2022 • By Carl Davis, Matthew Gardner

The big problem with the Index is that it peddles a solution that not only falls short of the goal of generating business investment, but one that actively harms state lawmakers’ ability to provide the kinds of public goods – like good schools and modern, efficient transportation networks – that businesses need and want.
Racial Discrimination in Home Appraisals Is a Problem That’s Now Getting Federal Attention
March 31, 2022 • By Brakeyshia Samms

With both assessments and appraisals being unfair, homeowners of color are stuck between a rock and a hard place when it comes to determining the worth of what is, for most homeowners, their most valuable asset.
The Pendulum Is Swinging Toward Tax Justice
January 5, 2022 • By ITEP Staff, Jenice Robinson, Kamolika Das

Tax justice is deeply connected to the movements for equality and racial justice. Progressive tax policy can ensure more of us share in the prosperous economy that our collective tax dollars make possible. It can mitigate economic disparities by class and race. And it can make sure the government has the resources it needs to function for all of us.
New Census Data Highlight Need for Permanent Child Tax Credit Expansion
September 14, 2021 • By Neva Butkus

The status quo was a choice, but the Census data released today shows that different policy choices can create drastically different outcomes for children and families. It is time for our state and federal legislators to put people first when it comes to recovery.
Why Local Governments Need an Anti-Racist Approach to Property Assessments
August 5, 2021 • By Ambika Sinha

Property taxes are among the oldest and most relied upon form of local taxes. Revenue raised from these taxes funds education, firefighting, law enforcement, street and infrastructure maintenance, and other essential services. Though all members of the community enjoy these public goods, homeowners of color, especially Black families, pay more as a share of home value in property taxes than their white counterparts.
Gentrification and the Property Tax: How Circuit Breakers Can Help
April 27, 2021 • By David Crawford

Property tax circuit breakers are effective because they provide property tax relief to families whose property taxes surpass a certain percentage of their income. If a family in a gentrifying area sees their property tax bill (or their rent) surge to an unaffordable level, a circuit breaker credit kicks in to offer relief. This targeted approach assists low- and middle-income families without significantly reducing overall tax revenue.
