
Tax Reform Options and Challenges
Fact-Checking Trump’s State of the Union Address on Tax Issues
January 31, 2018 • By Steve Wamhoff

Here are some claims the President made during his State of the Union address, along with the facts.
Moody’s and Conservative Economists Agree: The Trump Corporate Tax Cut Is Not Helping Workers
January 26, 2018 • By Steve Wamhoff

Moody’s does not believe that corporate tax cuts are trickling down to working people as bonuses and pay raises. The real problem with the corporate PR campaign is that even those economists who supported Trump’s corporate tax cut and claimed it would help workers do not believe that it works this way.

States’ attempts to work around the new federal tax law and ensure their residents continue to maximally benefit from state and local tax (SALT) deductions have been in the news since the beginning of the year. At a panel discussion for tax professionals in Washington Thursday, Thomas West, tax legislative counsel at the Treasury Department, cast doubt on proposed work-around schemes that would convert state income tax payments into “charitable contributions.”

The Walt Disney Corporation announced this week that in the wake of the new tax bill’s passage, it will spend $125 million on one-time bonuses and $50 million on an education program for some employees, all in 2018. This $175 million spending commitment is notable for two reasons: it’s temporary, and it’s a drop in the bucket for a company that’s likely to see annual tax savings of $1.2 billion a year and has already committed to a $50 billion-plus corporate acquisition of 21st Century Fox’s assets.
Repealing, or Working Around, the Cap on State and Local Tax Deductions Would Make the Trump-GOP Tax Law Even More Unfair
January 17, 2018 • By Steve Wamhoff

A bipartisan proposal in Congress to eliminate the new $10,000 cap on federal deductions for state and local taxes (SALT) would cost more than $86 billion in 2019 alone and two-thirds of the benefits would go to the richest 1 percent of households. Unfortunately, “work around” proposals in some states to allow their residents to avoid the new federal cap would likely have the same regressive effect on the overall tax code.
The Problems with State Workarounds to the Federal SALT Deduction
January 12, 2018 • By Alan Essig

From the outset, states—particularly wealthier states—objected to the GOP’s proposal to limit SALT deductions in part because it reduces the amount of state and local taxes that the federal government essentially picks up for taxpayers (by allowing a SALT deduction, the federal government is, in effect, paying part of taxpayers’ state and local tax bill), which could hinder states’ ability to raise revenue. Simply focusing on SALT, though, misses the bigger picture. The fact remains that the overall tax bill disproportionately benefits higher-income taxpayers even with the $10,000 SALT cap in place. Responding to federal tax cuts that disproportionately benefit…
The Walmart Smiley Face Is Lying: Corporate Tax Cuts Are Not Causing Pay Raises and Bonuses
January 12, 2018 • By Steve Wamhoff

Last night, Yahoo reported that 81 corporations had announced pay raises and bonuses that they claim result from the Trump-GOP tax law’s reduction in the official corporate tax rate from 35 percent to 21 percent. Of these 81 corporations, 13 were included in ITEP’s most recent corporate tax study, which focuses on the Fortune 500 companies that were profitable every year from 2008 through 2015. These 13 companies had a combined effective tax rate of just 19.1 percent, which undermines the idea that the federal corporate tax rate was holding back their ability to pay workers.
New Tax Breaks for Craft Beer Are a Drop in the Barrel: 76 percent of Tax Bill’s Beer Tax Cut Goes to a Handful of the Biggest Producers
January 10, 2018 • By Matthew Gardner

The $1.5 trillion tax cut that took effect on Jan.1 was never really going to be about small businesses, despite President Trump’s transparently false claims to the contrary. However, one economic sector still appears happy, for now, to hoist a mug to Congress’s successful sleight of hand: craft breweries.
Corporate America, You Just Got a $650 Billion Tax Cut! What Are You Going to Do Next?
December 22, 2017 • By Matthew Gardner

While many Fortune 500 CEO’s likely had to restrain themselves from preemptively shouting “we’re going to Disneyland” in an homage to the Disney Corporation’s trademark ad spot involving the winner of each year’s Super Bowl, it’s pretty understandable that several of them—including known tax avoiders AT&T, Boeing, Comcast and Wells Fargo—would preemptively make grandiose promises that they will reserve part of their tax cuts for the little people who made it all possible.
Final Tax Bill Hits Parents of College Students Harder than Other Taxpayers
December 19, 2017 • By Steve Wamhoff

While many provisions targeting higher education in previous versions of the tax plan were eventually dropped, little thought has been given to how the bill still raises taxes on parents at the time they are trying to pay for college tuition.
Corker Claims Provisions Benefiting Him Could Not Have Changed His Vote Because He Never Read the Bill
December 18, 2017 • By Matthew Gardner

Many Republicans who had previously claimed to be deficit hawks have been cheerfully supportive of major tax-cutting legislation as it has moved forward this fall. But one Republican Senator, Bob Corker of Tennessee, has taken a defiant stance on the issue, insisting that “passing off increased debt to future generations” would be a deal-breaker for him. When the Senate passed its version of the tax plan last week, Corker was the only Republican to vote No.
Final GOP-Trump Bill Still Forces California and New York to Shoulder a Larger Share of Federal Taxes Under Final GOP-Trump Tax Bill; Texas, Florida, and Other States Will Pay Less
December 17, 2017 • By Meg Wiehe
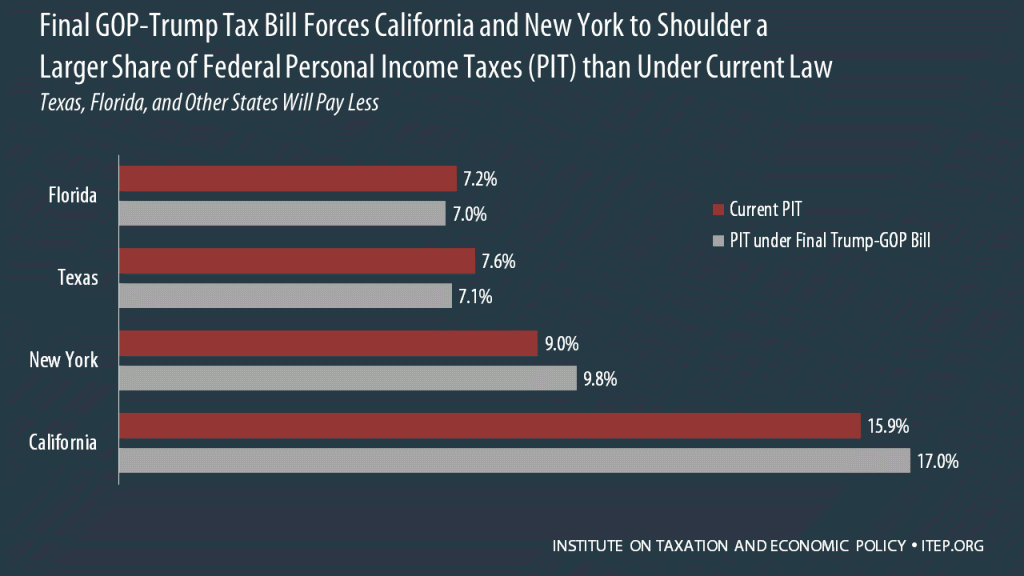
Residents of California and New York pay a large amount of the nation’s federal personal income taxes relative to their share of the population. As illustrated by the table below, the final GOP-Trump tax bill expected to be approved this week would substantially increase the share of total federal personal income taxes (PIT) paid by both states. Connecticut, Maryland, Massachusetts, and New Jersey would also see their share of federal PIT increase.
The Final Trump-GOP Tax Plan: National and 50-State Estimates for 2019 & 2027
December 16, 2017 • By ITEP Staff
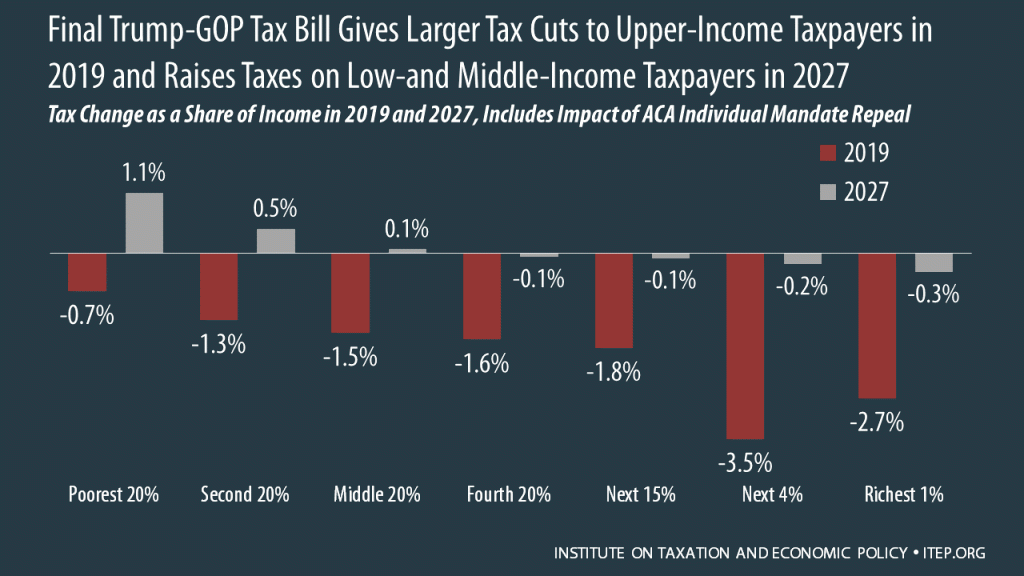
The final Trump-GOP tax law provides most of its benefits to high-income households and foreign investors while raising taxes on many low- and middle-income Americans. The bill goes into effect in 2018 but the provisions directly affecting families and individuals all expire after 2025, with the exception of one provision that would raise their taxes. To get an idea of how the bill will affect Americans at different income levels in different years, this analysis focuses on the bill’s impacts in 2019 and 2027.
Final Tax Bill Reported to Provide Senator Rubio With Much Smaller Improvement for Children than He Demanded
December 15, 2017 • By Steve Wamhoff
The latest news on the GOP tax bill is that, in order to secure the vote of Senator Marco Rubio, Republican leaders have agreed to expand the child tax credit — but only by a fraction of the amount that Rubio initially demanded.
GOP Leaders Scrounge Up Money to Lower Top Tax Rate for the Rich But Not to Help Low-Income Working Families with Children
December 15, 2017 • By Meg Wiehe
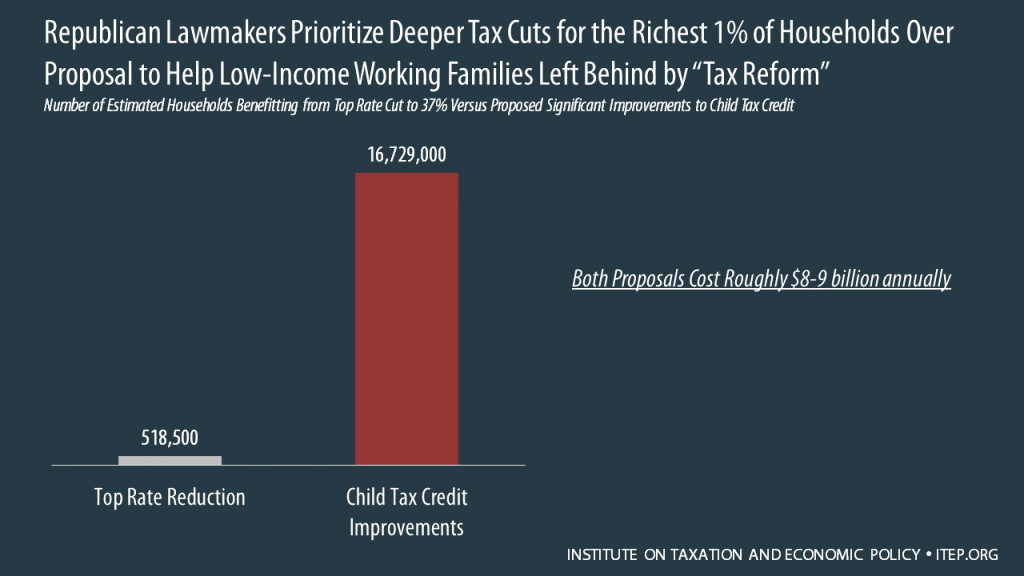
Republican leaders who rejected a proposal to have corporations pay a single percentage point higher tax rate to benefit families with children have tapped the exact same source of savings to provide more breaks for the richest 1 percent of taxpayers. The table below compares the number and share of households nationally and in all 50-states who would benefit from the proposal to reduce taxes for working families with children versus the ”compromise” to cut the top individual tax rate -- below either the House or Senate version – to 37 percent for couples with incomes above $1 million.
ITEP researchers have produced new reports and analyses that look at various pieces of the tax bill, including: the share of tax cuts that will go to foreign investors; how the plans would affect the number of taxpayers that take the mortgage interest deduction or write off charitable contributions, and remaining problems with the bill in spite of proposed compromises on state and local tax deductions.
Tax Bill Would Increase Abuse of Charitable Giving Deduction, with Private K-12 Schools as the Biggest Winners
December 14, 2017 • By Carl Davis
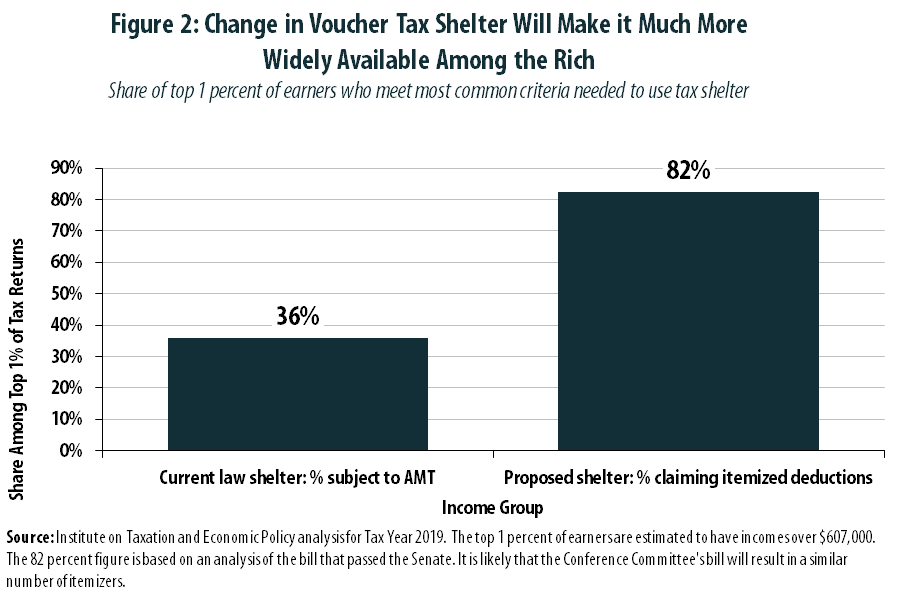
In its rush to pass a major rewrite of the tax code before year’s end, Congress appears likely to enact a “tax reform” that creates, or expands, a significant number of tax loopholes.[1] One such loophole would reward some of the nation’s wealthiest individuals with a strategy for padding their own bank accounts by “donating” to support private K-12 schools. While a similar loophole exists under current law, its size and scope would be dramatically expanded by the legislation working its way through Congress.[2]
Latest “Compromise” for Tax Plan Is Even Worse than Previous Proposals, Would Reduce the Plans’ “Losers” by Less than 17,000 Taxpayers
December 13, 2017 • By Meg Wiehe, Steve Wamhoff
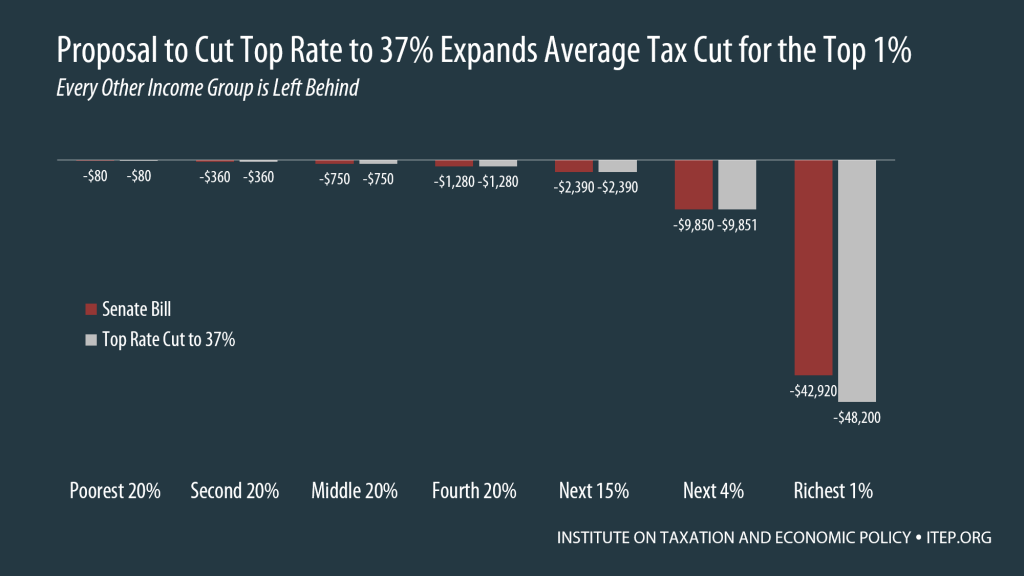
Earlier this week, ITEP explained that two possible “compromises” to improve the Senate tax bill would accomplish very little other than make the plan more expensive. Incredibly, Republican leaders are now discussing a third possible “compromise” that is even worse — a further reduction in the top personal income tax rate to 37%. This would […]
Parents of College Students: The Tax Plans’ Losers that No One Is Talking About
December 13, 2017 • By Steve Wamhoff

Parents of college students or kids in their last years of high school are more likely to face a tax hike than others under the tax legislation moving through Congress. Higher education has entered the tax debate because the House bill (but not the Senate bill) would repeal several provisions that make college and graduate education more accessible. But little thought has been given to how the tax bills would affect the parents of college students in more direct ways and make it difficult for them to finance college for their kids. If tax legislation were allowed a reasonable number…
Who Is “America First” Under the Tax Plan? The Rich First, Foreign Investors Second, Then the Rest of Us.
December 12, 2017 • By Steve Wamhoff

In his inaugural speech, President Trump told the world that Washington would be driven by a principle of “America First.” But the tax plans moving through Congress only put the richest Americans first. Everyone else comes after foreign investors.
Treasury’s 1-Page Memo Reasserts False Claims that Tax Cuts Largely Pay for Themselves — But Only When Accompanied by Spending Cuts
December 12, 2017 • By Steve Wamhoff

Treasury Secretary Steven Mnuchin claimed for weeks that his department would release a study showing that the $1.5 trillion tax cut moving through Congress would “pay for itself.” On Monday he released a one-page memo that asserts, without evidence, that economic growth resulting from President Trump’s policies would raise enough revenue to more than offset the costs of the tax cuts.
“Compromises” Under Discussion for the State and Local Tax Deduction Do Not Fix Flawed Tax Bills
December 10, 2017 • By Meg Wiehe, Steve Wamhoff
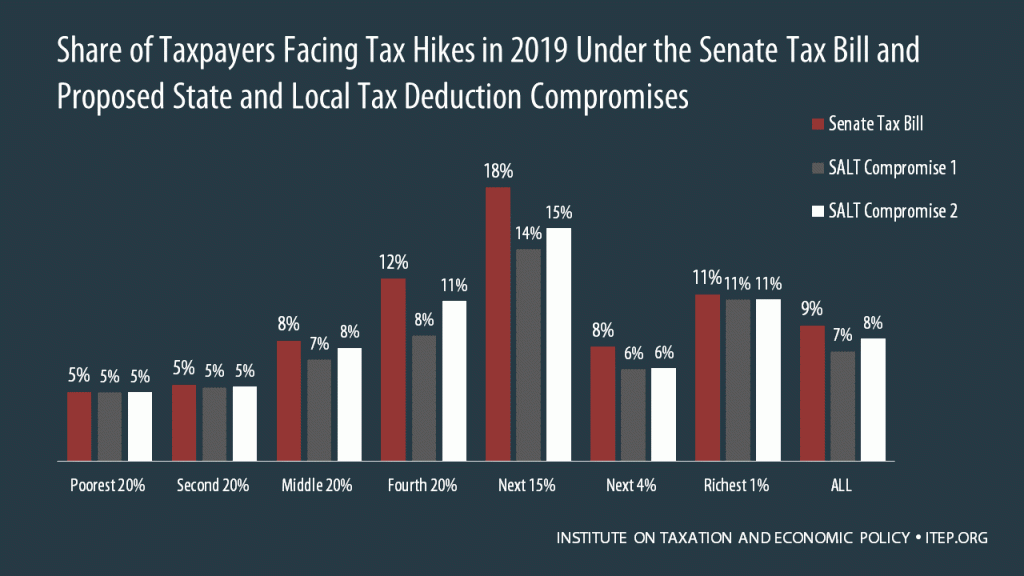
Republicans in Congress are reported to be considering two versions of a change they claim would “improve” the current bills by making them more generous to residents of higher-taxed states. As illustrated by these estimates, the reality is that these proposals would make little difference on those states and taxpayers hit hardest.
Even with Potential SALT Compromises, Senate Bill Forces California and New York to Shoulder a Larger Share of Federal Taxes While Texas, Florida, and Other States Will Pay Less
December 10, 2017 • By Meg Wiehe, Steve Wamhoff
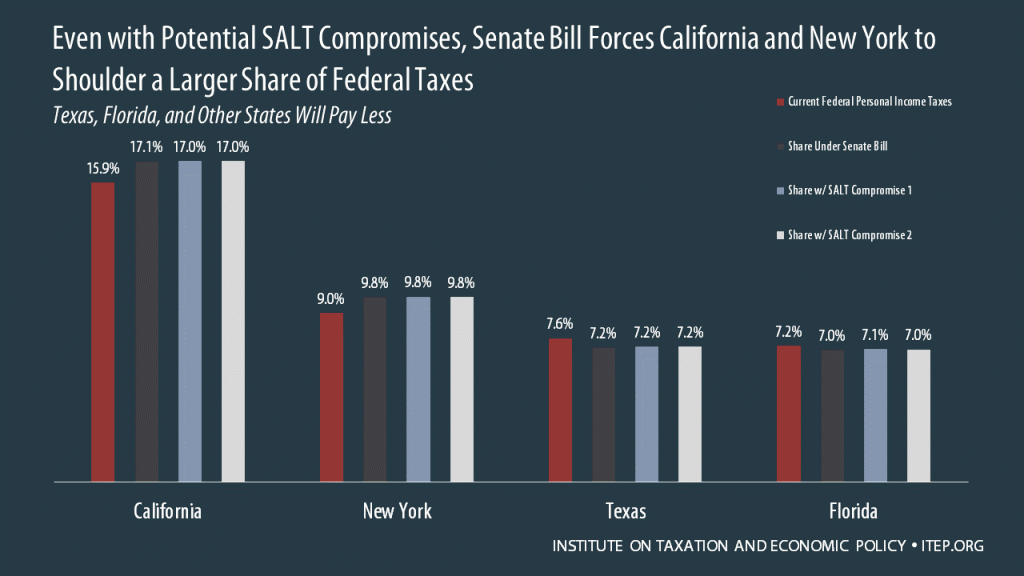
The Senate tax bill, with or without either of the compromises that could be added to it, would shift personal income taxes away from Florida and Texas to states like California and New York, which are already paying a high share relative to their populations.
Charitable, Property Tax, and Mortgage Interest Deductions Would Be Wiped Out for Two-Thirds of Current Claimants Under Congressional Tax Plans
December 7, 2017 • By Carl Davis
In the ongoing debate over major federal tax legislation, there is significant focus on how House and Senate bills would eliminate the deduction for state income tax payments and cap the deduction for property taxes at $10,000 per year. At the same time, tax writers have retained deductions for charitable gifts and mortgage interest with what appear to be comparatively minor changes, at least at first glance.
National and 50-State Impacts of House and Senate Tax Bills in 2019 and 2027
December 6, 2017 • By ITEP Staff
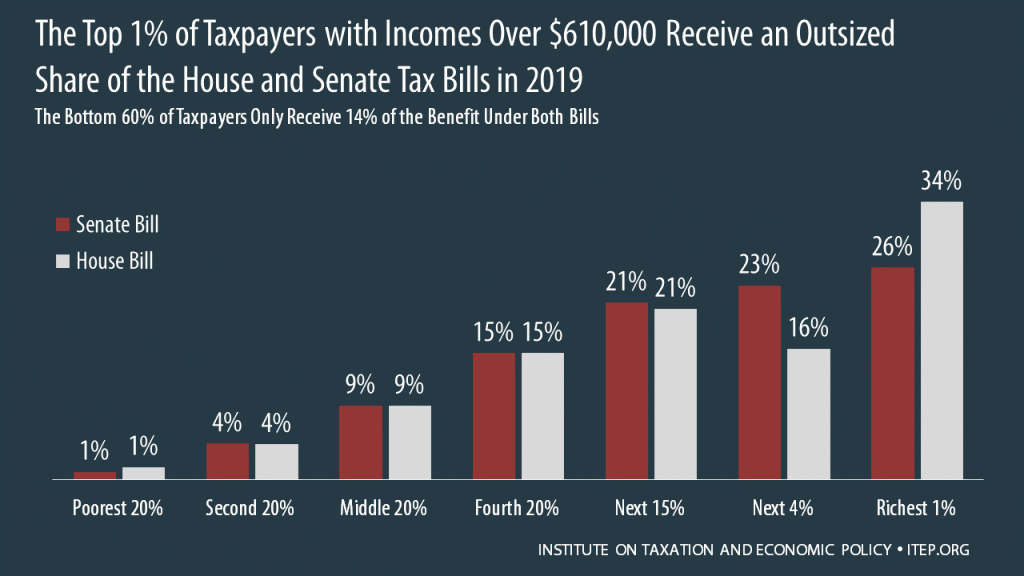
The House passed its “Tax Cuts and Jobs Act” November 16th and the Senate passed its version December 2nd. Both bills would raise taxes on many low- and middle-income families in every state and provide the wealthiest Americans and foreign investors substantial tax cuts, while adding more than $1.4 trillion to the deficit over ten years. National and 50-State data available to download.
In addition to distributional analyses of existing and proposed tax law, ITEP provides policy recommendations for lawmakers to build a more equitable tax code, from progressive revenue-raising options to corporate tax reform to establishing a model for a wealth tax.
