
ITEP's Research Priorities
- 2025 tax debate
- Blog
- Cannabis Taxes
- Corporate Taxes
- Corporate Taxes
- Earned Income Tax Credit
- Education Tax Breaks
- Estate Tax
- Federal Policy
- Fines and Fees
- Georgia
- Immigration
- Income & Profits
- Income Taxes
- Inequality and the Economy
- ITEP Work in Action
- Local Income Taxes
- Local Policy
- Local Property Taxes
- Local Refundable Tax Credits
- Local Sales Taxes
- Maps
- Media Quotes
- News Releases
- OBBBA
- Other Revenues
- Personal Income Taxes
- Property & Wealth
- Property Taxes
- Property Taxes
- Publications
- Refundable Tax Credits
- Sales & Excise
- Sales, Gas and Excise Taxes
- Sales, Gas and Excise Taxes
- SALT Deduction
- Select Media Mentions
- Social Media
- Staff
- Staff Quotes
- State Corporate Taxes
- State Policy
- State Reports
- States
- Tax Analyses
- Tax Basics
- Tax Credits for Workers and Families
- Tax Credits for Workers and Families
- Tax Guide
- Tax Principles
- Tax Reform Options and Challenges
- Taxing Wealth and Income from Wealth
- Toolkits
- Trump Tax Policies
- Video
- Webinar
- Who Pays?
The New Orleans Advocate: James Gill: Louisiana’s Tax System Isn’t the Most Unfair in the Nation, But It’s not for Lack of Trying
November 3, 2018
According to a study just released by the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy in Washington, Washington State sets the regressive standard, while we rank 14th. If your income is $17,100 or less in Louisiana, you'll pay 11.9 percent of it in taxes. That number shrinks the further you go up on the income scale and is roughly halved by the time you reach fat-cat territory. Sales and excise taxes take 9.2 percent from the poorest, and 1.2 percent from the richest.
The New Yorker: If Jeff Bezos Makes Washington the Second Headquarters of Amazon
November 3, 2018
Earlier this year, Seattle’s city council passed a tax on large corporations aimed at raising an estimated forty-seven million dollars a year for affordable-housing initiatives. But after about a month the city council repealed the tax—in response to a ballot challenge funded in part by Amazon, which threatened to leave Seattle if the tax was implemented. Matthew Gardner, a tax-policy analyst at the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy, told the Washington Post, “Nobody on Seattle’s city council wants to be the one who chased Amazon out of town.”
Kansas Center for Economic Growth: Kansans of Color Often Pay More Than Their Fair Share of Taxes
November 2, 2018
Kansans believe in fairness. However, a recent study by the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy (ITEP) and the Kansas Center for Economic Growth finds that the lowest-income Kansans are contributing a higher share of their income to fund our priorities. Without an equitable tax structure, we will struggle to make necessary investments in great […]
New Mexico Voices for Children: The Next Governor Should Improve Our Tax System and Increase Wages
November 2, 2018
When it comes to fairness, New Mexico’s tax system is backwards. Those who earn the smallest incomes pay the highest rates in state and local taxes, according to a new report from the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy. The responsibility for taxes should not fall hardest on those with the least ability to pay, but it does. There are several ways we can make our tax system fairer.
Oregon Center for Public Policy: It’s Time to Fix Oregon’s Regressive Tax Structure
November 2, 2018
Oregon’s poorest families pay more in taxes as a share of income than any group of taxpayers in the state, while the richest Oregonians pay the smallest share of any group. That is the conclusion of a new report by the Washington, D.C.-based Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy (ITEP).
Cherokee Tribune & Ledger-News: Financial Watchdog: Pritzker’s Spending Promises Would Raise Taxes on Middle Class
November 1, 2018
The Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy says Illinois has one of the most regressive taxes in the nation, largely due to its flat income tax. In its annual “Who pays?” report, the institute said the poorest 20 percent of Illinois households pay 14 percent of their income in taxes because of the flat tax in addition to high sales and property taxes.
Inside Higher Ed: Democratic Contenders Get Ambitious With Equity Proposals
October 30, 2018
The Harris tax credit bill, called the LIFT the Middle Class Act, could also have implications for higher ed access -- although the legislation wouldn’t have the same focus on assisting students from the poorest families. The proposal would function like a beefed-up version of the earned income tax credit and phase in quickly for individuals and married couples who work. It would offer substantial immediate benefits. Families earning up to $60,000 could receive up to $6,000 annually under the proposal. The Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy estimated that one million Pell-eligible students would qualify for a $3,000 tax…
Common Dreams: Time for a Tax on Billionaire Wealth Dynasties
October 30, 2018
The public should also rally to levy a modest tax on wealth over $20 million. A direct tax on wealth paid by the wealthiest one tenth of one percent could generate significant revenue to be reinvested in creating and restoring opportunities for low wealth households to prosper. A 1 percent annual tax on the wealthiest 0.1 percent of households, those with wealth over $20 million, would generate an estimated $1.899 trillion in revenue over the next decade, according to a forthcoming report from the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy.
Voices for Illinois Children: Who Pays In Illinois? Mostly The Poor And Middle Class
October 29, 2018
A new report from the Institute of Taxation and Economic Policy (ITEP) shows the poorest 20 percent of Illinois households pay nearly twice as much in state and local taxes as the richest one percent. As a result, ITEP ranks Illinois as the eighth most regressive tax system in the country.
NJ Spotlight: GOP Leaders Call on NJ Democrats to Reconsider Middle-class Tax Cuts
October 29, 2018
The related tax-cut bills — and another that would shield most retirement-savings contributions from state income taxes — were introduced at the start of the year but have not been posted for votes by the Democratic leaders who control the Assembly’s agenda. Bucco suggested a report released earlier this month by the left-leaning Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy that found middle-income taxpayers in New Jersey pay a higher effective tax rate than any other group — including the top 1 percent of earners — as a reason to begin prioritizing adoption of the GOP bills.
California Budget & Policy Center: Last Year’s Federal Tax Law Exacerbates the Racial Wealth Gap
October 29, 2018
Much has been written about how the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), pushed by Republican leaders in Congress and signed into law by President Trump in December 2017, mostly benefits wealthy households while driving up the federal deficit by $1.9 trillion over the next 10 years. This growing deficit — already 17% higher in the federal fiscal year that ended on September 30 than in the previous year — threatens federal funding for critical investments and services that provide economic security and opportunity for low- and middle-income households.
PolitiFact: Does Vermont Have the ‘Most Progressive’ Tax System in the Country?
October 29, 2018
Carl Davis, the research director for ITEP, said he doesn’t believe it would be accurate to call Vermont the most progressive state. California has a much higher top rate for the wealthiest taxpayers, he said. "In our research Vermont does not have the most progressive system in the nation, but it is certainly far less regressive than the vast majority of states," Davis said.
Charleston Gazette-Mail: Statehouse Beat: Fake History on Teacher Strike Hard to Fathom
October 27, 2018
Speaking of the Senate, the nonpartisan Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy put out its annual “Who Pays” report on tax equity, which found the vast majority of states have tax systems that are inequitable, with lower- and middle-income families paying a larger percentage of income in taxes than upper-income families.It singled out the “Terrible 10” states with the most regressive tax systems, with the common denominator among those states being that they have no or very low income taxes, which they make up through having very high and broad-based sales taxes.
KUOW: A $40,000 Salary Is no Longer Middle Class in Washington State. Here’s Why.
October 26, 2018
Look what's happened to an income of $40,000. In 2015, the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy (ITEP), based in Washington, D.C., looked at incomes in Washington state and found that a salary of $40,000 was still middle class. It was smack-dab in the middle of middle-earning incomes in the state. In 2018, ITEP looked again. This time, $40,000 had slipped a notch, to the second-lowest 20 percent of earners. The reason: More people in the state were making higher-end incomes.
The Olympian: Olympia Went to Court to Block an Income Tax Proposal. Two Years Later, It’s Backing Seattle’s Version.
October 26, 2018
In 2016, an Olympia household earning $25,000 a year paid about 13 percent of its income in state and local taxes, while a household earning $250,000 paid less than 4 percent, according to the resolution. A report this month from the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy said Washington has the most regressive tax structure in the country, thanks to its lack of a personal income tax and comparatively high sales taxes.
We’re sorry to see you go…
October 25, 2018 • By ITEP Staff
Thank you for your response! We understand that in this age of rapid communication, too many emails can bring unwanted clutter to your inbox while too few emails can leave you without timely information on tax policy. Remember, you can always resubscribe using the form below and tailor your ITEP email subscription to fit your […]
Massachusetts Budget and Policy Center: Who Pays? Low and Middle Earners in Massachusetts Pay Larger Share of their Incomes in Taxes
October 25, 2018
Taxes are the main way communities pay for the things we do together. Taxes pay for essential programs and infrastructure we take for granted, like fire protection, public education, and health inspectors; roads, bridges, and public transit; and the support for people facing hard times. Examining how much people at different income levels pay in taxes is important when considering the fairness of tax policy.
Oregon Center for Public Policy: Measure 105 Would Set Oregon Back
October 25, 2018
Immigrants, regardless of their immigration status, give the economy a boost. In Marion County alone, undocumented immigrants pay more than $14 million in taxes every year to local and state authorities. Oregon is better for having immigrants, and will be better for it for generations to come. Read more here
News and Tribune: In Indiana and Illinois, Taxes Hit Low-earners Hard
October 25, 2018
TERRE HAUTE -- Low-earning residents of Indiana and Illinois pay a greater share of state and local taxes than those in all other Midwestern states, and those in most states nationally, according to a new study by a non-partisan think tank.
U.S.: Who Pays? 6th Edition
October 25, 2018 • By ITEP Staff
The Columbia Missourian: New Tax on Motor Fuels Would Rev up Road and Bridge Spending
October 25, 2018
As it stands, only Alaska has a lower fuel tax than Missouri. Every neighboring state’s tax is higher. And more than 20 states increased their fuel taxes between 2013 and 2017, according to Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy website. Read more
The Garden Island: Gap Keeps Growing Between Rich, Poor
October 25, 2018
The study finds that those in the bottom fifth of the income spectrum in Hawaii pay 15 percent of their income in state and local taxes, while those in the top 1 percent pay only 8.9 percent, “which exacerbates inequality in our state,” according to a press release about the study.
Bloomberg: Kamala Harris Tax Plan Would Cost $2.8 Trillion, Conservative Group Says
October 24, 2018
ITEP’s Wiehe said the plan is more highly targeted than the 2017 tax law to help low-income workers. The poorest 20 percent would see a $2,100 benefit under the Harris plan, compared with $80 under the GOP plan, she said. About 123 million workers would receive tax breaks under the plan, according to Wiehe.
Shaking up TCJA: How a Proposed New Credit Could Shift Federal Tax Cuts from the Wealthy and Corporations to Working People
October 24, 2018 • By Aidan Davis
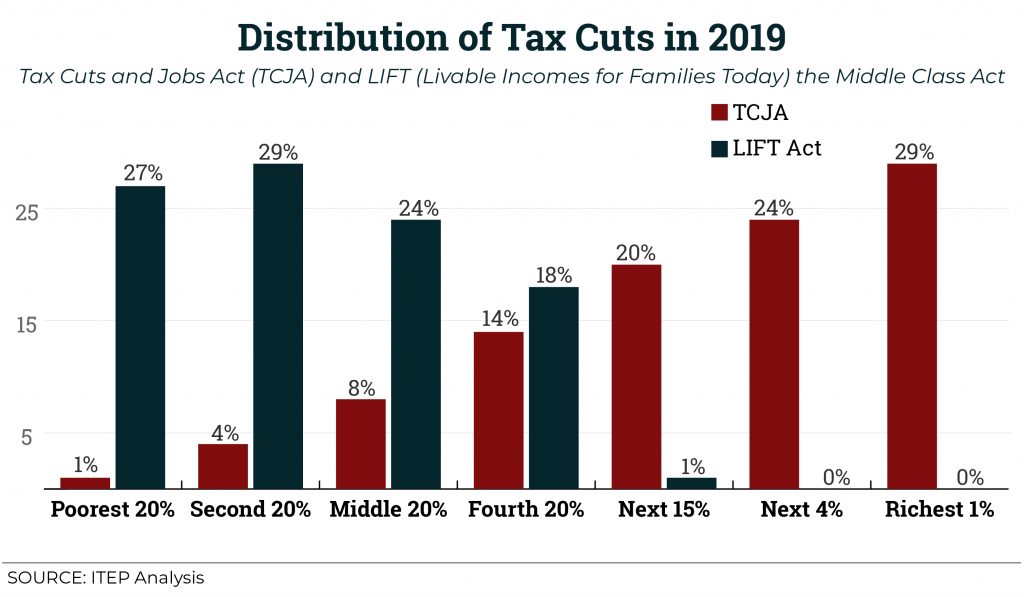
A new federal proposal, the Livable Incomes for Families Today (LIFT) the Middle Class Act, would create a new refundable tax credit for low- and middle-income working families who were little more than an afterthought in last year’s federal tax overhaul. This proposal would take the place of TCJA, providing tax cuts similar in cost to the recent federal tax law but targeted toward working people rather than the wealthy. ITEP analyzed the bill, proposed by California Senator Kamala Harris, and compared its potential impact to TCJA.
Real Change: Study: Washington Bottoms Out on US Tax Assessment
October 24, 2018
Guess what? Washington state’s taxation system continues to be one of the most regressive in the country. This news comes from the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy (ITEP), which did a deep dive into the taxation policies of all 50 states.
