
ITEP's Research Priorities
- 2025 tax debate
- Blog
- Cannabis Taxes
- Corporate Taxes
- Corporate Taxes
- Earned Income Tax Credit
- Education Tax Breaks
- Estate Tax
- Federal Policy
- Fines and Fees
- Georgia
- Immigration
- Income & Profits
- Income Taxes
- Inequality and the Economy
- ITEP Work in Action
- Local Income Taxes
- Local Policy
- Local Property Taxes
- Local Refundable Tax Credits
- Local Sales Taxes
- Maps
- Media Quotes
- News Releases
- OBBBA
- Other Revenues
- Personal Income Taxes
- Property & Wealth
- Property Taxes
- Property Taxes
- Publications
- Refundable Tax Credits
- Sales & Excise
- Sales, Gas and Excise Taxes
- Sales, Gas and Excise Taxes
- SALT Deduction
- Select Media Mentions
- Social Media
- Staff
- Staff Quotes
- State Corporate Taxes
- State Policy
- State Reports
- States
- Tax Analyses
- Tax Basics
- Tax Credits for Workers and Families
- Tax Credits for Workers and Families
- Tax Guide
- Tax Principles
- Tax Reform Options and Challenges
- Taxing Wealth and Income from Wealth
- Toolkits
- Trump Tax Policies
- Video
- Webinar
- Who Pays?
Daily Mail: REVEALED: Amazon pays NOTHING in federal corporate taxes for the second year running despite doubling its profits to more than $11billion
February 14, 2019
In last year's filing Amazon similarly paid no corporate income taxes on its $5.6billion earnings. The Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy revealed the negative tax rate was the result of unspecified 'tax credits' and other benefits.

The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), enacted by President Trump and Congressional Republicans at the end of 2017, has caused quite a bit of confusion, and a recent “Fact Checker” column by the Washington Post’s Glenn Kessler does not help. TCJA created real problems that can't be resolved without real tax reform. To begin that process fact checkers, lawmakers, and everyone else need to be clear about what TCJA did, and did not, do to our tax system.
Fear, Not Facts: Netflix Misleads Media Reporting on Corporate Tax Avoidance
February 13, 2019 • By Matthew Gardner

In an age when even the most incontrovertible facts are routinely dismissed as “fake news,” reporting on corporate taxes can be a daunting challenge for members of the media. ITEP’s recent analysis of the income tax disclosures made by Netflix in its annual financial report last week provide an excellent reminder of this.

On Monday a group of Senators and Representatives from the Northeast announced their latest proposal to repeal the cap on deductions for state and local taxes (SALT), this time offsetting the costs by restoring the top personal income tax rate to 39.6 percent. This is an improvement over previous proposals to repeal the cap on SALT deductions without offsetting the costs at all. But the new approach does not improve our tax system overall. Instead, it trades one tax cut for the rich (a lower top income tax rate) for another (repeal of the cap on SALT deductions).
ORT: 2017 Tax Reform Helps Corporations The Most. Who Knew?
February 13, 2019
The Tax Reform bill of 2017 was supposed to close loopholes which had allowed corporations to avoid paying taxes, but a study by Matt Gardner, Senior Fellow at the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy (ITEP), of Netflix has shown that it reduced corporate taxes without closing the loopholes. He talks to Jan Miyasaki about the issues and how the trend to shift tax burden to the poor continues.
Amazon in Its Prime: Doubles Profits, Pays $0 in Federal Income Taxes
February 13, 2019 • By Matthew Gardner

Amazon, the ubiquitous purveyor of two-day delivery of just about everything, nearly doubled its profits to $11.2 billion in 2018 from $5.6 billion the previous year and, once again, didn’t pay a single cent of federal income taxes.
MassBudget: Why Highest Incomes in Massachusetts Receive Most Tax Benefits from Charitable Deduction
February 11, 2019
Our Commonwealth does best when all people experience rising prosperity. But for several decades, the wealth and income of the top 1 percent of households has grown briskly while others have been left behind. While there are many reasons for this trend, one contributing factor is the way the federal tax deduction for charitable giving […]
A Tale of Two States: How State Tax Systems Perpetuate Income Inequality
February 11, 2019 • By ITEP Staff
To explain how state tax systems make income inequality worse, we compared tax systems in New Jersey and Texas which, before taxes, have similar levels of income inequality. This comparison provides an example of how policymakers’ decisions affect the economic wellbeing of their constituents.
This year is full of opportunity for state policymakers and advocates seeking to improve upside-down tax systems and generate needed funding for shared priorities. In a series of blog posts, ITEP staff summarize key trends we are watching in statehouses this year, with special attention to the many efforts underway to reduce racial and economic inequities and better prepare state budgets for the next recession and reduced federal investments. Along the way, we’ll also draw attention to some of the more destructive policy ideas to watch for in 2019.
Trends We’re Watching in 2019: Attempting to Double Down on Failed Trickle-Down Regressive Tax Cuts
February 7, 2019 • By Lisa Christensen Gee

It’s always troubling for those concerned with adequate and fair public finance systems when states prioritize tax cuts at the cost of divesting in important public priorities and exacerbating underlying tax inequalities. But it’s even more nerve-racking when it happens on the eve of what many consider to be an inevitable economic downturn.
Trends We’re Watching in 2019: Cannabis Tax Implementation and Reform
February 7, 2019 • By Carl Davis

Few areas of state tax policy have evolved as rapidly as cannabis taxation over the last few years. The first legal, taxable sale of recreational cannabis in modern U.S. history did not occur until 2014. Now, just five years later, a new ITEP report estimates that recreational cannabis is generating more than $1 billion annually in excise tax revenues and $300 million more in general sales tax dollars.
Trends We’re Watching in 2019: Consumption Taxes: the Good, Bad and the Ugly
February 7, 2019 • By ITEP Staff

Consumption taxes are a significant source of state and local revenue, and we expect that lawmakers will continue to adjust state consumption tax levies to adapt to budget needs and a changing economy.
Trends We’re Watching in 2019: Addressing Lingering Federal Conformity Questions and Opportunities
February 7, 2019 • By Dylan Grundman O'Neill

In our last update on state responses to the federal tax cut (Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, or TCJA), we noted that several states were waiting until 2019 to make their final decisions, giving them additional time to (hopefully) respond in ways that improve their fiscal situations and upside-down tax codes. The TCJA is affecting the 2018 federal taxes people are filing now, in some cases adding urgency and/or confusion to these debates.
Trends We’re Watching in 2019: Raising Revenue and Spending Surpluses to Prioritize Critical Public Investments
February 7, 2019 • By Lisa Christensen Gee

A second notable trend in 2019 is states raising revenue to address longstanding needs and states allocating their surpluses to invest in critical public priorities such as early childhood programs, education and other human services.
Trends We’re Watching in 2019: The Use of Targeted Tax Breaks to Help Address Poverty and Inequality
February 7, 2019 • By Aidan Davis

Continuing to build upon the momentum of previous years, states are taking steps to create and improve targeted tax breaks meant to lift their most in-need state residents up and out of poverty. Most notably, a range of states are exploring ways to restore, enhance or create state Earned Income Tax Credits (EITC). EITCs are an effective tool to help struggling families with low wages make ends meet and provide necessities for their children. The policy, designed to bolster the earnings of low-wage workers and offset some of the taxes they pay, allows struggling families to move toward meaningful economic…
Maine Center for Economic Policy: To Fund Shared Prosperity, We Must End LePage-Era Tax Cuts for the Wealthiest
February 6, 2019
For years under Gov. Paul LePage, budget-busting tax cuts robbed our state of the revenue we need to build a stronger, fairer economy. Tax cuts delivered windfalls to the wealthiest households in our state, making it harder for our schools and communities to make ends meet. Read more
Shared Prosperity: A Progressive Approach to Marginal Tax Rates
February 6, 2019 • By Steve Wamhoff
Panel: In recent years, economists have been engaged in robust academic debate over the top marginal tax rate, with leading researchers estimating the optimal rate to be 73 percent or even higher. Yet despite widespread public support for raising the rate from its current level of 37 percent, many policymakers and media figures have demonstrated misunderstandings over what marginal tax rates are and how they work.
New ITEP Report Shows How Congress Can Meet Public Demand for Progressive Taxes
February 5, 2019 • By Steve Wamhoff

A recent headline tells us that bold tax plans proposed by lawmakers today reflect a “profound shift in public mood.” But, in fact, the public’s mood has not changed at all. Americans have long wanted progressive taxes but few, if any, lawmakers publicly backed this view. What’s happening now isn’t a shift in public opinion, rather it’s Washington finally catching up with the American people.
Wrong Priorities: It Doesn’t Make Sense to Give a Tax Cut to the Rich While Arizona Asks Children in Public Schools to Wait
February 5, 2019
Arizona stands to gain $130 million to $230 million in General Fund revenues if it conforms the Arizona tax code to the federal tax changes enacted in 2017. Rather than directing those additional revenues to better prepare for the next economic downturn or toward increased investments in our public schools, SB1143 and HB2522 will direct the additional revenues toward a tax cut that will benefit the wealthiest Arizonans.
Montana Budget & Policy Center: House Bill 300: Sales Tax Proposal Makes Montana’s Taxes More Regressive and Reduces State Revenue
February 5, 2019
Replacing property taxes with a sales tax is both impractical and unfair for Montana families. HB 300 would make Montana’s tax system more regressive, increasing the taxes paid by families living on lower- and middle-incomes in the state while decreasing the taxes paid by the wealthy. Read more here
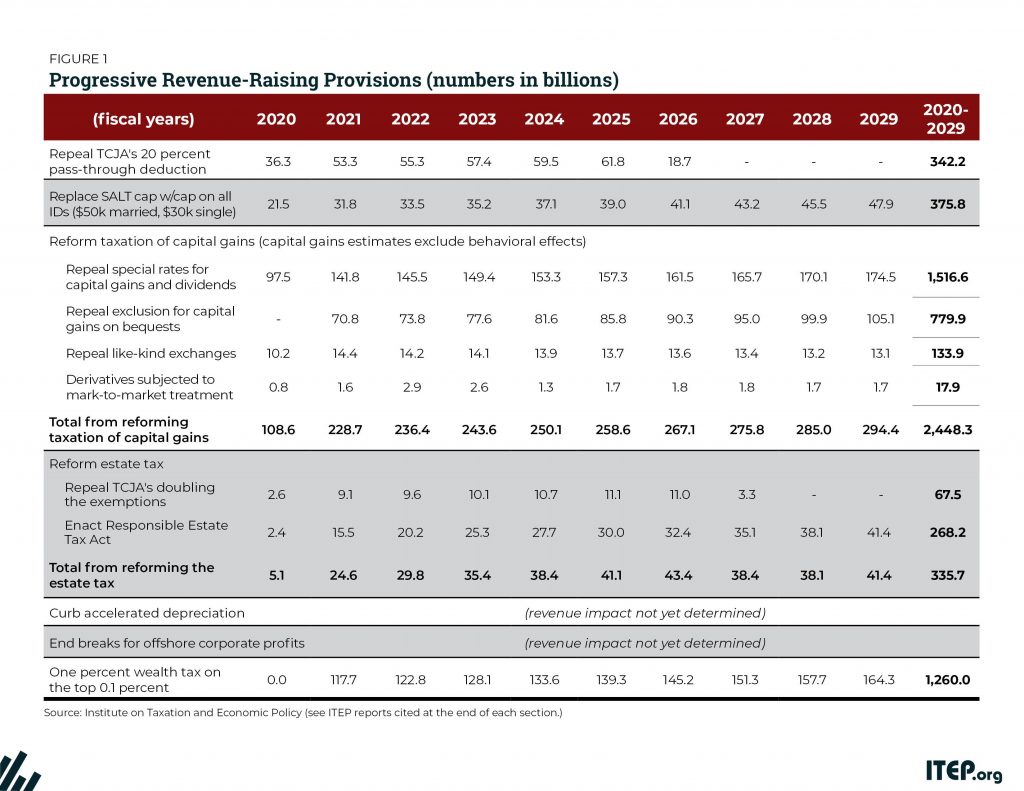
America has long needed a more equitable tax code that raises enough revenue to invest in building shared prosperity. The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), enacted at the end of 2017, moved the federal tax code in the opposite direction, reducing revenue by $1.9 trillion over a decade, opening new loopholes, and providing its most significant benefits to the well-off. The law cut taxes on the wealthy directly by reducing their personal income taxes and estate taxes, and indirectly by reducing corporate taxes.

Progressive tax proposals are finally being discussed with the urgency and seriousness they deserve. Following Rep. Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez’s call for a much higher marginal tax rate for multi-millionaires and Sen. Elizabeth Warren’s proposal to introduce a wealth tax for those at the very top, Sen. Bernie Sanders has introduced a revised version of his proposal to reform the federal estate tax.
Congress Should Reduce, Not Expand, Tax Breaks for Capital Gains
February 1, 2019 • By Steve Wamhoff
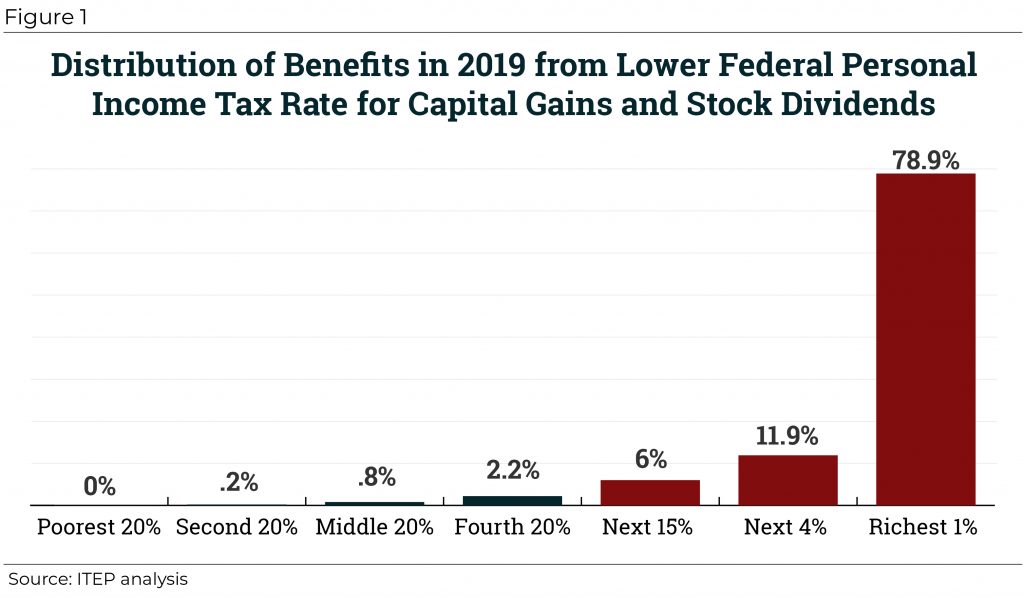
Even though income derived from capital gains receives a special lower tax rate and is therefore undertaxed, some proponents of lower taxes on the wealthy claim that capital gains are overtaxed due to the effects of inflation. But existing tax breaks for capital gains more than compensate for any problem related to inflation. Congress should repeal or restrict special tax provisions for capital gains rather than creating even more breaks.
Arkansas Advocates for Children and Families: Tax Cut Bill Filed: Plan Revised But Not Fixed
January 31, 2019
An analysis by the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy (ITEP) shows that the benefits of this proposal are even more heavily skewed towards the richest taxpayers than the previous version. That’s because there are no changes to the standard deduction, and all the significant changes in marginal tax rates only affect taxpayers with more […]
Data for the Win: Advocating for Equitable State and Local Tax Policy (Webinar)
January 30, 2019 • By Aidan Davis, Dylan Grundman O'Neill, ITEP Staff, Meg Wiehe
Watch the video recording below for discussion on how ITEP’s distributional data can be part of an advocacy and communications strategy for securing state tax policies that raise enough revenue to fund various priorities. Outline includes a brief overview of findings from the sixth edition of Who Pays? A Distributional Analysis of the Tax Systems in All 50 States as well as insight from state advocates who use Who Pays? and other tax policy analyses research to pursue their legislative agendas.
