
Blog
1303 posts
Lawmakers Want Working People to Foot the Bill for Top-Heavy Tax Cuts
October 18, 2018 • By ITEP Staff

Earlier this week, the Treasury Department reported that the federal deficit this fiscal year climbed by 17 percent to $779 billion, and next year is expected to be at least $1 trillion. The increased deficit comes after Congress last December passed an unpopular tax cut (The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act) that will cost nearly $2 trillion over a decade. GOP leaders repeatedly claimed the measure would pay for itself and not increase annual deficits, in spite of multiple economic predictions to the contrary.

Policymakers and residents in all 50 states and the District of Columbia got new ITEP data this week on how their tax structures and decisions affect their high-, middle-, and low-income residents. As our “Who Pays?” report outlines, most state and local tax codes exacerbate economic inequalities and all states have room to improve. The data can serve as an important informative backdrop to all state and local tax policy debates, such as whether to change the valuation of commercial property in California, how to improve funding for early childhood education in Indiana, and how to evaluate tax-related ballot measures…
New Report Finds that Upside-down State and Local Tax Systems Persist, Contributing to Inequality in Most States
October 17, 2018 • By Aidan Davis
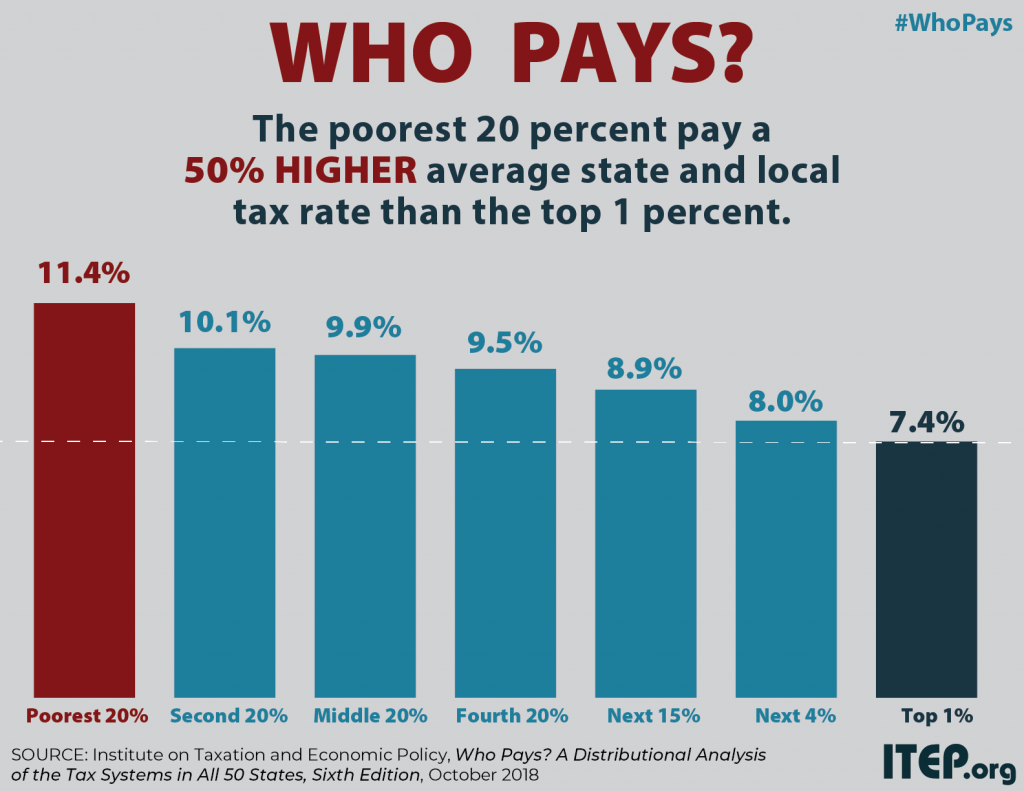
State and local tax systems in 45 states worsen income inequality by making incomes more unequal after taxes. The worst among these are identified in ITEP’s Terrible 10. Washington, Texas, Florida, South Dakota, Nevada, Tennessee, Pennsylvania, Illinois, Oklahoma, and Wyoming hold the dubious honor of having the most regressive state and local tax systems in the nation. These states ask far more of their lower- and middle-income residents than of their wealthiest taxpayers.
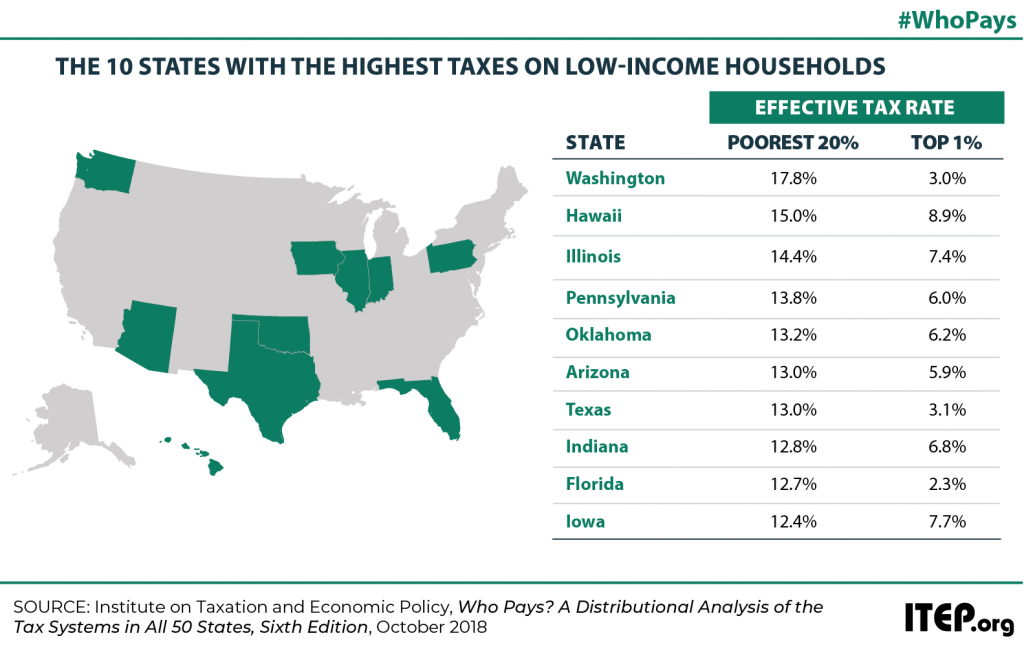
ITEP analysis reveals that many states traditionally considered to be “low-tax states” are actually high-tax for their poorest residents. The “low tax” label is typically assigned to states that either lack a personal income tax or that collect a comparatively low amount of tax revenue overall. But a focus on these measures can cause lawmakers to overlook the fact that state tax systems impact different taxpayers in very different ways, and that low-income taxpayers often do not experience these states as being even remotely “low tax.”
State Rundown 10/12: Local Jurisdictions Fighting for Revenues, Independence
October 12, 2018 • By ITEP Staff

Voters all around the country are educating themselves for the upcoming elections, notably this week around ballot initiatives in Arizona and Colorado and competing gubernatorial tax proposals in Georgia and Illinois. But not all eyes are on the elections, as the relationship between state and local policy made news in Delaware, Idaho, North Dakota, and Ohio.
‘Financial Exposure’ Showcases Tax Misconduct by Powerful Individuals and Corporations
October 10, 2018 • By Peter Della-Rocca

Elise J. Bean’s Financial Exposure reiterates the point that tax avoidance and tax evasion were endemic to our financial system long before allegations against a sitting president brought them to the forefront of the public consciousness.

South Carolina lawmakers have finally passed a federal conformity bill in response to last year’s federal tax-cut legislation. Voters in many states are hearing a lot about tax-related questions they’ll see on the ballot in November, particularly residents of Florida, Montana, and Oregon, where corporate donors and other anti-tax interests are spending major sums to alter policy in their states. And states continue to work on ensuring they can collect online sales taxes and, in some states, online sports betting taxes.
Twelve States Offer Profitable Tax Shelter to Private School Voucher Donors; IRS Proposal Could Fix This
October 2, 2018 • By Carl Davis
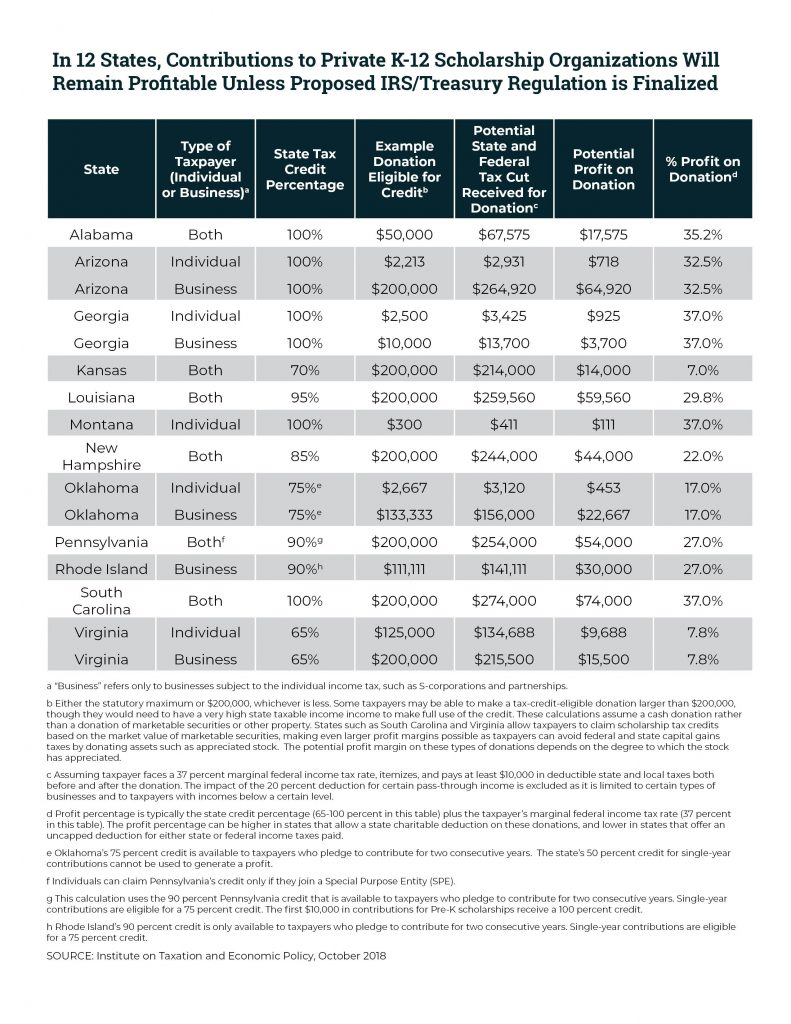
A proposed IRS regulation would eliminate a tax shelter for private school donors in twelve states by making a commonsense improvement to the federal tax deduction for charitable gifts. For years, some affluent taxpayers who donate to private K-12 school voucher programs have managed to turn a profit by claiming state tax credits and federal tax deductions that, taken together, are worth more than the amount donated. This practice could soon come to an end under the IRS’s broader goal of ending misuse of the charitable deduction by people seeking to dodge the federal SALT deduction cap.
So-Called “Universal Savings Accounts” in Tax Cuts 2.0 Are a Giveaway to the Most Affluent Taxpayers
September 27, 2018 • By Steve Wamhoff
This week, House Republicans have taken up bills they call tax cuts “2.0.” Most of the attention, so far, has focused on the bill that extends—at great cost—the temporary parts of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA). But other legislation in the package contains provisions that make the whole deal even more tilted toward the richest households, including one that would create “Universal Savings Accounts.” Far from being universal, these new savings vehicles would benefit the same high-income households that enjoy the bulk of the tax cuts from TCJA.
State Rundown 9/26: States Cleaning Up from Florence, Gearing Up for November
September 26, 2018 • By ITEP Staff

Affordable housing efforts made news in Minnesota and Virginia this week, as tax breaks for homeowners and other victims of Hurricane Florence were made available in multiple states. Meanwhile, New Jersey is still looking into legalizing and taxing cannabis, and Wyoming continues to consider a corporate income tax. And gubernatorial candidates and ballot initiative efforts will give voters in many states much to consider in the November elections.
An Unhappy Anniversary: Federal Gas Tax Reaches 25 Years of Stagnation
September 25, 2018 • By Carl Davis
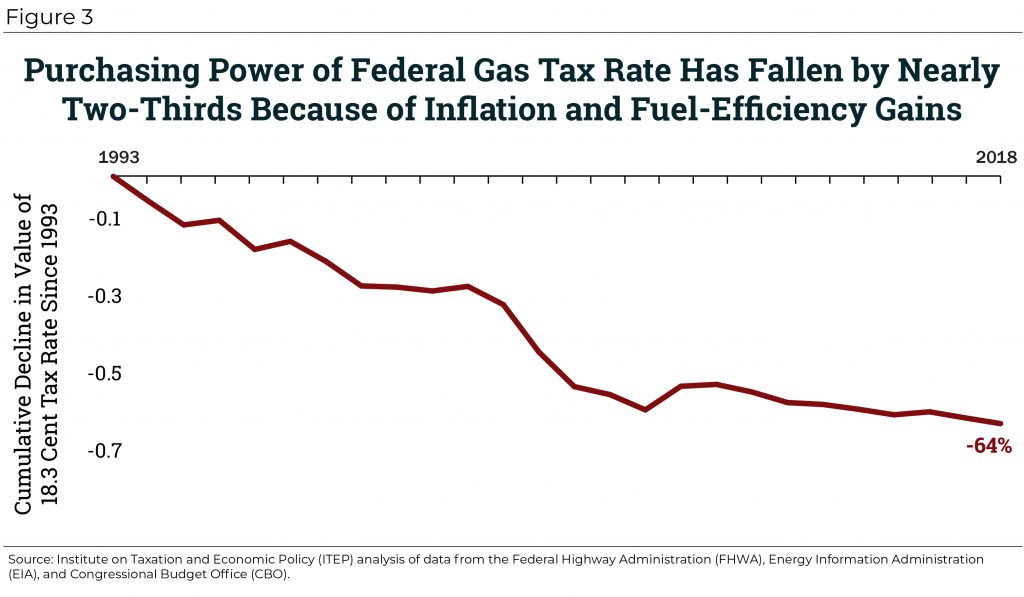
The federal gas tax was last raised on Oct. 1, 1993, the same year that the classic movie Groundhog Day was unveiled to the American public. In the film, Phil Connors (played by Bill Murray) gets caught in a time loop and spends decades reliving the same cold, February day in Punxsutawney, Penn. Those of us lamenting the 25-year stagnation of the federal gas tax can’t help but feel some of that same sense of repetition. Federal lawmakers occasionally discuss updating the gas tax, but top lawmakers have yet to put in the effort needed to shepherd such a change…
Oxfam Report Finds Pharmaceuticals Profiteering Off Crises in Developing Countries
September 20, 2018 • By Peter Della-Rocca

The report indicates, pharmaceutical companies have taken steps to hide their profits in low-tax countries, sapping billions in revenue from the governments that invest in the science that drives their products and safeguard the patents that undergird their business. Pharmaceutical companies made use of a familiar battery of methods to exploit the international system this way, including inversions to disguise an American company as a foreign one and passing profits into low-tax jurisdictions through artificial usage fees on intangible assets like intellectual property.
State Tax Codes Can Help Mitigate Poverty and Impact of Federal Tax Cuts on Low- and Middle-Income Families
September 20, 2018 • By Misha Hill

The national poverty rate declined by 0.4 percentage points to 12.3 percent in 2017. According to the U.S. Census, this was not a statistically significant change from the previous year. 39.7 million Americans, including 12.8 million children, lived in poverty in 2017. Median household income also increased for the third consecutive year, but this was […]
IRS Reopens Tax Loophole Sought by Sen. Toomey, but it Won’t Work in Pennsylvania
September 20, 2018 • By Carl Davis

A recent IRS clarification, which appears to have been a pet project of Sen. Pat Toomey (R-PA), has been widely interpreted as reopening a loophole the agency had proposed closing just weeks earlier. But while the announcement creates an opening for aggressive tax avoidance in many states, Pennsylvania, ironically enough, isn’t one of them.

The Rundown is back after a few-week hiatus, with lots of state fiscal news and quality research to share! Maine lawmakers found agreement on a response to the federal tax-cut bill, states continue to sort out how they’ll collect online sales taxes in the wake of the Wayfair decision, and policymakers in several states have been working on summer tax studies and other preparations for 2019 legislative sessions. Meanwhile, work on ballot measures and candidate tax plans to go before voters in November has been even more active, particularly in Arizona, California, Florida, Hawaii, and Missouri. Our “What We’re Reading” section has lots of great research and reading on inequalities, cities turning…
Today's poverty and income data show that income continues to concentrate at the top; in fact, the top 20 percent continue to capture 51.5 percent of income. Meanwhile, average income for the poorest 20 percent of households is less today than it was 18 years ago.
We Crunched Some Numbers to Show What Tax Reform for Working People Really Looks Like
September 12, 2018 • By ITEP Staff
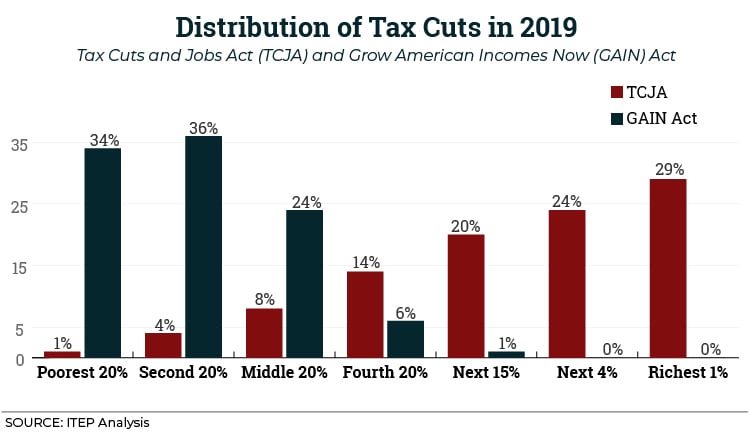
Throughout President’s Trump’s presidential campaign and from his first day in office until now, his administration has favored and promoted policies that benefit the wealthy and corporations even as it claims to be the working people’s champion. If more recent economic data are a reflection of what we’ll see in the long-term due to the Trump Administration’s recent tax cuts, wealth will continue to accrue at the top while income remains stagnant or barely budges for low- and moderate-income families. Policy can make a difference: ITEP Staff shows how the Grow American Incomes Now (GAIN) Act would help millions of…
Repealing the Federal Tax Law’s Cap on State and Local Tax (SALT) Deductions Is No Improvement
September 11, 2018 • By Steve Wamhoff
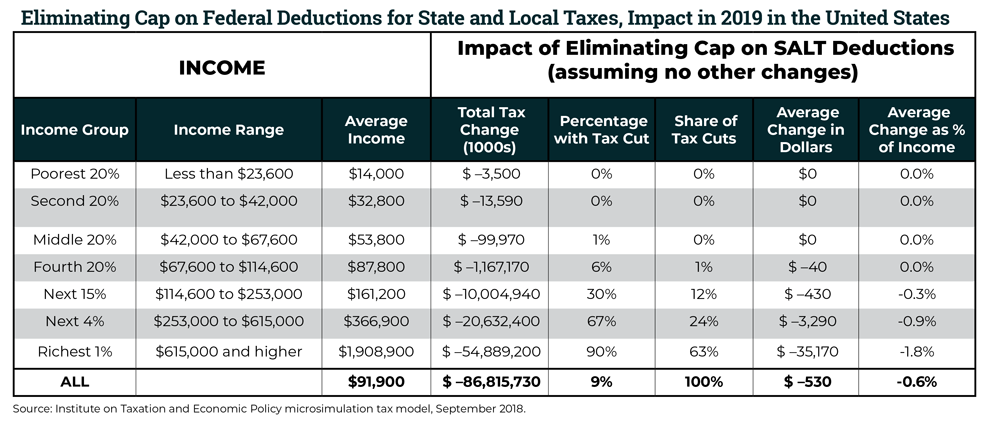
National and State-by-State Data Available for Download Nearly Two-Thirds of Benefits from Repealing the SALT Cap Would Go to the Richest 1 Percent Lawmakers who opposed the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), the federal tax law enacted by President Trump and his allies in Congress last December, rightfully pointed out that the law benefits […]

ITEP's analysis found that when all the major provisions of TCJA are in effect, the richest fifth of households will receive 71 percent of the law’s benefits. It also found that if the temporary provisions are extended at through 2026, the richest fifth of households will receive 65 percent of the benefits of that extension that year.
New Study Confirms Offshore Earnings are Flowing into Stock Buybacks, Not Jobs and Investments
September 7, 2018 • By Richard Phillips

A new study by the Federal Reserve found that the evidence so far suggests that the new repatriation tax break has resulted in a surge in stock buybacks and little discernable impact in investment by its biggest beneficiaries, just as critics predicted.
State Rundown 8/22: Wayfair Fallout Could Hit the Pavement Soon
August 22, 2018 • By ITEP Staff

Arizona voters learned this week that they will have an opportunity this fall to restore school funding through a progressive tax measure. The effects of the Supreme Court’s Wayfair decision could soon be seen on Michigan and Mississippi roads, as leaders in both states have proposed devoting new online sales tax revenues to infrastructure needs. And new research highlighted in our “What We’re Reading” section discredits one-size-fits-all prescriptions for state economic growth such as supply-side tax-cut orthodoxy, advocating instead for more nuanced and state-specific policymaking.
State Rundown 8/16: November Ballots and 2019 Debates Coming into Focus
August 16, 2018 • By ITEP Staff

Even as the haze from western wildfires reduced visibility across the nation this week, voters got more clarity on what to expect to see on their ballots this fall, particularly in California (commercial property taxes and corporate surcharges), Colorado (income taxes for education), Missouri (gas tax update), and North Dakota (recreational cannabis). Meanwhile, although Virginia lawmakers won’t return until 2019, they got a preview of a clear-headed federal conformity plan they should strongly consider. And look to our “What We’re Reading“ section for further enlightenment from researchers on the [in]effectiveness of charitable contribution credits, the [lack of] wage growth for…
1964: Unconditional War on Poverty; 2018: Unconditional War on the Poor
August 15, 2018 • By Misha Hill

During his first State of the Union address in January 1964, Lyndon Baines Johnson declared a War on Poverty in response to a national poverty rate of more than 19 percent. The legislative result of this war was an early education program, expanded funding for secondary education, job training and work opportunity programs and the […]
How Opportunity Zones Benefit Investors and Promote Displacement
August 10, 2018 • By ITEP Staff
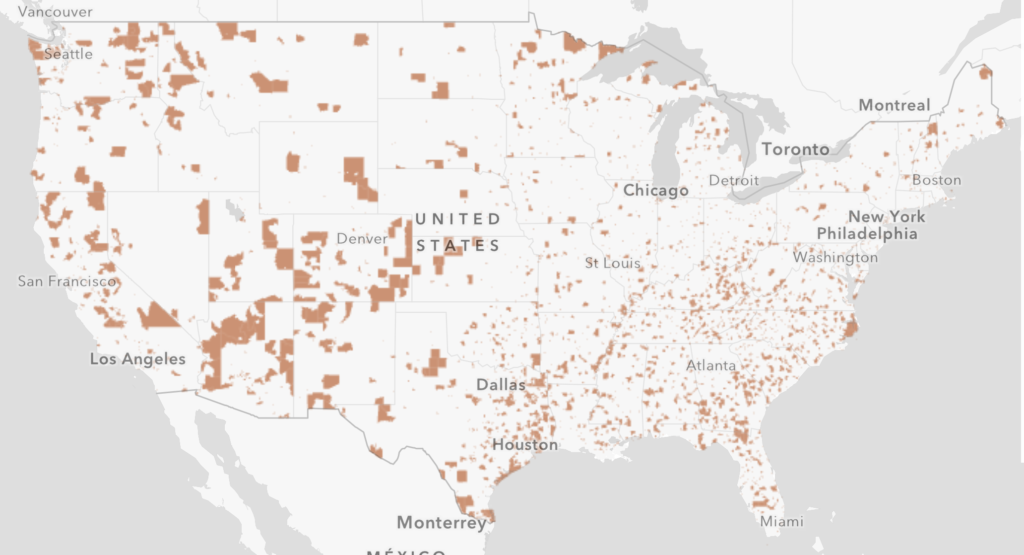
The idea behind the new tax break is to provide an incentive for wealthy individuals to invest in the economies of struggling communities. Despite alleged intentions, it appears opportunity zones are turning into yet another windfall for wealthy investors and may encourage displacement of people in low-income areas, working against the provision’s intended goal.
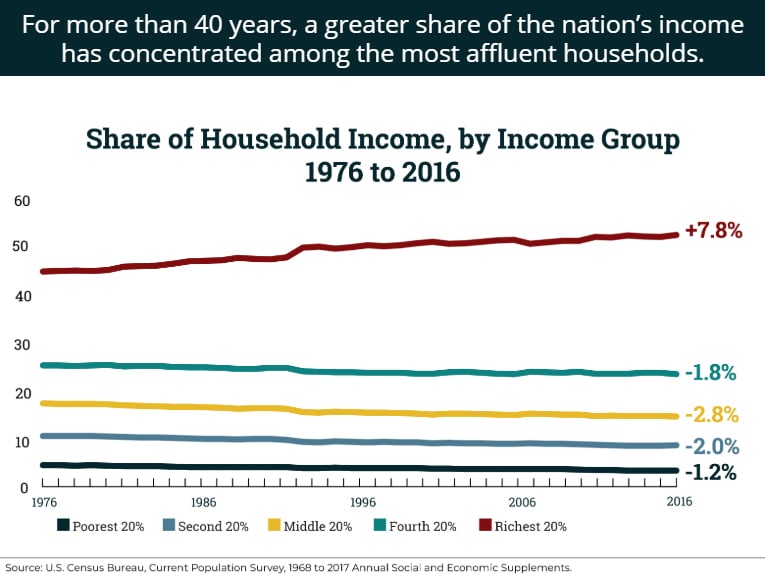
In this illustrated breakdown of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) and Tax Cuts 2.0, ITEP staff examine TCJA's role in growing income inequality, broken promises from corporations pledging to invest tax savings into workers and wages, and the embarrassment of riches flowing to the wealthiest Americans as a result of these “middle-class tax cuts.”
