
ITEP's Research Priorities
- 2025 tax debate
- Blog
- Cannabis Taxes
- Corporate Taxes
- Corporate Taxes
- Earned Income Tax Credit
- Education Tax Breaks
- Estate Tax
- Federal Policy
- Fines and Fees
- Georgia
- Immigration
- Income & Profits
- Income Taxes
- Inequality and the Economy
- ITEP Work in Action
- Local Income Taxes
- Local Policy
- Local Property Taxes
- Local Refundable Tax Credits
- Local Sales Taxes
- Maps
- Media Quotes
- News Releases
- OBBBA
- Other Revenues
- Personal Income Taxes
- Property & Wealth
- Property Taxes
- Property Taxes
- Publications
- Refundable Tax Credits
- Sales & Excise
- Sales, Gas and Excise Taxes
- Sales, Gas and Excise Taxes
- SALT Deduction
- Select Media Mentions
- Social Media
- Staff
- Staff Quotes
- State Corporate Taxes
- State Policy
- State Reports
- States
- Tax Analyses
- Tax Basics
- Tax Credits for Workers and Families
- Tax Credits for Workers and Families
- Tax Guide
- Tax Principles
- Tax Reform Options and Challenges
- Taxing Wealth and Income from Wealth
- Toolkits
- Trump Tax Policies
- Video
- Webinar
- Who Pays?
Yes, It’s Time to Talk about Progressive Taxes, Even a Wealth Tax
January 24, 2019 • By Alan Essig

Earlier today, several news organizations reported that Sen. Elizabeth Warren is set to formally propose a federal wealth tax. Immediately after, social media was atwitter with comments that ranged from praise to predictable outcries of how will the wealthy cope if forced to pay more in taxes.
West Virginia Center on Budget & Policy: Fixing the Social Security Tax Bill with a Bottom-Up Tax Cut for Working Families
January 24, 2019
The fact that so few West Virginians pay income tax on their Social Security benefits should tell us that this is not a middle-class tax cut. As the graph and analysis by the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy (ITEP) below shows, the average tax change from eliminating the state income tax on Social Security […]
Law360: Montana Mulls Statewide Sales Tax To Replace Property Taxes
January 24, 2019
Montana could become the first state in the nation to eliminate residential and commercial property taxes in exchange for creating a new 2.5 percent statewide sales tax...
NC Policy Watch: Report: Corporations Are Stiffing North Carolina on $373 Million in State Taxes
January 23, 2019
It turns out that state leaders can ensure that companies pay the proper amount of taxes on income generated from business conducted in their jurisdictions, but existing tax codes at the state level often allow loopholes for smart corporate tax lawyers to exploit. Corporations often use accounting sleights of hand to move income around within […]

A federal wealth tax on the richest 0.1 percent of Americans is a viable approach for Congress to raise revenue and is one of the few approaches that could truly address rising inequality. As this report explains, an annual federal tax of only 1 percent on the portion of any taxpayer’s net worth exceeding the threshold for belonging to the wealthiest 0.1 percent (likely to be about $32.2 million in 2020) could raise $1.3 trillion over a decade.
Thoughts about a Federal Wealth Tax and How It Could Raise Revenue, Address Income Inequality
January 23, 2019 • By Steve Wamhoff

Wealth inequality is much greater than income inequality. The 1 percent of Americans with the highest incomes receive about a fifth of the total income in the United States. In contrast, the top 1 percent of wealth holders in the United States own 42 percent of the nation’s wealth, according to estimates from University of California at Berkley economists Emmanuel Saez and Gabriel Zucman.
New Report Makes the Case for a Wealth Tax; Analysis Finds Such a Tax Could Raise More Than $1 Trillion Over a Decade
January 23, 2019 • By ITEP Staff

A federal wealth tax on the top 0.1 percent of households could raise significant tax revenue, curb growing economic inequality and help make the tax system fairer, a new report released today by the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy (ITEP) finds.
Five Years in, Cannabis Tax Haul Rivals or Exceeds Alcohol Taxes in Many States
January 23, 2019 • By ITEP Staff

A first-of-its-kind look at state excise taxes on legal cannabis sales finds that taxing the substance can be a meaningful source of state revenue but cautions that achieving sustainable revenues over time will be difficult under the price-based tax structures adopted in most states thus far.

State policy toward cannabis is evolving rapidly. While much of the debate around legalization has rightly focused on potential health and criminal justice impacts, legalization also has revenue implications for state and local governments that choose to regulate and tax cannabis sales. This report describes the various options for structuring state and local taxes on cannabis and identifies approaches currently in use. It also undertakes an in-depth exploration of state cannabis tax revenue performance and offers a glimpse into what may lie ahead for these taxes.
Cannabis Tax Debates are Ramping Up; Here’s What We’ve Learned from Five Years of Cannabis Taxation Thus Far
January 23, 2019 • By Carl Davis
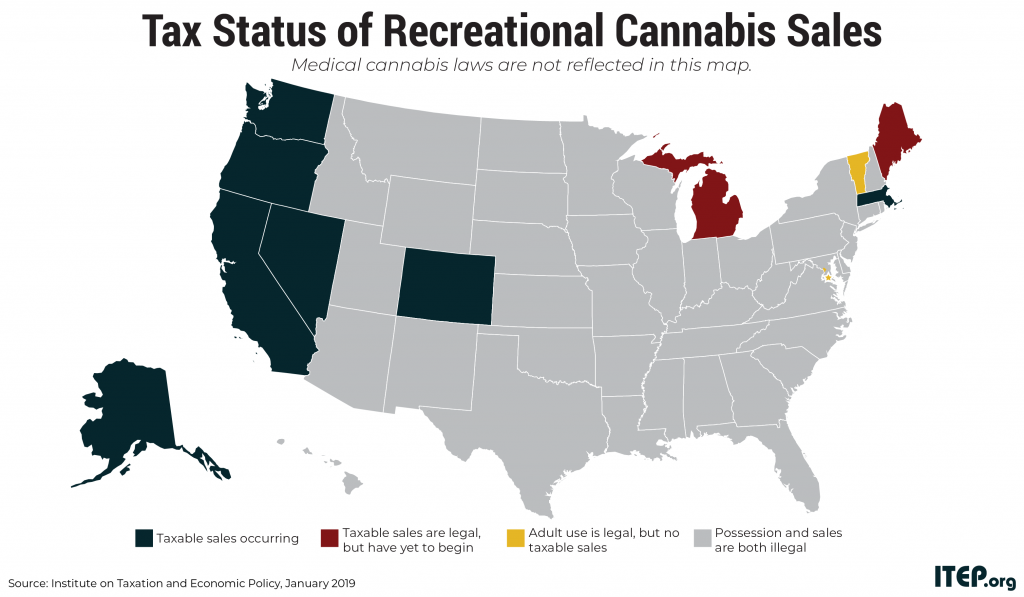
This year lawmakers in Connecticut, Delaware, Hawaii, Illinois, New Jersey, New York, Rhode Island, and Vermont will all be debating the taxation of recreational cannabis. A new ITEP report reviews the track record of recreational cannabis taxes thus far and offers recommendations for structuring cannabis taxes to achieve stable revenue growth over the long haul.
Time to restore fairness to the personal income tax and break the boom-or-bust cycle
January 22, 2019
Our citizen legislators have lots of choices to make when they meet for the annual legislative session every January – how to prioritize spending on public services like education, health care and public safety, which laws to enact, and whether to make changes to our state’s tax code.
Beacon Journal/Ohio.com Editorial Board: How Ohio’s Tax System Puts a Heavier Burden on the Poor
January 17, 2019
The Institute for Taxation & Economic Policy performed the analysis for Policy Matters. Consider that those Ohio families with annual incomes below $19,000 paid an average 12.3 percent of their income in state and local taxes. For those in the middle three quintiles, with incomes from $19,000 to $91,800 a year, the burden holds steady, […]
A Simple Fix for a $17 Billion Loophole: How States Can Reclaim Revenue Lost to Tax Havens
January 17, 2019 • By Richard Phillips

Enacting Worldwide Combined Reporting or Complete Reporting in all states, this report calculates, would increase state tax revenue by $17.04 billion dollars. Of that total, $2.85 billion would be raised through domestic Combined Reporting improvements, and $14.19 billion would be raised by addressing offshore tax dodging (see Table 1). Enacting Combined Reporting and including known tax havens would result in $7.75 billion in annual tax revenue, $4.9 billion from income booked offshore.
How States Can Help Shut Down Tax Havens by Cracking Down on Profit Shifting
January 17, 2019 • By Richard Phillips

A core problem with our corporate income tax laws at the federal and state levels is that they allow companies to use accounting gimmicks to shift significant amounts of their profits into low or zero-tax jurisdictions. Federal lawmakers had an opportunity to address this with the 2017 tax law, but they failed to do so, and, in fact, the law may incentivize more offshore tax avoidance. State lawmakers, however, can buck the federal trend and crack down on profit shifting themselves.
Who Pays and Why It Matters | MECEP Policy Insights Conference Keynote Address
January 16, 2019 • By Aidan Davis
States have broad discretion in how they secure the resources to fund education, health care, infrastructure, and other priorities important to communities and families. Aidan Davis with the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy will offer a national perspective on state-level approaches to funding public investments and the implications of those approaches on tax fairness and revenue adequacy, and their economic outcomes. She’ll also provide insight on what’s in store for 2019 among the states.
Missouri Budget Project: Senate Tax Bills Provide Unfair Giveaways, Leave Communities Reeling
January 16, 2019
An analysis by the Institute on Taxation & Economic Policy found that 91% of the tax cut would flow to the wealthiest 20% of Missourians.
Maine Center for Economic Policy: The Prosperity Budget
January 15, 2019
Where State of Working Maine 2018 investigated the nature of work in the modern economy and made recommendations to reaffirm our values of fairness and respect in the workplace, the Prosperity Budget examines the opportunity to leverage state budget and tax policy to build a stronger economy where every Mainer has an equal opportunity to […]
Gov. Cuomo Has the Right Idea on How to Tax Recreational Cannabis
January 15, 2019 • By ITEP Staff
Following is a statement by Carl Davis, research director at the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy, regarding the cannabis tax structure unveiled by New York Gov. Andrew Cuomo.
MassBudget: 14 Options for Raising Progressive Revenue
January 14, 2019
People in Massachusetts seek to live in communities that provide a high quality of life for their family and neighbors. We value good schools, police and fire protection, libraries and parks, smooth roads and reliable transit, and supports to help families struggling through tough times. A community’s day-to-day well-being and its long-term prosperity are built […]
Policy Matters Ohio: New Research Underlines Need to Overhaul State Tax Code
January 11, 2019
Ohio’s upside-down tax system takes an especially heavy toll on black and Latino residents. That’s the finding of new research from the Institute on Taxation & Economic Policy (ITEP), a national nonprofit research group with a sophisticated model of the tax system, that was released today by Policy Matters Ohio. Read more

New and returning policymakers have a tremendous opportunity to improve their constituents’ lives and their states’ economies through tax policy. This report distills the findings of “Who Pays?” into policy recommendations that can serve as a guide to new lawmakers, advocates, and others seeking to improve their state’s tax codes. It explains the importance of favoring taxes on income and wealth over taxes on consumption, the value of certain targeted tax benefits for families living in poverty, the need to abandon ineffective, unnecessary tax subsidies for high-income households, and the promise of bold new options for improving the regressive distributional…
How to Think About the 70% Top Tax Rate Proposed by Ocasio-Cortez (and Multiple Scholars)
January 8, 2019 • By Steve Wamhoff

The uproar deliberately steers clear of any real policy discussion about what a significantly higher marginal tax rate would mean. Her critics are mostly the same lawmakers who enacted a massive tax cut for the rich last year that was not debated seriously or supported by serious research. Meanwhile, multiple scholarly studies conclude a 70 percent top tax rate would be an optimal way to tax the very rich. Ocasio-Cortez has brought more attention to the very real need to raise revenue and do it in a progressive way.
Arizona Center for Economic Progress: Wrong Priorities: It Doesn’t Make Sense to Give a Tax Cut to the Rich While Arizona Asks Children in Public Schools to Wait
January 2, 2019
Arizona stands to gain $130 million to $230 million in General Fund revenues if it conforms the Arizona tax code to the federal tax changes enacted in 2017. Rather than directing those additional revenues to better prepare for the next economic downturn or toward increased investments in our public schools, SB1143 and HB2522 will direct […]

Sometimes policy developments move at a rapid-fire pace, so we’re taking time over the next 12 days to reflect on some of the most significant federal and state tax policy developments and/or tax policy analyses that happened this year.
Economic Progress Institute: Rhode Island Standard of Need
December 20, 2018
The RISN calculates a household budget for families with two young children, and for single adults. The no-frills budget includes the costs of housing, food, transportation, health care, child care and other necessities including clothing, toiletries and telephone service. The RISN also demonstrates how work supports like food assistance, tax credits, and child care and health care subsidies help close the gap between income and basic need expenses. By taking all of these factors into account, the RISN provides a more realistic measure of the economic security of Rhode Islanders than the federal poverty level.
