
ITEP's Research Priorities
- 2025 tax debate
- Blog
- Cannabis Taxes
- Corporate Taxes
- Corporate Taxes
- Earned Income Tax Credit
- Education Tax Breaks
- Estate Tax
- Federal Policy
- Fines and Fees
- Georgia
- Immigration
- Income & Profits
- Income Taxes
- Inequality and the Economy
- ITEP Work in Action
- Local Income Taxes
- Local Policy
- Local Property Taxes
- Local Refundable Tax Credits
- Local Sales Taxes
- Maps
- Media Quotes
- News Releases
- OBBBA
- Other Revenues
- Personal Income Taxes
- Property & Wealth
- Property Taxes
- Property Taxes
- Publications
- Refundable Tax Credits
- Sales & Excise
- Sales, Gas and Excise Taxes
- Sales, Gas and Excise Taxes
- SALT Deduction
- Select Media Mentions
- Social Media
- Staff
- Staff Quotes
- State Corporate Taxes
- State Policy
- State Reports
- States
- Tax Analyses
- Tax Basics
- Tax Credits for Workers and Families
- Tax Credits for Workers and Families
- Tax Guide
- Tax Principles
- Tax Reform Options and Challenges
- Taxing Wealth and Income from Wealth
- Toolkits
- Trump Tax Policies
- Video
- Webinar
- Who Pays?
The Wall Street Journal: From Gas Taxes to Vaping Rules, New State Laws Take Effect Across U.S.
July 2, 2019
Drivers in a number of states will now pay higher taxes on gas as part of a broader push to fund infrastructure improvements. In Illinois, the gas tax has doubled to 38 cents from 19 cents, making it the largest increase for any of these states, according to the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy, […]

Mercury is rising, presidential primary debates are underway and most state legislative sessions have adjourned for summer. Whether you’re curling up with a good book (or your favorite e-Reader) or looking for a new television show to binge-watch, check out these recommendations on ITEP’s Summer Reading (and Watching) List.
Bloomberg: Horse Racing Tax Credit Backers Not Deterred by House Setback
July 1, 2019
Matthew Gardner, a senior fellow at the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy, said there are sensible reasons to ask whether these tax breaks are more generous than they should be. ITEP is among organizations that have criticized the practice of extending temporary tax break and asked Congress to do away with them. “This sounds […]
Nevada Business: Taxes and Nevada: The Give and Take
July 1, 2019
Many of those breaks and loop holes were left in place by the new policies, said Steve Wamhoff, director of federal tax policy at the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy. “There are a lot of breaks and loopholes that allow a company not to pay,” Wamhoff told Yahoo Finance. “People, when they think of […]
Bloomberg: Gas Tax Hike Takes Effect in Five States This Month
July 1, 2019
All state gas taxes are tacked onto the federal government’s 18.4 cent-per-gallon levy, according to the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy. Read more
Gaps in Sales Tax Collection Linger at Amazon.com and Among Other E-Retailers
July 1, 2019 • By Carl Davis
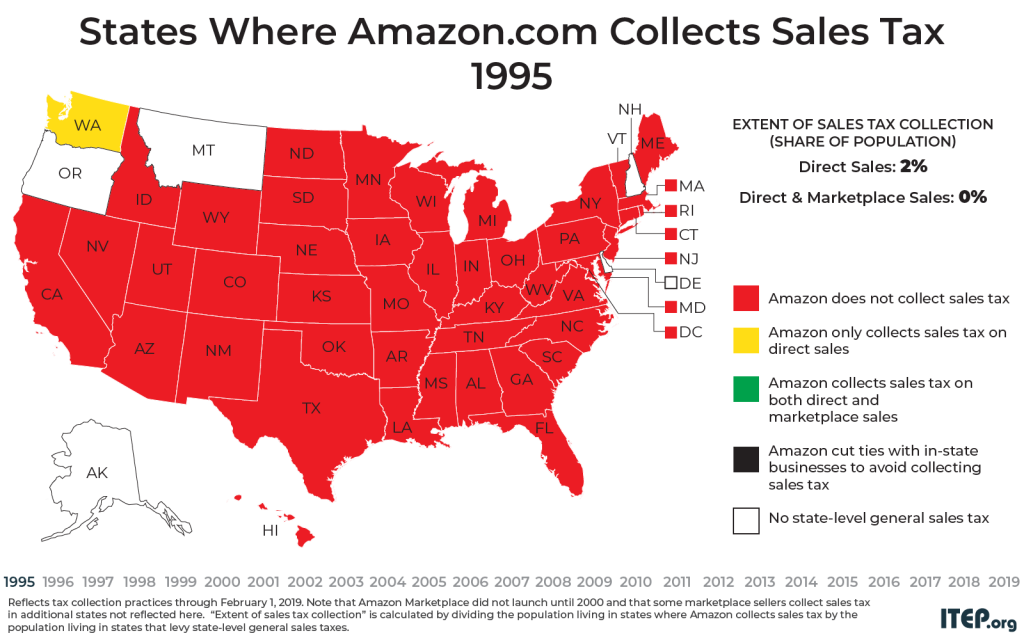
The last few years have brought big changes to sales tax collection for purchases made at Amazon.com and other e-retail websites. As recently as 2011, Amazon was only collecting sales tax on its direct sales in five states – a fact that gave the company a competitive edge over brick and mortar stores during a critical time in its growth. Today, Amazon is collecting state-level sales taxes on all its direct sales, but it still usually fails to collect sales tax on the large volume of sales it makes through the “Amazon Marketplace.” This points to a broader problem in…
Why Trump Administration’s Plan to Index Capital Gains to Inflation Is Just Another Giveaway to the Wealthy
June 28, 2019 • By Steve Wamhoff

The White House is reported to be planning to unilaterally adjust the way capital gains are assessed to benefit the wealthiest Americans. The proposal would adjust capital gains for inflation, reducing taxes disproportionately for the wealthiest households who own most assets by limiting their taxable gains to those above and beyond the inflation rate.

A summary of ITEP reports, analyses and blogs this month.
Wealth Tax Is Supported by Basically Everyone Who Is Not a Politician
June 27, 2019 • By Steve Wamhoff

A February survey found that 61 percent of registered voters supported a wealth tax proposal, including 51 percent of Republican voters. And it’s not just the non-rich wanting to tax the very rich. A June survey found that 60 percent of millionaires support the idea.
Travelers in 12 States Will Pay More in Gas Taxes Beginning Monday
June 27, 2019 • By Carl Davis

Drivers in 12 states who hit the road during this summer driving season will be paying more in gas tax beginning Monday, July 1. While the federal gas tax has remained stagnant for nearly 26 years, many states have stepped up and increased their taxes so they can raise revenue to fund infrastructure and other projects. California, Indiana, Maryland, Michigan, Montana, Nebraska, Ohio, Rhode Island, South Carolina, Tennessee and Vermont all will raise their gas taxes.
Gas Taxes Rise in a Dozen States, Including an Historic Increase in Illinois
June 27, 2019 • By Carl Davis
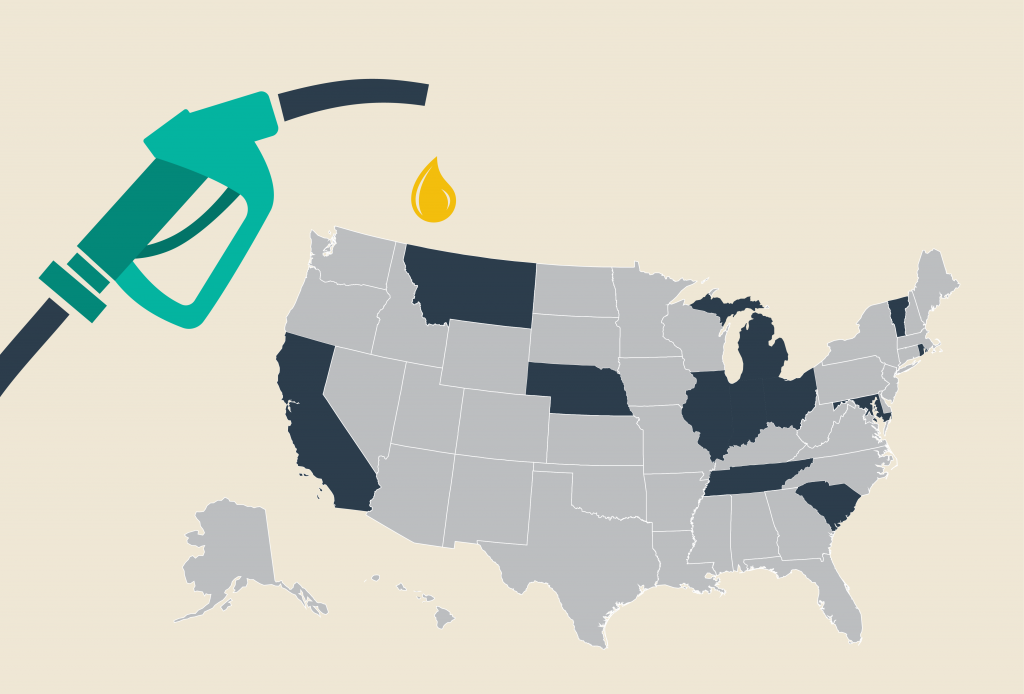
On July 1, 12 states will boost their gasoline taxes and 11 will boost their diesel taxes. The reasons for these increases vary, but they’re generally intended to fund maintenance and improvement of our nation’s transportation infrastructure–a job at which Congress has not excelled in recent years.
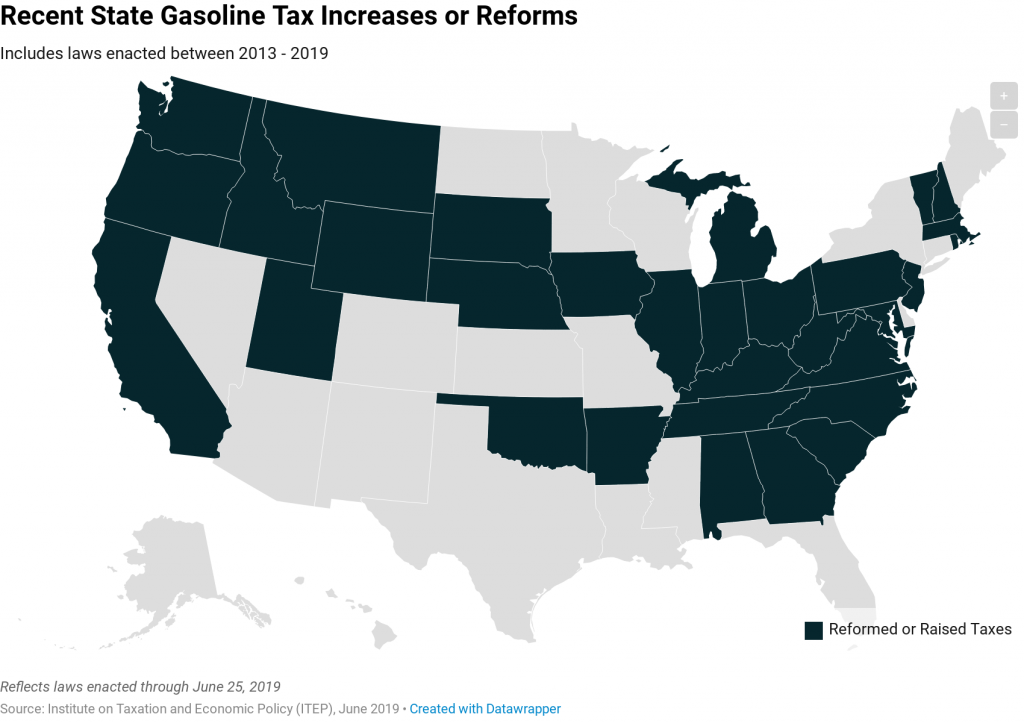
Gas taxes are the most important revenue source that states have available to pay for transportation infrastructure. In recent years, state lawmakers across the country have increasingly agreed that gas taxes must be increased to fund the maintenance and improvement of their infrastructure networks.
Ohio now enjoys the distinction of being the 30th state to raise or reform its gas tax this decade, and the third state to do so this year, under a bill signed into law by Gov. Mike DeWine. While state tax policy can be a contentious topic, there has been a remarkable level of agreement on the gasoline tax. Increasingly, state lawmakers are deciding that outdated gas taxes need to be raised and reformed to fund infrastructure projects that are vital to their economies. These actions are helping reverse losses in gas tax purchasing power caused by rising construction costs…
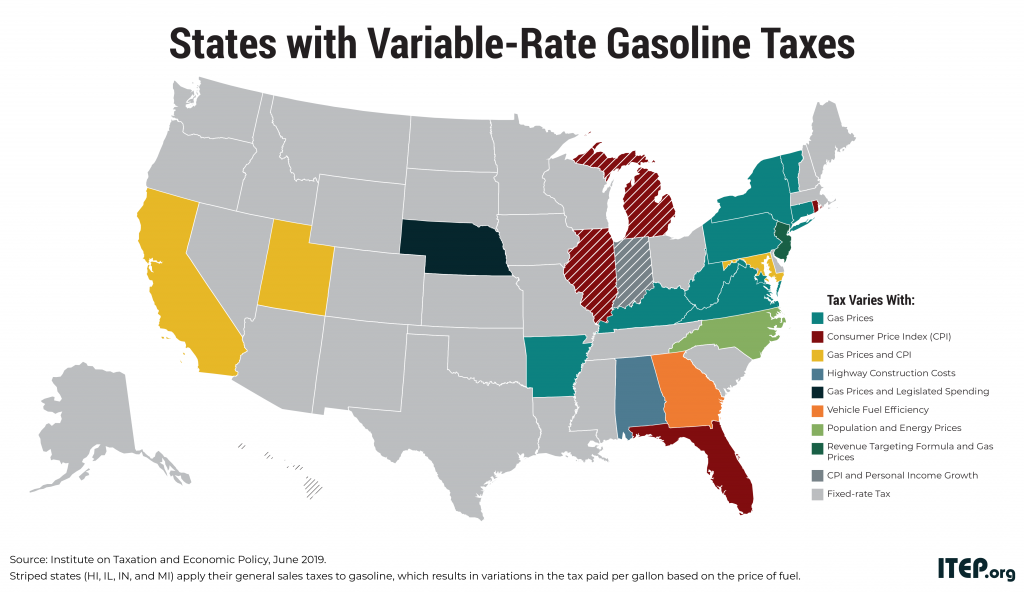
The flawed design of federal and state gasoline taxes has made it exceedingly difficult to raise adequate funds to maintain the nation’s transportation infrastructure. Twenty-eight states and the federal government levy fixed-rate gas taxes where the tax rate does not change even when the cost of infrastructure materials rises or when drivers purchase more fuel-efficient vehicles and pay less in gas tax. The federal government’s 18.4-cent gas tax, for example, has not increased in over 25 years. Many states have waited a decade or more since last raising their own gas tax rates.
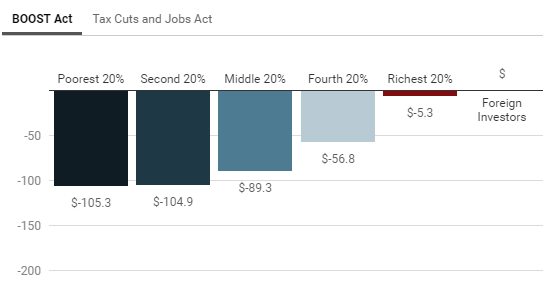
A refundable tax credit proposed by Rep. Rashida Tlaib (D-MI) would be more expansive than other recent tax credit proposals, new estimates from ITEP show. Rep. Tlaib’s proposal, unlike others, does not require households to work to receive the benefit.

The BOOST Act would provide a new tax credit of up to $3,000 for single people and up to $6,000 for married couples, which would be in addition to existing tax credits. Income limits would prevent well-off households from receiving the credit. Unlike other refundable tax credit proposals, the BOOST Act would not be limited to people with earnings or people with children.
What to Watch for on Tax Policy During the Presidential Primary
June 25, 2019 • By Steve Wamhoff

America needs a new tax code. The Democratic presidential debates beginning this week present an opportunity for candidates to make clear how they would address inequality or to raise enough revenue to make public investments that make the economy work for everyone. Here are some of the big tax issues that we hope they will touch on.
The SALT Cap Isn’t Harming State and Local Revenues. Myths About It May Be.
June 24, 2019 • By Carl Davis

A House Ways and Means subcommittee hearing on Tuesday will explore a highly controversial provision of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) that prevents individuals and families from writing off more than $10,000 in state and local tax (SALT) payments on their federal tax forms each year. The focus of the hearing will be whether the cap negatively affects state and local revenue streams that fund schools, firefighters, and other services. There are at least three ways this could happen though only one of those is plausible, and it’s not the one that the organizers of this hearing likely…
UPDATED: New ITEP Data Shows the House Ways and Means Bill to Expand EITC and Child Tax Credit Would Benefit Low- and Moderate-Income People and Families
June 20, 2019 • By Steve Wamhoff
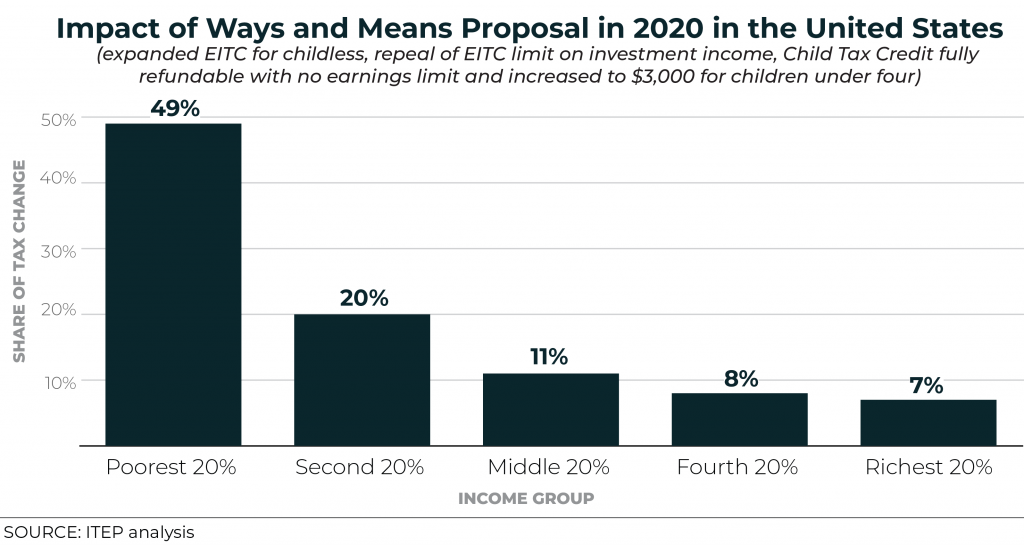
Today the House Ways and Means Committee is marking up the Economic Mobility Act of 2019, a bill introduced by Chairman Richard Neal to expand some key tax credits to help low- and moderate-income people and families. New data generated with the ITEP microsimulation tax model show how adults and children would benefit nationally and in each state.

Join our team! ITEP has an opening for a Senior Software Engineer (Full Stack) to join our creative, passionate and productive staff as Lead Tax Model Platform Developer. This position will work directly with the technical engine behind our work: ITEP’s Microsimulation Tax Model. The Lead Tax Model Platform Developer reports directly to ITEP’s senior economist and works closely with the entire policy analyst team.
Calling Progressive Tax Proposals “Extreme” Are Taunts Meant to Distract
June 18, 2019 • By Steve Wamhoff
Dismissing calls for progressive taxes as “radical,” “extreme,” or “socialism” are taunts meant to distract from the real question: Why should we ignore the bottom half of Americans, whose share of the economic pie shrank and now have negative net worth, while allowing the wealthy and powerful, whose net worth more than tripled, to dictate our public policies?
Vox, The Weeds: 5 Big Ideas to Use Tax Credits to Fight Poverty
June 14, 2019
Meg Wiehe from the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy explains the leading progressive tax plans in Congress and how they differ from Trump’s tax cuts. Listen to the podcast

States are putting evidence into practice with multiple efforts to improve services and tax codes through more progressive taxes on the wealthy. Clear evidence has spread widely this year, informing a national conversation about progressive taxation and leading lawmakers in multiple states to eschew supply-side superstition and act on real evidence instead. Taxing the rich works, and in this Just Taxes blog we review state-level efforts to put these proven findings into effect.
New SALT Workaround Regulations Narrow a Tax Shelter, but Work Remains to Close it Entirely
June 11, 2019 • By Carl Davis

Today the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) released its final regulations cracking down on a tax shelter long favored by private and religious K-12 schools, and more recently adopted by some “blue state” lawmakers in the wake of the 2017 Trump tax cut. The regulations come more than a year after the IRS first announced the […]
Does Your State Offer Tax Credits for Private K-12 School Voucher Donations?
June 10, 2019 • By ITEP Staff
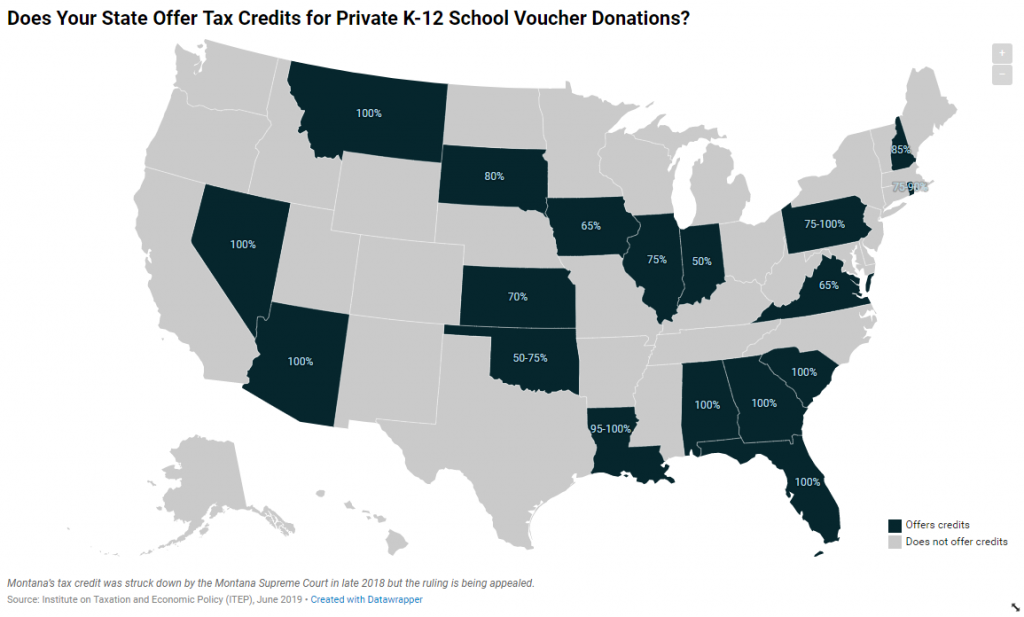
Eighteen states provide public support to private and religious K-12 schools through large tax credits for taxpayers who contribute money to K-12 school voucher funds. These credits range from 50 percent to 100 percent of the amount contributed, which far exceeds the tax benefit available for charitable contributions to other organizations such as homeless shelters […]
