
ITEP's Research Priorities
- 2025 tax debate
- Blog
- Cannabis Taxes
- Corporate Taxes
- Corporate Taxes
- Earned Income Tax Credit
- Education Tax Breaks
- Estate Tax
- Federal Policy
- Fines and Fees
- Georgia
- Immigration
- Income & Profits
- Income Taxes
- Inequality and the Economy
- ITEP Work in Action
- Local Income Taxes
- Local Policy
- Local Property Taxes
- Local Refundable Tax Credits
- Local Sales Taxes
- Maps
- Media Quotes
- News Releases
- OBBBA
- Other Revenues
- Personal Income Taxes
- Property & Wealth
- Property Taxes
- Property Taxes
- Publications
- Refundable Tax Credits
- Sales & Excise
- Sales, Gas and Excise Taxes
- Sales, Gas and Excise Taxes
- SALT Deduction
- Select Media Mentions
- Social Media
- Staff
- Staff Quotes
- State Corporate Taxes
- State Policy
- State Reports
- States
- Tax Analyses
- Tax Basics
- Tax Credits for Workers and Families
- Tax Credits for Workers and Families
- Tax Guide
- Tax Principles
- Tax Reform Options and Challenges
- Taxing Wealth and Income from Wealth
- Toolkits
- Trump Tax Policies
- Video
- Webinar
- Who Pays?
Tax Cuts 2.0 – Virginia
September 26, 2018 • By ITEP Staff
The $2 trillion 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) includes several provisions set to expire at the end of 2025. Now, GOP leaders have introduced a bill informally called “Tax Cuts 2.0” or “Tax Reform 2.0,” which would make the temporary provisions permanent. And they falsely claim that making these provisions permanent will benefit […]
Tax Cuts 2.0 – Washington
September 26, 2018 • By ITEP Staff
The $2 trillion 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) includes several provisions set to expire at the end of 2025. Now, GOP leaders have introduced a bill informally called “Tax Cuts 2.0” or “Tax Reform 2.0,” which would make the temporary provisions permanent. And they falsely claim that making these provisions permanent will benefit […]
Tax Cuts 2.0 – West Virginia
September 26, 2018 • By ITEP Staff
The $2 trillion 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) includes several provisions set to expire at the end of 2025. Now, GOP leaders have introduced a bill informally called “Tax Cuts 2.0” or “Tax Reform 2.0,” which would make the temporary provisions permanent. And they falsely claim that making these provisions permanent will benefit […]
Tax Cuts 2.0 – Wisconsin
September 26, 2018 • By ITEP Staff
The $2 trillion 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) includes several provisions set to expire at the end of 2025. Now, GOP leaders have introduced a bill informally called “Tax Cuts 2.0” or “Tax Reform 2.0,” which would make the temporary provisions permanent. And they falsely claim that making these provisions permanent will benefit […]
Tax Cuts 2.0 – Wyoming
September 26, 2018 • By ITEP Staff
The $2 trillion 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) includes several provisions set to expire at the end of 2025. Now, GOP leaders have introduced a bill informally called “Tax Cuts 2.0” or “Tax Reform 2.0,” which would make the temporary provisions permanent. And they falsely claim that making these provisions permanent will benefit […]
Tax Cuts 2.0 – Connecticut
September 26, 2018 • By ITEP Staff
The $2 trillion 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) includes several provisions set to expire at the end of 2025. Now, GOP leaders have introduced a bill informally called “Tax Cuts 2.0” or “Tax Reform 2.0,” which would make the temporary provisions permanent. And they falsely claim that making these provisions permanent will benefit […]
An Unhappy Anniversary: Federal Gas Tax Reaches 25 Years of Stagnation
September 25, 2018 • By Carl Davis
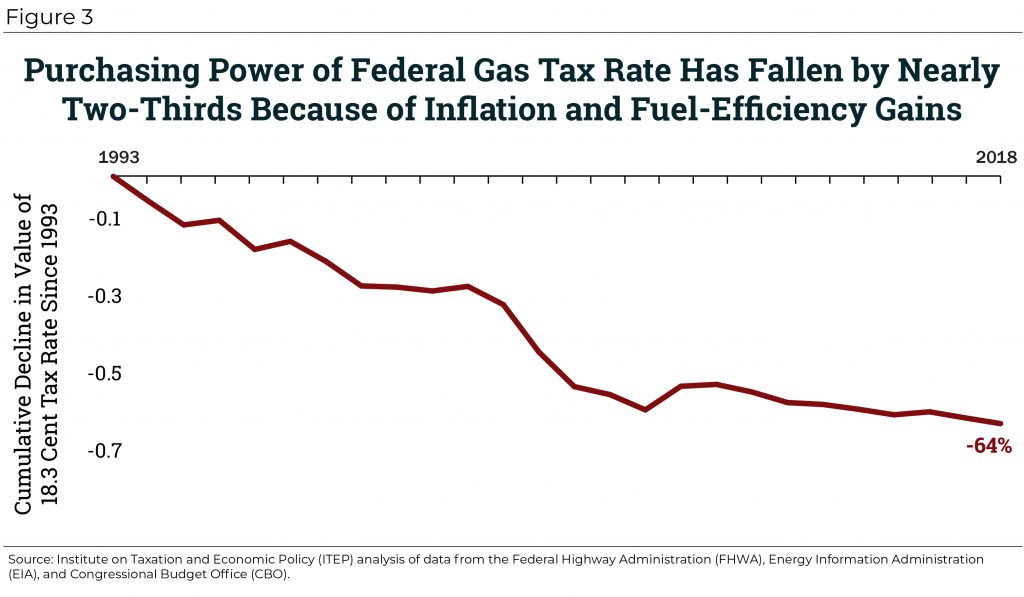
The federal gas tax was last raised on Oct. 1, 1993, the same year that the classic movie Groundhog Day was unveiled to the American public. In the film, Phil Connors (played by Bill Murray) gets caught in a time loop and spends decades reliving the same cold, February day in Punxsutawney, Penn. Those of us lamenting the 25-year stagnation of the federal gas tax can’t help but feel some of that same sense of repetition. Federal lawmakers occasionally discuss updating the gas tax, but top lawmakers have yet to put in the effort needed to shepherd such a change…
Oxfam Report Finds Pharmaceuticals Profiteering Off Crises in Developing Countries
September 20, 2018 • By Peter Della-Rocca

The report indicates, pharmaceutical companies have taken steps to hide their profits in low-tax countries, sapping billions in revenue from the governments that invest in the science that drives their products and safeguard the patents that undergird their business. Pharmaceutical companies made use of a familiar battery of methods to exploit the international system this way, including inversions to disguise an American company as a foreign one and passing profits into low-tax jurisdictions through artificial usage fees on intangible assets like intellectual property.
State Tax Codes Can Help Mitigate Poverty and Impact of Federal Tax Cuts on Low- and Middle-Income Families
September 20, 2018 • By Misha Hill

The national poverty rate declined by 0.4 percentage points to 12.3 percent in 2017. According to the U.S. Census, this was not a statistically significant change from the previous year. 39.7 million Americans, including 12.8 million children, lived in poverty in 2017. Median household income also increased for the third consecutive year, but this was […]
The Free Press: Think Tank Releases Blueprint to Fully Fund Education, Medicaid & Lower Property Taxes
September 20, 2018
Tax cuts passed by the Maine Legislature and Gov. Paul LePage over the past eight years will cost the state $864 million in revenue in the next biennium, according to an analysis by the Maine Center for Economic Policy and the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy. At the same time the state continues to ignore its legal obligations to fully fund education, Medicaid expansion and revenue sharing.
IRS Reopens Tax Loophole Sought by Sen. Toomey, but it Won’t Work in Pennsylvania
September 20, 2018 • By Carl Davis

A recent IRS clarification, which appears to have been a pet project of Sen. Pat Toomey (R-PA), has been widely interpreted as reopening a loophole the agency had proposed closing just weeks earlier. But while the announcement creates an opening for aggressive tax avoidance in many states, Pennsylvania, ironically enough, isn’t one of them.
West Virginia Center on Budget & Policy: Don’t Double Down on Failed Federal Tax Cuts
September 18, 2018
Extending most of these provision does more of the same and is a huge and alarming waste of resources. According to the Institute on Taxation and Economy Policy, if the individual tax provisions are extended to 2026 and beyond, the richest 1 percent – those making on average $762,000 – in West Virginia would receive an average tax cut of over $20,000. Meanwhile, the poorest 20 percent with an average income of $12,900 will see an average tax increase of $40.
State Tax Codes as Poverty Fighting Tools: 2018 Update on Four Key Policies in All 50 States
September 17, 2018 • By Aidan Davis, Misha Hill

This report presents a comprehensive overview of anti-poverty tax policies, surveys tax policy decisions made in the states in 2018, and offers recommendations that every state should consider to help families rise out of poverty. States can jumpstart their anti-poverty efforts by enacting one or more of four proven and effective tax strategies to reduce the share of taxes paid by low- and moderate-income families: state Earned Income Tax Credits, property tax circuit breakers, targeted low-income credits, and child-related tax credits.
Rewarding Work Through State Earned Income Tax Credits in 2018
September 17, 2018 • By ITEP Staff

The Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) is a policy designed to bolster the earnings of low-wage workers and offset some of the taxes they pay, providing the opportunity for struggling families to step up and out of poverty toward meaningful economic security. The federal EITC has kept millions of Americans out of poverty since its enactment in the mid-1970s. Over the past several decades, the effectiveness of the EITC has been magnified as many states have enacted and later expanded their own credits. The effectiveness of the EITC as an anti-poverty policy can be increased by expanding the credit at…
Reducing the Cost of Child Care Through State Tax Codes in 2018
September 17, 2018 • By Aidan Davis
Families in poverty contribute over 30 percent of their income to child care compared to about 6 percent for families at or above 200 percent of poverty. Most families with children need one or more incomes to make ends meet which means child care expenses are an increasingly unavoidable and unaffordable expense. This policy brief examines state tax policy tools that can be used to make child care more affordable: a dependent care tax credit modeled after the federal program and a deduction for child care expenses.

Sales taxes are one of the most important revenue sources for state and local governments; however, they are also among the most unfair taxes, falling more heavily on low- and middle-income households. Therefore, it is important that policymakers nationwide find ways to make sales taxes more equitable while preserving this important source of funding for public services. This policy brief discusses two approaches to a less regressive sales tax: broad-based exemptions and targeted sales tax credits.

State lawmakers seeking to make residential property taxes more affordable have two broad options: across-the-board tax cuts for taxpayers at all income levels, such as a homestead exemption or a tax cap, and targeted tax breaks that are given only to particular groups of low- and middle-income taxpayers. One such targeted program to reduce property taxes is called a “circuit breaker” because it protects taxpayers from a property tax “overload” just like an electric circuit breaker: when a property tax bill exceeds a certain percentage of a taxpayer’s income, the circuit breaker reduces property taxes in excess of this “overload”…
Today's poverty and income data show that income continues to concentrate at the top; in fact, the top 20 percent continue to capture 51.5 percent of income. Meanwhile, average income for the poorest 20 percent of households is less today than it was 18 years ago.
We Crunched Some Numbers to Show What Tax Reform for Working People Really Looks Like
September 12, 2018 • By ITEP Staff
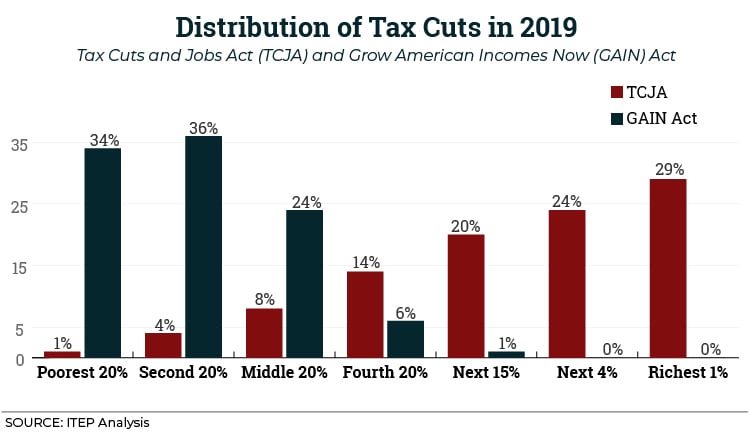
Throughout President’s Trump’s presidential campaign and from his first day in office until now, his administration has favored and promoted policies that benefit the wealthy and corporations even as it claims to be the working people’s champion. If more recent economic data are a reflection of what we’ll see in the long-term due to the Trump Administration’s recent tax cuts, wealth will continue to accrue at the top while income remains stagnant or barely budges for low- and moderate-income families. Policy can make a difference: ITEP Staff shows how the Grow American Incomes Now (GAIN) Act would help millions of…
More of the Same: Tax Cuts 2.0 Will Benefit the Rich
September 10, 2018 • By Alan Essig

Media Contact Following is a statement from Alan Essig, executive director of the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy, regarding the tax bill introduced today by House GOP leadership. “Once again, lawmakers are attempting to force tax cuts that primarily benefit the wealthy on an unwilling public. Nearly nine months after the tax law passed, […]
WRAL: Meg Wiehe: Capping North Carolina’s top income tax rate isn’t good for our communities
September 4, 2018
ITEP Deputy Director Meg Wiehe writes for WRAL.com that it would be unwise to constitutionally cap the North Carolina state income tax rate, pointing out that school funding in the state is already down and faltering revenues in other states have led to teacher pay crises and strikes.
Keystone Research: The State of Working Pennsylvania 2018
August 30, 2018
“The State of Working Pennsylvania 2018,” Keystone Research Center’s 23rd annual review of the Pennsylvania economy and labor market finds that, nearly a decade into the current national economic expansion, many Pennsylvania workers are still waiting for a raise. The report points to three factors that help explain this.
ITEP Testimony “Regarding the Final Report of the Arkansas Tax Reform and Relief Legislative Task Force”
August 23, 2018 • By Lisa Christensen Gee
Read the testimony in PDF WRITTEN TESTIMONY SUBMITTED TO: THE ARKANSAS TAX REFORM AND RELIEF TASK FORCE Lisa Christensen Gree, Senior State Tax Policy Analyst Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy Regarding the Final Report of the Arkansas Tax Reform and Relief Legislative Task Force August 22, 2018 Thank you for the opportunity to submit these […]
Kentucky Center for Economic Policy: Clean Up the Tax Code to Invest in Our Commonwealth
August 22, 2018
To move our tax code in the right direction, Kentucky should rejoin 32 other states with a graduated income tax based on ability to pay. Income below $37,500 single/$75,000 married should still be taxed at 5 percent, between that point and $75,000 single/$150,000 married at 6 percent and above those incomes at 7 percent, phasing […]
Press Herald: Will Maine Referendum On Home Care Result In ‘Marriage Penalty’ Tax?
August 17, 2018
Aidan Davis, senior policy analyst at the nonpartisan Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy, wrote a letter to the Secretary of State’s Office on June 15 stating that the income threshold would be double for married couples filing jointly. “We found the language of the initiative to be clear in describing that individual (not household) […]
