
ITEP's Research Priorities
- 2025 tax debate
- Blog
- Cannabis Taxes
- Corporate Taxes
- Corporate Taxes
- Earned Income Tax Credit
- Education Tax Breaks
- Estate Tax
- Federal Policy
- Fines and Fees
- Georgia
- Immigration
- Income & Profits
- Income Taxes
- Inequality and the Economy
- ITEP Work in Action
- Local Income Taxes
- Local Policy
- Local Property Taxes
- Local Refundable Tax Credits
- Local Sales Taxes
- Maps
- Media Quotes
- News Releases
- OBBBA
- Other Revenues
- Personal Income Taxes
- Property & Wealth
- Property Taxes
- Property Taxes
- Publications
- Refundable Tax Credits
- Sales & Excise
- Sales, Gas and Excise Taxes
- Sales, Gas and Excise Taxes
- SALT Deduction
- Select Media Mentions
- Social Media
- Staff
- Staff Quotes
- State Corporate Taxes
- State Policy
- State Reports
- States
- Tax Analyses
- Tax Basics
- Tax Credits for Workers and Families
- Tax Credits for Workers and Families
- Tax Guide
- Tax Principles
- Tax Reform Options and Challenges
- Taxing Wealth and Income from Wealth
- Toolkits
- Trump Tax Policies
- Video
- Webinar
- Who Pays?
NJPP: A Grain of ‘SALT’: New Jersey Needs More Than Workarounds to Respond to GOP Tax Plan
January 25, 2018
That’s because these workarounds would disproportionately benefit the wealthiest households in New Jersey, to make no mention of the fact that the Trump administration is unlikely to allow them to stand.
DCFPI: As High-Income DC Taxpayers Reap Large Federal Tax Windfalls, DC Can Make Our Tax Code More Progressive
January 22, 2018
According to recent estimates from the Institute for Taxation and Economic Policy (ITEP), District of Columbia residents can expect to receive an $850 million federal tax break this year.
MassBudget: What Does the Federal Tax Law Mean for Massachusetts and How Might the Commonwealth Respond?
January 22, 2018
The tax cuts are also skewed toward high-income tax filers when measured as a portion of their own incomes.
Pennsylvania Budget and Policy Center: The Pennsylvania Promise: Making College Affordable and Securing Pennsylvania’s Economic Future
January 22, 2018
Three recent briefs by the Keystone Research Center laid out the case for more affordable access to post-secondary education in Pennsylvania. The global race for raising incomes and increasing opportunity hinges critically on access to post-secondary education and training. If Pennsylvania does not expand access to higher education to more of its citizens, the Commonwealth’s economy will suffer and living standards will lag behind growth elsewhere. With a modest and smart investment, Pennsylvania can build a more prosperous future for its citizens and reinvigorate the American Dream in every corner of the keystone state. “The Pennsylvania Promise,” outlined below, shows…

Last week, a federal court judge in California ruled that the Trump administration cannot end DACA (Deferred Action for Childhood Arrivals) while the case works its way through the courts. Although this is reassuring news for the roughly 685,000 young people currently enrolled or seeking renewals for their DACA status it does not extend protections to new applicants, and it does not lessen the need for congressional action to protect Dreamers.
MassBudget: Sweeter than SALT: Highest-Income Households Get Federal Tax Cuts More Than Twice SALT Losses
January 11, 2018
For Massachusetts’ highest-income households – those with annual incomes over $1 million – the average tax cuts from other federal changes in the law are more than twice the average size of the impact from the loss of SALT deductibility.
It’s All About the Context: A Closer Look at Arkansas’s Income Tax
January 10, 2018
The tax task force is rounding out its extensive review of the Arkansas tax code this week by looking at one of the most contentious tax topics these days: income taxes. So, are we a high-income-tax state or a low-income-tax state? In Arkansas, it depends a lot on how much money you make, and how you make it. For example, retirement income is exempt for the first $6,000; military retirement income is completely exempt; there are border-city exemptions if you work in Texarkana; and capital gains income from things like stocks or real estate sales is taxed much more leniently…
Kentucky Center for Economic Policy: Passage of the Dream Act Would Benefit Kentucky
December 21, 2017
The Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy (ITEP) estimates that 6,000 (formerly) DACA-eligible Kentuckians currently contribute a total of $8.1 million in local and state taxes annually through sales and excise taxes, property taxes and income taxes. Their effective tax rate of 9.1 percent is higher than that paid by the wealthiest 1 percent of […]
Policy Matters Ohio: Crackdown on Dreamers could cost Ohio millions
December 21, 2017
If DACA recipients stay in Ohio after losing work authorization they could earn lower wages and become less likely to file income tax returns. Without the Dream Act, Ohio can expect to lose at least $5 million in tax revenue, according to the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy (ITEP). Read more here
Wisconsin Budget Project: Giving Young Immigrants a Pathway to Citizenship Would Boost Wisconsin’s Farm Economy
December 20, 2017
According to a new report from the Wisconsin Budget Project, passing the Dream Act and establishing a pathway to citizenship for immigrant youth would help Wisconsin farms and communities by: Expanding Wisconsin’s economy by up to $600 million a year by improving the access that immigrants have to educational and economic opportunity; Increasing state and […]
Wisconsin Budget Project: Dream Act Would Boost Wisconsin Economy and Tax Revenues: Revoking DACA Hurts Both
December 20, 2017
There are 10,000 young immigrants potentially eligible for DACA who call Wisconsin home. They currently contribute a total of $16 million to local and state taxes annually through sales and excise taxes, property taxes, and income tax. Read more here
Michigan League for Public Policy: The benefits of Deferred Action for Childhood Arrivals (DACA) on immigrants in Michigan
December 20, 2017
Researchers at the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy (ITEP) estimate that nationwide, DACA enrollees contribute $2 billion in state and local taxes each year. In Michigan, these young adults contribute $13 million in state and local taxes annually. If federal elected officials fail to pass a replacement to DACA and beneficiaries’ work permits expire, […]
New Jersey Policy Perspectives: Failure to Act on DACA and Dream Act Would Harm New Jersey’s Tax Revenues
December 20, 2017
There are 53,000 young immigrants who were potentially eligible for DACA that call New Jersey home. They have attended our public schools, graduated high school and many have enrolled in our public colleges. And many are our coworkers, our neighbors and loved ones. They currently pay a total of $57 million to state and local […]
Florida Policy Institute: Dream Act: What’s at Stake for Florida?
December 20, 2017
There are 72,000 young immigrants who were potentially eligible for DACA that call Florida home. They currently contribute a total of $78 million to local and state taxes annually through sales and excise taxes, property taxes and income tax. Read more here
The Commonwealth Institute: Dream Act Would Boost Virginia Families, Communities, State Economy, and Tax Revenues; Revoking DACA Hurts All
December 20, 2017
There are 30,000 young immigrants who were potentially eligible for DACA and call Virginia home. They currently contribute a total of $29.3 million to local and state taxes annually through sales and excise taxes, property taxes and income tax. Read more here
NC Policy Watch: Devastating consequences if Congress fails to replace DACA in three months
December 20, 2017
State and local government coffers would also take a hit if Congress fails to pass the Dream Act, or another effective solution. The Institute for Taxation and Economic Policy estimates that current DACA recipients pay almost $58 million in state and local taxes, contributions which could grow to $78 million if the Dream Act were […]
Center for Public Policy Priorities: The National Dream Act: What’s at stake for Texas?
December 18, 2017
Researchers estimate that approximately 177,000 young Texas immigrants are potentially eligible for DACA, and they currently contribute a total of $241 million to local and state taxes annually through sales and excise taxes, property taxes and income tax. Without the national Dream Act, Texas can expect to lose at least $79 million in state and […]
Minnesota Budget Project: 4 Reasons DACA should be restored ASAP
December 18, 2017
DACA results in increased economic activity in our communities and increased tax revenues. DACA recipients in Minnesota contribute an estimated $15 million in state and local taxes annually. Read more here
Corker Claims Provisions Benefiting Him Could Not Have Changed His Vote Because He Never Read the Bill
December 18, 2017 • By Matthew Gardner

Many Republicans who had previously claimed to be deficit hawks have been cheerfully supportive of major tax-cutting legislation as it has moved forward this fall. But one Republican Senator, Bob Corker of Tennessee, has taken a defiant stance on the issue, insisting that “passing off increased debt to future generations” would be a deal-breaker for him. When the Senate passed its version of the tax plan last week, Corker was the only Republican to vote No.
Final GOP-Trump Bill Still Forces California and New York to Shoulder a Larger Share of Federal Taxes Under Final GOP-Trump Tax Bill; Texas, Florida, and Other States Will Pay Less
December 17, 2017 • By Meg Wiehe
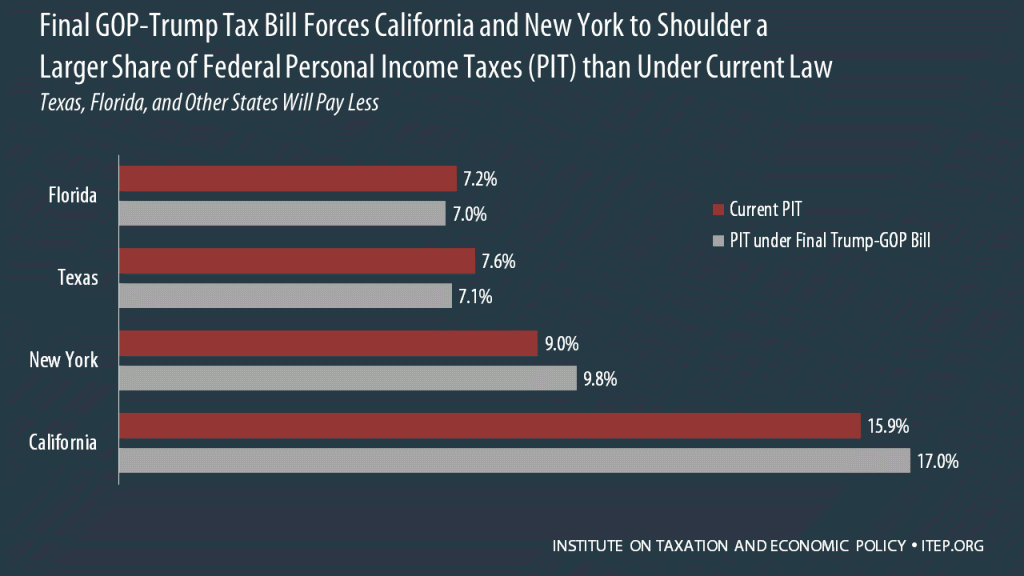
Residents of California and New York pay a large amount of the nation’s federal personal income taxes relative to their share of the population. As illustrated by the table below, the final GOP-Trump tax bill expected to be approved this week would substantially increase the share of total federal personal income taxes (PIT) paid by both states. Connecticut, Maryland, Massachusetts, and New Jersey would also see their share of federal PIT increase.
GOP Leaders Scrounge Up Money to Lower Top Tax Rate for the Rich But Not to Help Low-Income Working Families with Children
December 15, 2017 • By Meg Wiehe
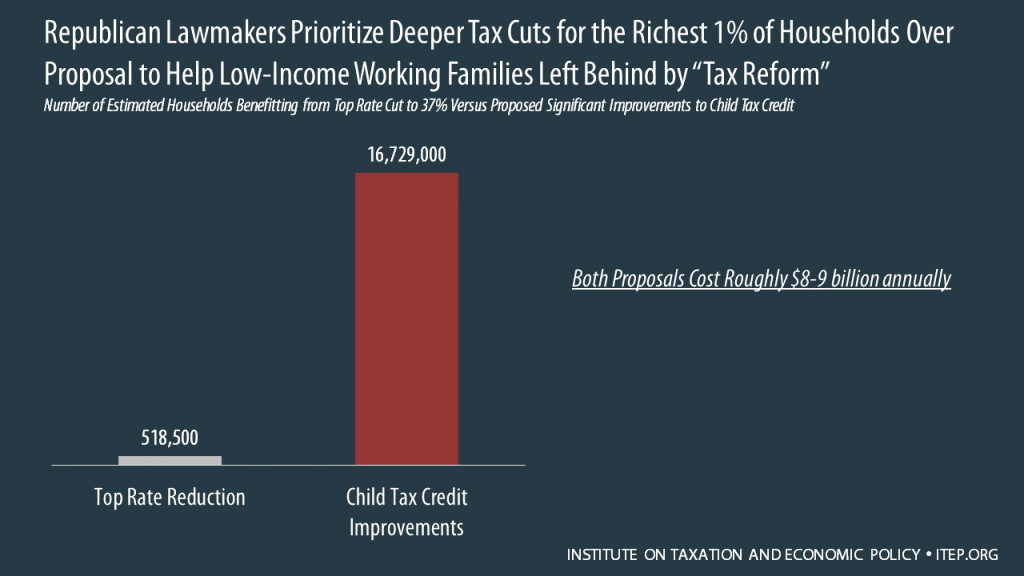
Republican leaders who rejected a proposal to have corporations pay a single percentage point higher tax rate to benefit families with children have tapped the exact same source of savings to provide more breaks for the richest 1 percent of taxpayers. The table below compares the number and share of households nationally and in all 50-states who would benefit from the proposal to reduce taxes for working families with children versus the ”compromise” to cut the top individual tax rate -- below either the House or Senate version – to 37 percent for couples with incomes above $1 million.

As 2017 draws to close, Congress has yet to take legislative action to protect Dreamers. The young undocumented immigrants who were brought to the United States as children, and are largely working or in school, were protected by President Obama’s 2012 executive action, Deferred Action for Childhood Arrivals (DACA). But in September, President Trump announced that he would end DACA in March 2018. Instead of honoring the work authorizations and protection from deportation that currently shields more than 685,000 young people, President Trump punted their lives and livelihood to a woefully divided Congress which is expected to take up legislation…
Updated Tax Contributions of Young Undocumented Immigrants
December 13, 2017 • By ITEP Staff
In September 2017, US Citizenship and Immigration Services released updated enrollment data for the program Deferred Action for Childhood Arrivals (DACA). The updated data included estimates of the number of former DACA enrollees that were now legal permanent residents and those that failed to reapply or their reapplication was denied. The table below provides updated estimates of their tax contributions.
Charitable, Property Tax, and Mortgage Interest Deductions Would Be Wiped Out for Two-Thirds of Current Claimants Under Congressional Tax Plans
December 7, 2017 • By Carl Davis
In the ongoing debate over major federal tax legislation, there is significant focus on how House and Senate bills would eliminate the deduction for state income tax payments and cap the deduction for property taxes at $10,000 per year. At the same time, tax writers have retained deductions for charitable gifts and mortgage interest with what appear to be comparatively minor changes, at least at first glance.
Fiscal Policy Institute: Dream Act: What’s At Stake for New York
December 1, 2017
There are 76,000 young immigrants who were potentially eligible for DACA that call New York home. They currently contribute a total of $115 million to local and state taxes annually through sales and excise taxes, property taxes and income tax. Read more
